Tutorial for calibrating realsense camera on panda franka emika wrist
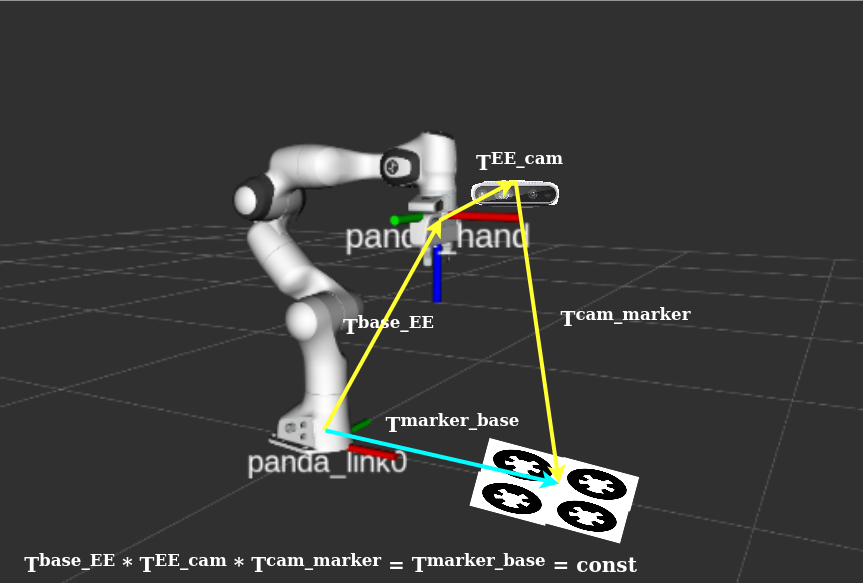
In eye-on-hand case the camera is fixed on the robot end-effector and we need to find the transformation between camera frame to panda_hand frame (T_cam-PH). As such, from robot forward kinematic we know the transformation between base frame to panda_hand (T_base-PH) and from a marker detection package we know the transformation between marker frame and camera optical frame (T_marker-cam). From homogenous transformations and consecutive transformations we know that T_base-PH * T_cam-PH * T_marker-cam should give marker pose in base frame (T_marker-base). And since the marker array is fixed on the table so T_marker-base is a constant matrix. In that sense, what we do for camera to robot calibration is that we pick some poses for the robot in which the marker board is fully visible to camera field of view and and for these poses we save the T_base-PH (forward kinematic (franka_control)) and T_marker-cam (Whycon and OrientationGroundTruth.py). Here we have a optimization problem in which T_cam-PH is initialized with a [0, 0, 0, 0, 0 , 0, 1] and optimized in such a way that the sum of squared errors of T_marker-base values will be minimized.
For completing the calibration process you need to have the following ROS packages already installed:
If issues building the Whycon in with catkin_make citing package "magick++", install it with:
sudo apt-get install libmagick++-dev
Step 1.Save four different whycon markers and put them in one A4 page and print it. You can see the instruction on how to print the markers on whycon github page. Fix the page on a suitable place on the table which can be easily detectable by the realsense camera. you can see the detected markers by "roslaunch whycon_ros whycon.launch". In the opened GUI correct the marker size and the number of markers to 4.
Step 2. First we need to launch the realsense_calib.launch file which includes launching: 1- franka_control/franka_control.launch, 2- panda_moveit_config/panda_moveit.launch, 3- panda_moveit_config/moveit_rviz.launch, 4- realsense2_camera/rs_camera.launch, and 5- whycon_ros/whycon.launch files.
roslaunch <your calibration package name> realsense_calib.launch
What you need is to take the robot EE to 15 different poses and save the corresponding joint space consiguration of these poses in the realsense_calibration.py script. You can have access to robot joint space configuration by echoing the target topic from franka_state_controller. The issue with the whycon markers is that the id of the detected markers may change for different perspective so you have to run the OrientationGroundTruth.py as well and print the id of the detected markers and pick those 15 poses in such a way that for all of them the ids are the same. Try to cover both near and far views in order for the optimization to converge easier.
step3. After saving the joint state values in the calibration script you can now run it alongside launching realsense_calib.launch and running OrientationGroundTruth.py. this will move the robot to all the poses and finally publishes the resulted TF from optimazation which you can see in TF tree in RVIZ. The resulted tf is between panda_hand and camera_link. You can save this value in your launch file to publish it automatically in future to connect the frames of the robot and the camera.
For launching whycon you may need to do:
roslaunch whycon_ros whycon.launch camInfo:=/camera/color/camera_info camRaw:=/camera/color/image_raw