This project is an implementation of a Circuit Breaker to ensure the resilience and stability of services that make calls to external resources. A Circuit Breaker is a design pattern used to detect failures and encapsulate the logic of preventing a failure from constantly recurring, helping to maintain system stability. It allows controlling and isolating failures in distributed systems, helping to prevent total system degradation.
To install the dependencies, run the following command:
npm install p-circuit-breakerYou can instantiate a Circuit Breaker with the following options:
import { CircuitBreaker } from 'p-circuit-breaker';
const breaker = new CircuitBreaker({
failureThresholdPercentage: 50,
windowSize: 10000,
timeout: 5000
});Here is an example of how to use the Circuit Breaker to protect an asynchronous operation:
function fetchTodo() {
return fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1');
}
async function exampleFunction() {
const breaker = new CircuitBreaker({ timeout: 2000 });
try {
const response = await breaker.execute(fetchTodo);
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Request failed:', error);
}
}This example shows how to catch failures during the execution of a function protected by the Circuit Breaker.
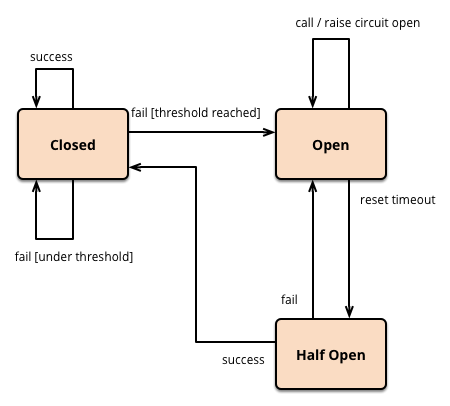
The Circuit Breaker can be in three different states:
- Closed: All requests are allowed normally.
- Open: Requests are immediately blocked to avoid overloading the resource.
- Half-Open: An intermediate state where only a few requests are allowed to test if the resource has recovered.
For more information, refer to Martin Fowler's article on Circuit Breaker.
- failureThresholdPercentage: Percentage of failures allowed before opening the circuit. (default: 5)
- windowSize: Number of requests considered in the window to calculate the failure rate. (default: 60000 ms)
- timeout: Maximum execution time before considering the request failed. (default: undefined)
- resetTimeout: Time after which the Circuit Breaker will attempt to change from "open" to "half-open" to check resource recovery. (default: undefined)
- isError: Custom function to determine if an error should count as a failure. (default: undefined)
- autoRenewAbortController: Defines whether the AbortController should be automatically renewed for each new request when the circuit is closed. (default: false)
- failureThresholdCount: Alternative to
failureThresholdPercentage; opens the circuit when failures reach this count within the window. (default: 0) - retryAttempts: Number of allowed retry attempts in the half-open state before opening the circuit again if failures persist. (default: 1)
- successThreshold: Number of consecutive successes required in the half-open state to fully close the circuit. (default: 1)
The Circuit Breaker emits different events during its execution:
- 'open': Occurs when the circuit is opened due to excessive failures.
- 'close': Occurs when the circuit closes and resumes normal execution.
- 'halfOpen': Occurs when the circuit enters the half-open state.
- 'success': Emitted when a request is successful.
- 'error': Emitted when a request fails.
You can use these events to log or trigger other actions:
breaker.event.on('open', () => {
console.log('Circuit opened');
});
breaker.event.on('close', () => {
console.log('Circuit closed');
});
breaker.event.on('halfOpen', () => {
console.log('Circuit is half-open: Testing if the resource has recovered');
});
breaker.event.on('success', () => {
console.log('Request succeeded while the circuit was closed or half-open');
});
breaker.event.on('error', () => {
console.log('Request failed: Recording failure in the circuit');
});Contributions are welcome! Please follow these steps to contribute:
- Fork this repository.
- Create a branch for your feature (
git checkout -b my-feature). - Submit a pull request for us to review your changes.
This project is licensed under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more details.
To run the tests:
npm test