Thunder Client is a lightweight Rest API Client Extension for Visual Studio Code, hand-crafted by Ranga Vadhineni with simple and clean design. The source code is not open source. You can report any Bugs Or Feature requests here.
- Voted as #10 Product of the day on Product Hunt
- Website - www.thunderclient.com
- Follow Us for updates - Twitter, LinkedIn
- Read Launch Blog Post on Medium
- How to Use
- Tech
- Features
- Team Features / Git Sync
- Testing
- Environments
- Set Environment Variable
- Auth
- Path Variables
- System Variables
- Code Snippet
- Proxy
- Http/2
- Import/Export
- Keyboard Shortcuts
- VS Code Settings
- Contribution
- Privacy
- Install the Extension, Click Thunder Client icon on the Action Bar.
- From Sidebar click
New Requestbutton to test API - Video: youtube.com/watch?v=NKZ0ahNbmak
- Thunder Client is built with Javascript, Typescript, Flexbox, Ace Editor, Got, Nedb.
- Send http/https API request using any of the methods GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, HEAD and OPTIONS.
- The Response data supports syntax hightlighting using ACE Editor which can handle large responses easily, you can also view response in Full Screen
- History, Collections and Environment Tabs in the Action Bar View for quick access.
- Authentication: Basic Auth, Bearer Token and OAuth 2.0 are supported.
- Post Body: For Post Content-Type header will be automatically set.
- Graphql: Send Graphql Query & Variables has syntax highlighting support.
- Environment Variables: Syntax highlighting support for environment variables just use
{{variable}}syntax in most fields - Scriptless Testing: Test APIs with GUI based functionality, no scripting knowledge needed.
- Themes: The extension also supports VS Code themes.
The team features are useful to share requests with team by saving data in git project.
Integration with the Git project is supported by below vscode settings, choose any one as required. To view Thunder Client settings, open vscode settings UI and search for Thunder Client to view all the extension settings.
- Save To Workspace: select this option when you like to spilt requests data per project, it will create
thunder-testsfolder in root of workspace. This option loads the data when you open the project in vscode automatically.- (Optional) The default location of
thunder-testsfolder is root of workspace. Use settingWorkspace Relative Pathto specify different relative path. see below examples - Make sure the
Workspace Relative Pathsetting is Workspace setting not User setting. - Example 1: To save in Child folder of workspace then relative path is
FolderNameorChild/FolderName - Example 2: To save in Parent folder of workspace then relative path is
../
- (Optional) The default location of
- Custom Location: select this option when you like save all the requests data in one fixed location, enter the full folder path to save the data.
- Supports relative path to Home directory. use $HOME prefix e.g
$HOME/Documents/ProjectName
- Supports relative path to Home directory. use $HOME prefix e.g
- WARNING: The Environment file which stores the secrets also saved in the same git folder, see Note: 1 below.
- Note 1: The environments will be stored in
thunderEnvironment.dbfile, which will be part of thunder-tests folder. If you like to exclude any secrets fromthunderEnvironment.dbfile then useLocal Environmentto store values locally on your computer - Note 2: Files changes are not detected by the extension yet, if you pulled changes from git, click Reload icon in sidebar.
- Note 3: Please restart vscode after updating settings.
