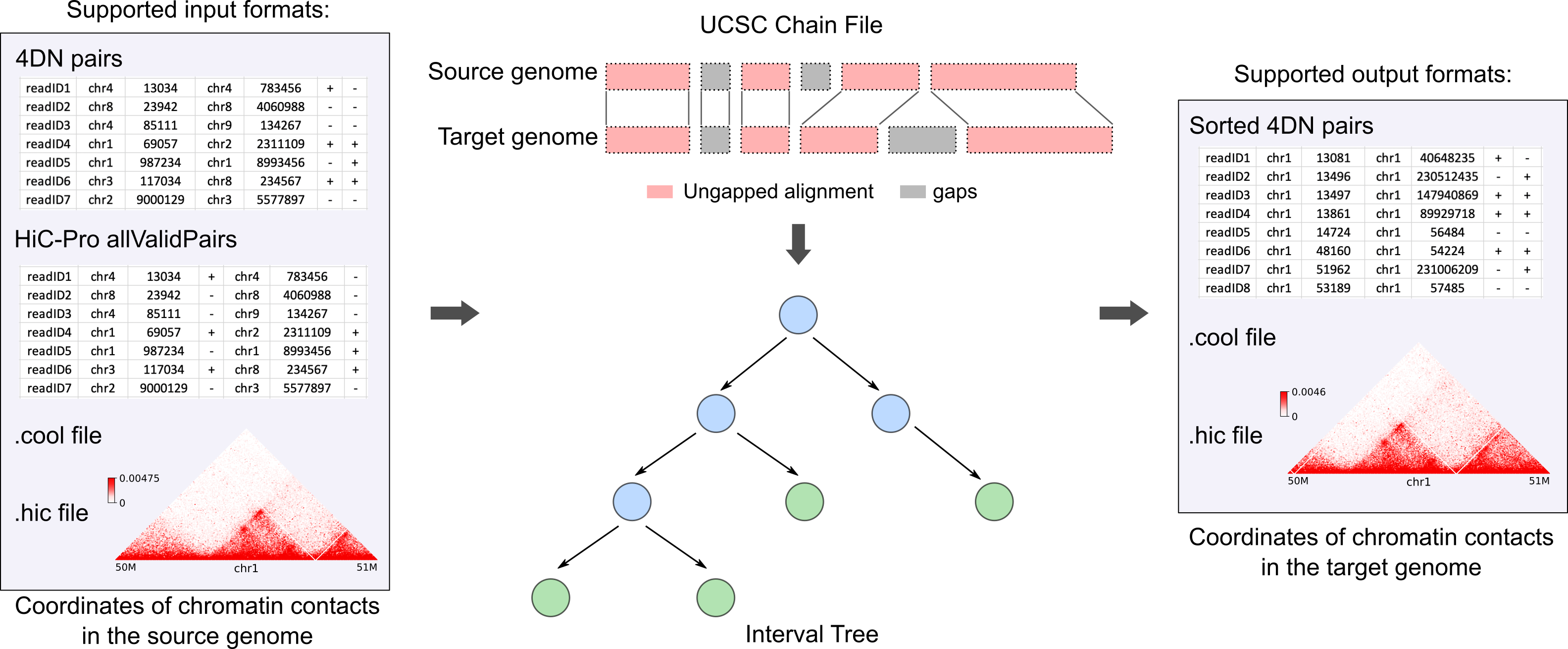
pairLiftOver
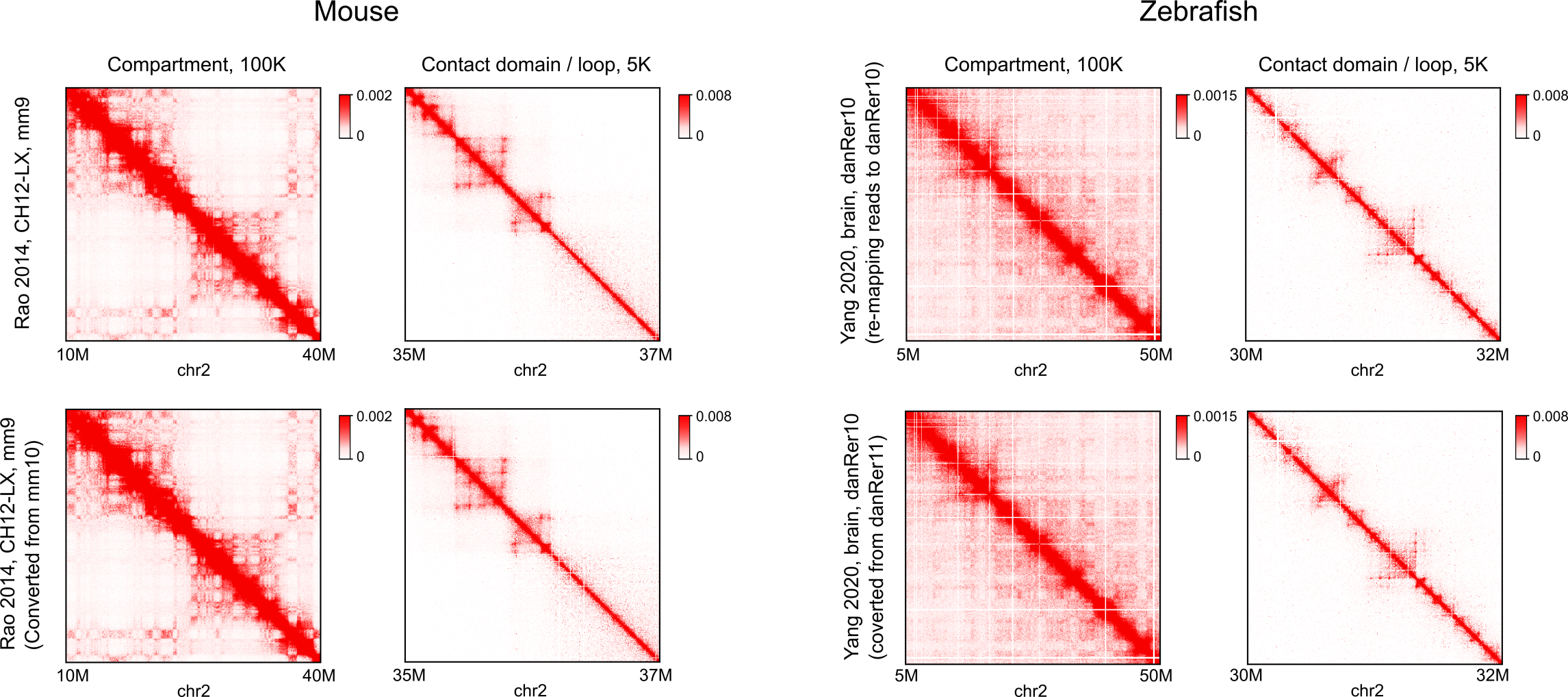
With the continuous effort to improve the quality of human reference genome and the generation of more and more personal genomes, the conversion of genomic coordinates between genome assemblies is critical in many integrative and comparative studies. Several tools have been developed for this task. However, despite the importance of 3D genome organization in gene regulation and disease, no tool exists to convert genome assemblies for chromatin interaction data. Here we present pairLiftOver, a UCSC-chain-file-based tool, for converting the genomic coordinates of chromatin contacts from one assembly to another. Using large Hi-C datasets of different species as a benchmark, we show that compared with the strategy directly re-mapping raw reads to a different genome, pairLiftOver runs on average 42 times faster, while outputs nearly identical contact matrices.
Installation
pairLiftOver and all the dependencies can be installed through either conda or pip:
$ conda config --add channels defaults $ conda config --add channels bioconda $ conda config --add channels conda-forge $ conda create -n pairliftover cooler pairtools kerneltree $ conda activate pairliftover $ pip install pairLiftOver hic-straw
Overview
The inputs to pairLiftOver include two parts. The first part is a file containing the chromatin contacts information. This file can be either a pairs file (4DN pairs or HiC-Pro allValidPairs) with each row representing a pair of interacting genomic loci in base-pair resolution, or a matrix file (.cool or .hic), which stores interaction frequencies between genomic intervals of fixed size. The second part is a UCSC chain file, which describes