Welcome to the official GitHub repository for XMPro's Multi-Agent Generative Systems (MAGS). This innovative technology represents a groundbreaking approach to industrial process optimization and advanced predictive maintenance, leveraging the power of AI to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making.
XMPro's Multi-Agent Generative Systems (MAGS) deploy teams of AI agents that function as virtual workers, collaborating to complete operational tasks in industrial settings. These agents integrate computational software with large language models (LLMs), working together to optimize processes and enhance advanced predictive maintenance. Importantly, MAGS are designed to augment human experts in operational scenarios, combining AI capabilities with human expertise for optimal results. This innovative approach leverages generative AI to simulate, optimize, and execute complex industrial operations in real-time.
XMPro's MAGS implementation utilizes three distinct types of agents, each with specialized roles and capabilities:
-
Content Agents: These agents leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate, curate, and manage information. They excel in tasks related to content creation, documentation management, and compliance support, forming the backbone of information processing in MAGS.
-
Decision Agents: Acting as the strategic core of MAGS, Decision Agents simulate human-like reasoning and decision-making processes to optimize industrial operations. These agents observe, reflect, plan, and act autonomously, managing complex, dynamic environments where rapid, data-driven decisions are crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
-
Hybrid Agents: Combining the strengths of Content and Decision Agents, Hybrid Agents are versatile problem-solvers capable of handling tasks that require both data synthesis and strategic decision-making. They excel in roles that demand flexibility, integrating content generation with real-time decision execution.
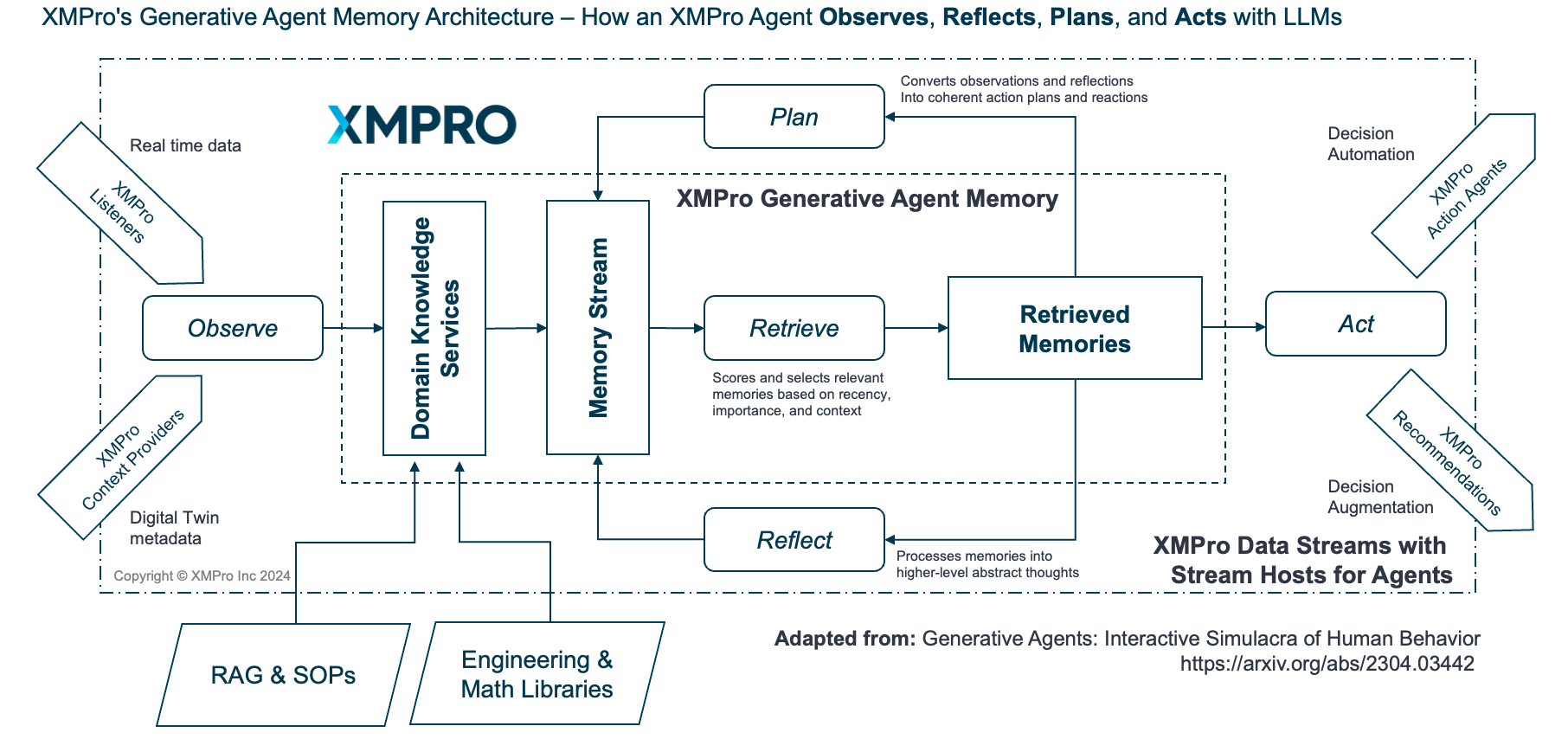
XMPro's Decision Agents, in particular, were inspired by groundbreaking research from Stanford University, as detailed in "Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior" by Joon Sung Park, Joseph C. O'Brien, Carrie J. Cai, Meredith Ringel Morris, Percy Liang, and Michael S. Bernstein. This research introduced the concept of generative agents - computational software agents that simulate believable human behavior. These agents can perform a wide range of human-like activities, from daily routines to complex social interactions, and are capable of forming opinions, initiating conversations, and planning future actions based on past experiences. [2304.03442] Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior (arxiv.org)
The Stanford research describes an architecture that extends large language models to store a complete record of an agent's experiences in natural language, synthesize those memories into higher-level reflections over time, and dynamically retrieve them to plan behavior. This approach allows for the creation of believable individual and emergent social behaviors in simulated environments.