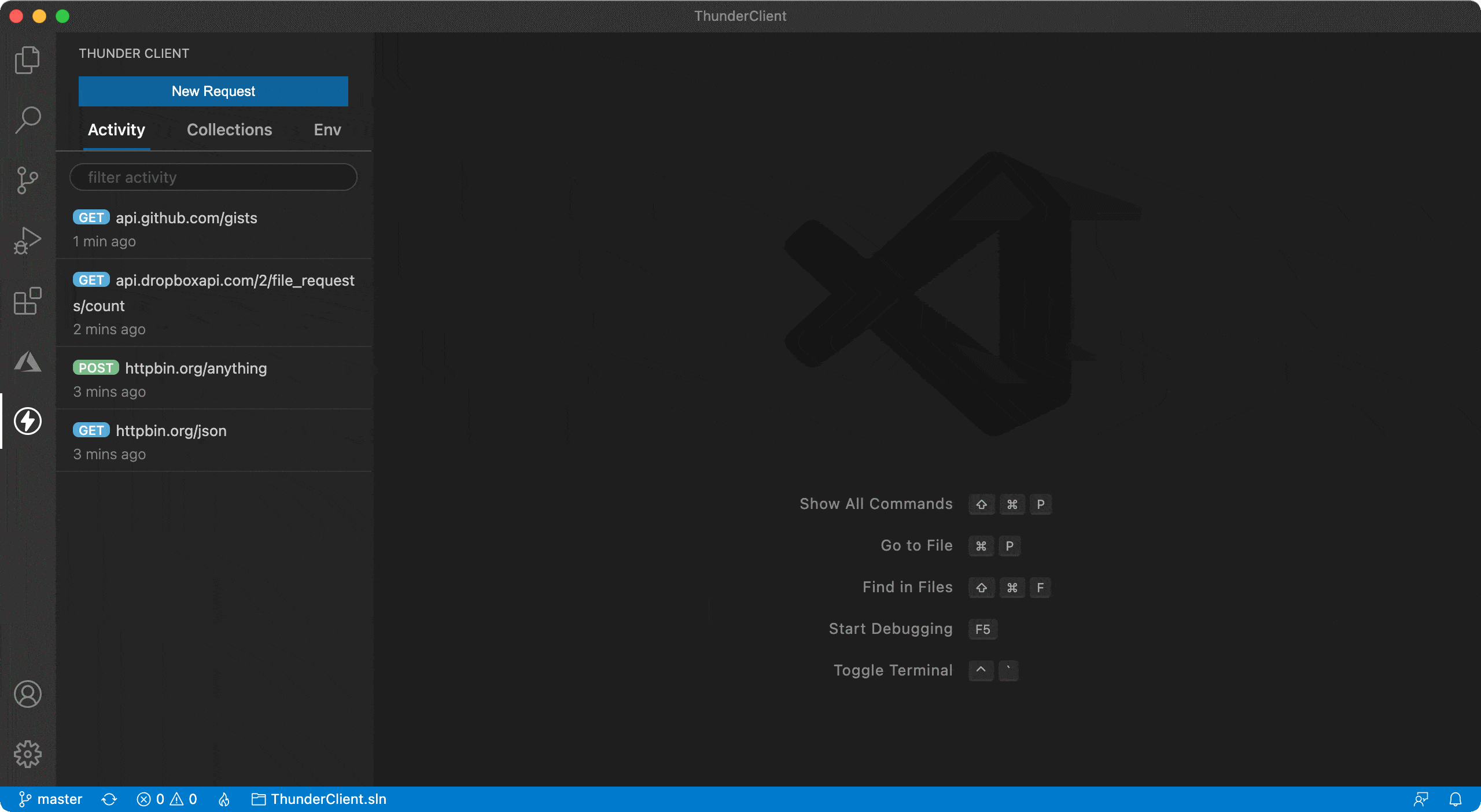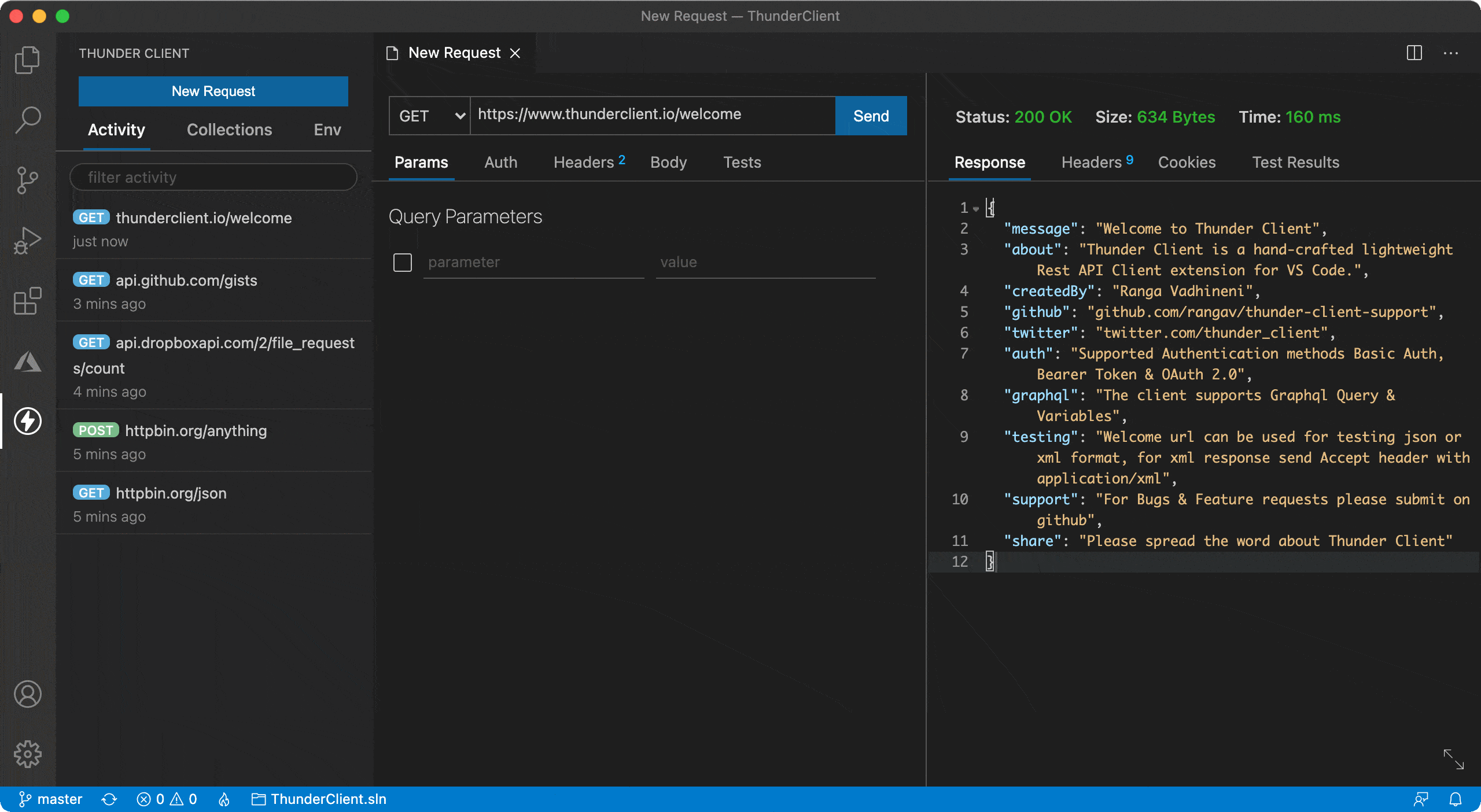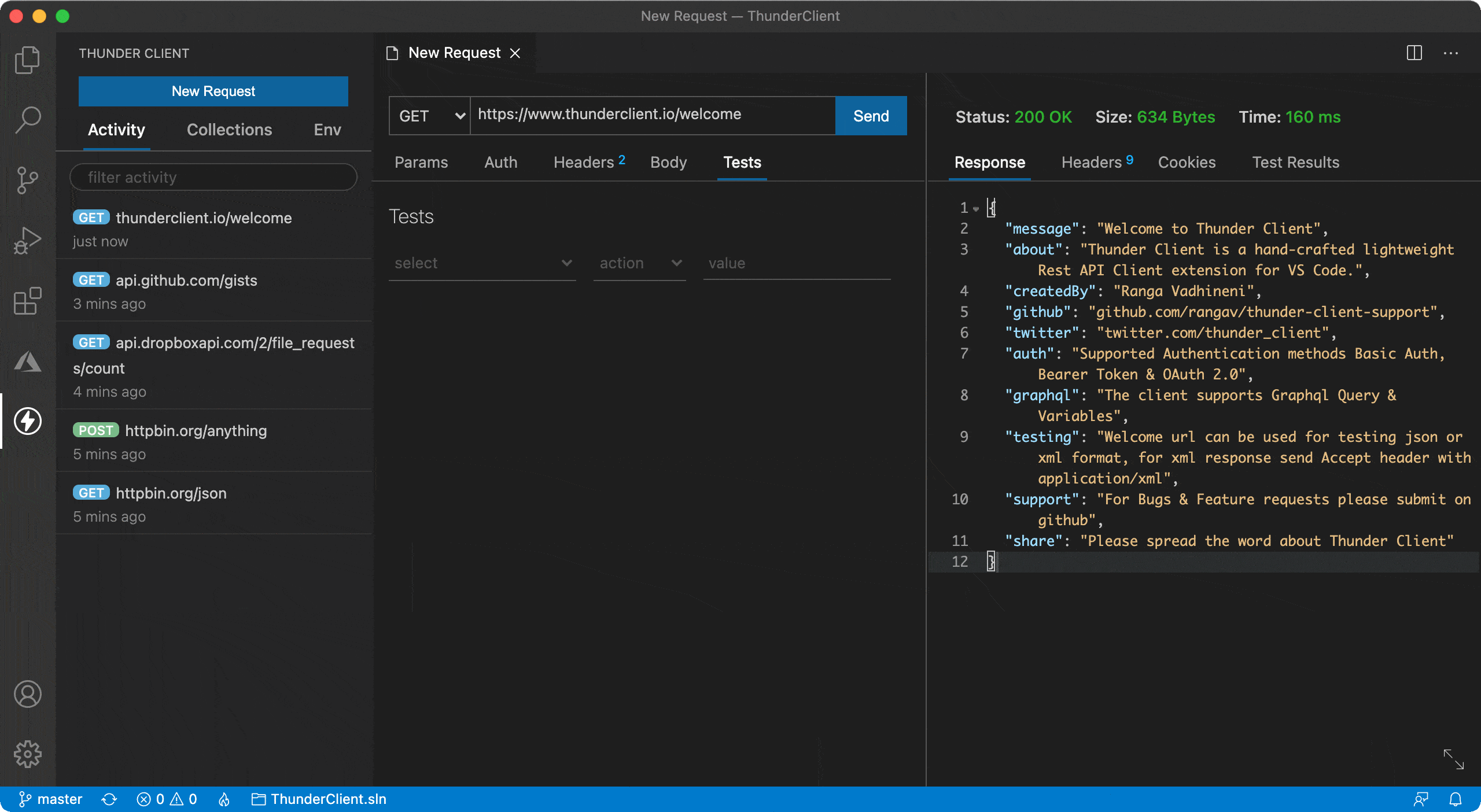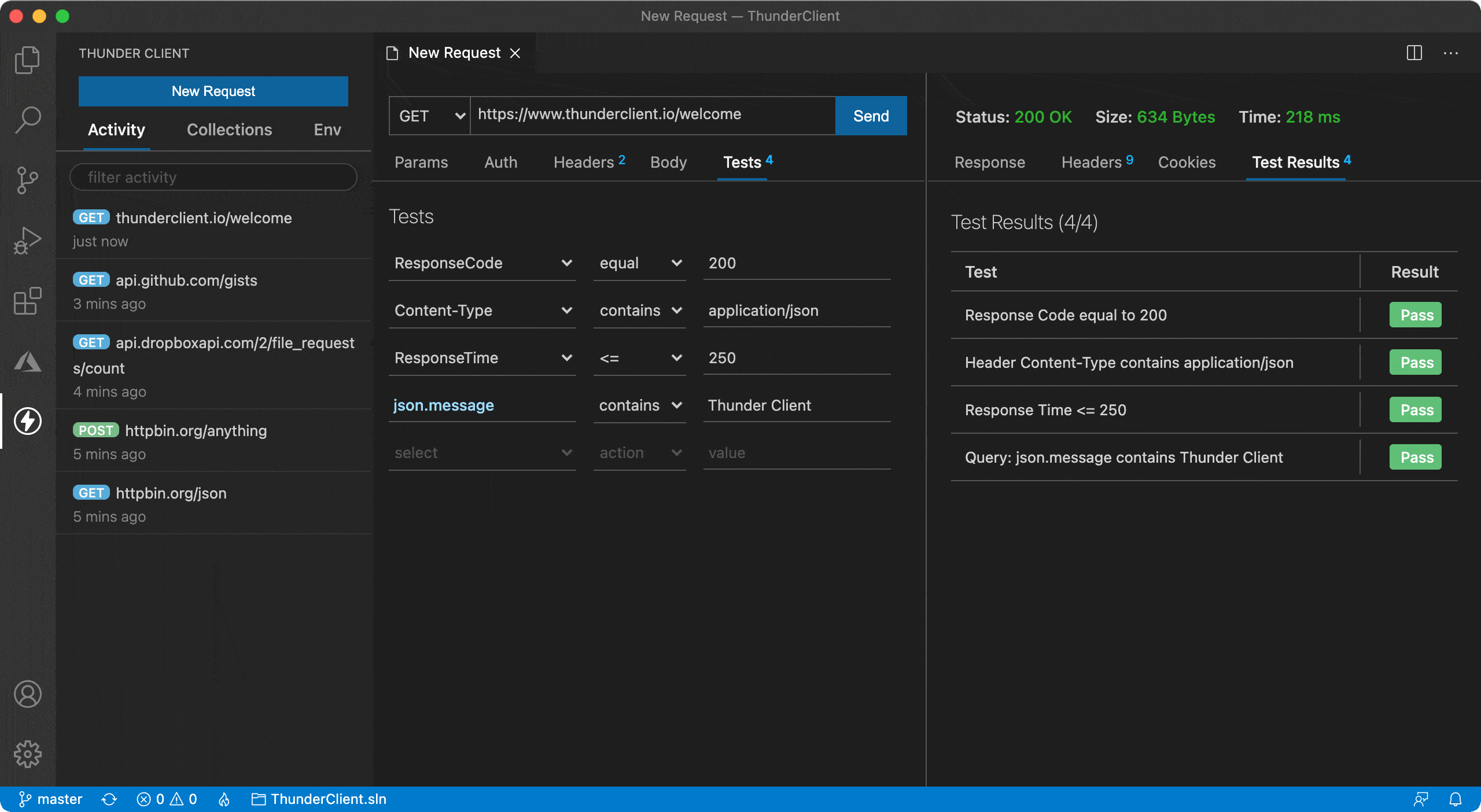
- We need to write a lot of boilerplate code in Postman and other clients to do basic testing using scripting like status code equal 200. So I implemented GUI based tests, where you select couple of dropdowns to do most standard tests very easily without any scripting knowledge.
- Tests can be done for strings, number, count and type checking
Json schemavalidation- Setting
Env variablealso possible in Tests section - Re-arrange tests order using drag and drop
The following environments can be used in Thunder Client from least precedence to high precedence are listed below.
-
Local Environment: Use Local Environment to save secrets and transient tokens locally on your computer, which you dont want to save in the git project. This environment is a
global typeand the variables are available to all collections. (See above image option 3) -