pairwise alignment that allows gaps in both assemblies simultaneously. Internally, pairLiftOver represents a chain file as IntervalTrees, with one tree per chromosome, to efficiently search for a specific genomic position in a chain file and locate the matched position in the target genome. The converted chromatin contacts will be reported in either a sorted 4DN pairs file, which can be directly used to generate contact matrix in various formats, or a matrix file in .cool or .hic formats.
Usage
Open a terminal, type pairLiftOver -h for help information.
Here is an example command which uses a 4DN pairs file in hg19 coordinates as input, and outputs an mcool file with chromatin contacts in hg38 coordinates:
$ pairLiftOver --input test.hg19.pairs.gz --input-format pairs --out-pre test-hg38 \ --output-format cool --out-chromsizes hg38.chrom.sizes --in-assembly hg19 --out-assembly hg38 \ --logFile pairLiftOver.log
Since the version 0.1.3, pairLiftOver has added a function to perform a pure
format conversion. For example, the following command transforms a contact matrix
from the .cool format to the .hic format, without the coordinate liftover. Note that
the values of --in-assembly and --out-assembly need to be the same to turn
on this function:
$ pairLiftOver --input Rao2014-K562-MboI-allreps-filtered.5kb.cool --input-format cooler \ --out-pre K562-format-conversion-test --output-format hic --out-chromsizes hg19.chrom.sizes \ --in-assembly hg19 --out-assembly hg19 --memory 40G
Performance
Using large Hi-C datasets of different species as a benchmark, we show that compared with the strategy directly re-mapping raw reads to a different genome, pairLiftOver runs on average 42 times faster, while outputs nearly identical contact matrices.