XMPro's Decision Agents build upon this foundation, adapting and extending these concepts for industrial applications. By incorporating the principles of observation, planning, and reflection from the Stanford research, XMPro's Decision Agents can make complex, context-aware decisions in industrial settings, continuously learning and adapting to changing conditions.
- APEX AgentOps: AgentOps for Scaling Multi Agent Generative Systems in complex industrial environments
- Adaptive Decision Making: Agents can create and modify plans to achieve goals, adapting to changing circumstances in their environment.
- Generative AI Agents: Autonomous AI entities capable of recognizing patterns, generating predictions, and performing complex tasks.
- Integration: Seamless connection with real-time sensors, business applications, and other data sources through XMPro Data Streams, for continuous improvement in equipment failure prevention and process optimization.
- Multi-Agent Collaboration: AI agents functioning as virtual workers to perform various operational roles and tasks.
- Real-time: Execution of specialized functions such as reliability engineering and root cause analysis by agent teams.
- Scalable architecture: Capable of deploying multiple agent teams based on specific operational needs and complexities.
/docs: Comprehensive documentation (see Documentation section for details)/src: Source code for XMPro MAGS components
Our comprehensive documentation is organized in the /docs folder:
/accessibility: Guidelines and resources for web accessibility, including ARIA implementation/architecture: Detailed architecture diagrams for MAGS sub-processes/concepts: Exploration of key concepts, ideas, and methodologies underlying XMPro AI Agents/faq: Frequently Asked Questions about XMPro MAGSGlossary.md: A comprehensive glossary covering:- Fundamental concepts in generative AI
- Multi-Agent system architectures
- XMPro-specific terminology and tools
- Industry-standard AI and machine learning terms
/naming-conventions: Explanation of naming conventions used throughout the project/technical-details: In-depth technical explanations with diagrams
For a quick start, we recommend:
- Review the FAQ for common questions and answers
- Explore the Glossary to familiarize yourself with key concepts and terminology
- Dive into specific topics in the concepts folder
To set up the XMPro AI Agents system, follow these main steps:
- Ensure you have the pre-requisites installed and available
- Configure the Neo4j graph database
- Install system options
- Load the prompt library
- Load the tool library
For detailed installation instructions, please refer to the Installation Guide.
For detailed information about our agent structure, including concepts, ideas, and methodologies, please refer to the /docs/concepts directory. This section contains in-depth explanations of:
- Agent profiles and instances
- Multi-agent interaction paradigms
- Decision-making processes
- Memory and knowledge management
- Integration with XMPro Data Streams
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
The MIT License is a permissive license that allows you to do anything you want with the code as long as you provide attribution back to XMPro and don't hold us liable.
Important Legal Notice: This repository contains open-source components licensed under the MIT License. However, it is essential to understand that the core XMPro AI agent technology, including its proprietary algorithms and implementations, remains the exclusive intellectual property of XMPro. The open-source materials provided herein serve as a framework and reference implementation, and do not grant any rights to XMPro's commercially protected, proprietary agent technology. Any use, reproduction, or distribution of XMPro's proprietary components is strictly prohibited without express written permission from XMPro.
For support, questions, or inquiries about the XMPro AI Agents project, please contact XMPro at:
Email: support@xmpro.com
We value your feedback and are here to assist you with any issues or questions you may have regarding our AI Agents and Multi-Agent systems.
-
[2304.03442] Generative Agents - Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior (arxiv.org)
-
Part 1: From Railroads to AI - The Evolution of Game-Changing Utilities
-
Part 2: The Future of Work - Harnessing Generative Agents in Manufacturing
-
Part 3: AI at the Core - LLMs and Data Pipelines for Industrial Multi-Agent Generative Systems
-
Part 4: Pioneering Progress - Real-World Applications of Multi-Agent Generative Systems
-
Part 5: Rules of Engagement - Establishing Governance for Multi-Agent Generative Systems
We're excited to have you explore and contribute to the XMPro AI Agents project. Together, we're shaping the future of industrial AI!