Global Environment: Use Global Environment to save variables and share with all the collections. The values will stored in main
thunderEnvironment.dbfile. (See above image option 2) -
env file: You can use
.env filesin Thunder Client. To Use .env file follow below steps- Create an Environment (using option 1 in img)
- Open the Environment view, then you will see the option
Link to .env file - Select the .env file and save it, Now you can use the variables in the Requests using
{{variable}} - The env file variables format should be in
key=value name=thunder number=25543 -
Active Environment: To use an environment variables, you need to make it active using the options menu
...then selectSet Active. -
Attach Env to Collection: (Optional) You can attach a environment to collection from Collection Settings view. Use this option when you like to link multiple collections to multiple environments. The values in this Environment will take precedence over Active Environment. If you change environment frequently, this option is not recommended. Please see example below
CollectionA -> EnvA CollectionB -> EnvB CollectionC -> EnvC
- To use env variables use the format
{{variableName}}, you can use variables in Query Params, Headers, Body & Tests
- You can import Thunder Client, Postman and .env files using the Import Menu Option ( see above image option 4), more details here
Setting environment variables is supported in the Tests tab. Follow the steps below:
- Create an environment first from the Env tab if it's not already created.
- In the Tests tab, select the
Set Env Variabledropdown option. (The action will automatically becomesetTo.) - Enter the appropriate source of variable value in the left input box:
- Header: Enter
header.headerNamewhereheaderNameis the response header name. - Cookie: Enter
cookie.cookieNamewherecookieNameis the response cookie name. - JSON Response: Enter
json.propertyNamewherepropertyNameis the JSON key in the response body. - Text Response: Enter the
textkeyword. This sets the entire response body to the variable.
- Header: Enter
- In the value input, enter a variable name in the
{{variableName}}format.- When it matches a variable name in Env, it will turn green. If the variable doesn't exist, it will be created.
- Now execute the request. You will see the variable value set in the Env tab.
The default location will be Active Environment when you use {{variable}}. You can use scope to control which environment variable to set the value explicitly
- To set variable in local environment use
{{variable, local}} - To set variable in global environment use
{{variable, global}} - (optional) To set variable in active environment use
{{variable, active}}, Use this format only when you have attached Environment to Collection, otherwise{{variable}}format should be used
-
OAuth 2.0 when grant type is Authorization Code the callback url needs to be entered into your oauth server trusted redirect url list.
-
OAuth authentication credentials are sent via header or body, please select appropriate one based on your server requirement.
-
- Provide ssl certificate paths for auth, using relative path to workspace or absolute paths.
- Use the Certificates vscode setting, see example below
"thunder-client.certificates": [ { "host": "thunderclient.io", "certPath": "ssl/cert.pem", "keyPath": "ssl/keyfile.key", "pfxPath": "ssl/pfx.p12", "passphrase": "test" }, { "host": "localhost:8081", "pfxPath": "/Users/test/Documents/ssl/pfx.p12", "passphrase": "test" }, { "host": "testing.com", "certPath": "ssl/cert.pem", "keyPath": "ssl/keyfile.key" }, ]
Path variables are supported using the format {variable} in the url field
- e.g 1:
https://www.thunderclient.com/details/customer/{customerId} - e.g 2:
https://www.thunderclient.com/details/{customerId}{name}/
The system variables are useful to generate random/dynamic data for use in request query params or body. The format is {{#variableName}}
- {{#guid}} - generates random uuid
- {{#string}} - generates random string
- {{#number}} - generates random number between 1 to 1000000
- Custom Range: use
{{#number, min, max}}, e.g:{{#number, 100, 999}}
- Custom Range: use
- {{#email}} - generates random email
- {{#date}} - generates date timestamp
- Custom date format: use
{{#date, 'YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss:fff'}}, the format should be in single quote.
- Custom date format: use
- {{#dateISO}} - generates date ISO format
- {{#bool}} - generates true or false
- {{#enum, val1, val2, val3,...}} generates one of the enum values (comma separated) provided
- e.g
{{#enum, red, green, blue}} - e.g
{{#enum, 1, 2, 3}}
- e.g
The code snippet generation is available for following languages. Open request view and click icon {} to see Code Tab.
- C# - HttpClient
- cURL
- Dart Http
- Javascipt Fetch & Axios
- PowerShell
- Python requests & http.client
The feature is open for contribution - https://github.com/rangav/thunder-codegen
- Proxy is supported using vscode proxy setting. format
http://username:password@host:port - exclude Proxy Host List: Use this setting to exclude hosts from proxy, supports comma separated values e.g:
abc.com,xyz.com
- To send request using Http/2 protocol, please select
HTTP/2option in vscode settings for Http Version
- The following import of Collections & Environments supported
- Postman 2.1.0 format
- Insomnia v4 json file
- Open API v3 json or yaml files
- Thunder Client
- You can import or export Thunder Client collections and environment data.
- Import Curl is now supported from Activity tab. Keyboard shortcut
Cmd/Ctrl + u - Import of .env files also supported, select
Importfrom Env tab and choose .env file
- Select the
Collectiontab from the sidebar - Click
Menuicon near searchbar, and SelectImport - Now select file from Postman, Thunder Client, Insomnia or Open API.
- First Export Thunder Client collection to json file, Then convert to Postman format using below options
- From Command Palette -
Convert To Postman Formatoption available - From Sidebar menu at the Top
(...)selectConvert To Postman Format
Ctl+Shift+P: From Command Palette- Thunder Client - New Request
- Thunder Client - Run Last Request
- Thunder Client - Change Environment
- Thunder Client - Convert To Postman Format
Cmd/Ctrl + Enter: To execute the request.Enteron request url field to send request.Cmd/Ctrl + sSave Request without run.Cmd/Ctrl + clickon request in Sidebar will open in new tabCmd/Ctrl + sEnvironment view save data.Cmd/Ctrl + eChange Active Environment.Alt+Shft + fFormat Post Body data.Cmd/Ctrl + uImport CurlAlt + zToggle Word wrap on response
To see all the Thunder Client vscode settings
- Open vscode settings View, then search for
Thunder Client - From Sidebar View -> Click
...menu at the top, then clickExtension Settings
- Documentation: if you like to improve documentation, please submit PR.
- The following modules are open for contribution, let me know if you like to contribute
- Code Snippet Generation - https://github.com/rangav/thunder-codegen
- Basic anonymised analytics data is collected using vscode-extension-telemetry, No Personal or request data is collected. You can opt out using VS Code Settings details here
- There is no backend or cloud sync, all the data is stored locally on your computer.