[NEW!] Q-Diffusion is featured by NVIDIA TensorRT! Check out the official example.
Q-diffusion is able to quantize full-precision unconditional diffusion models into 4-bit while maintaining comparable performance (small FID change of at most 2.34 compared to >100 for traditional PTQ) in a training-free manner.

Our approach can also be plugged into text-guided image generation, where we run stable diffusion in 4-bit weights and achieve high generation quality for the first time.

This repository provides the official implementation for Q-Diffusion with calibrated (simulated) quantized checkpoints.
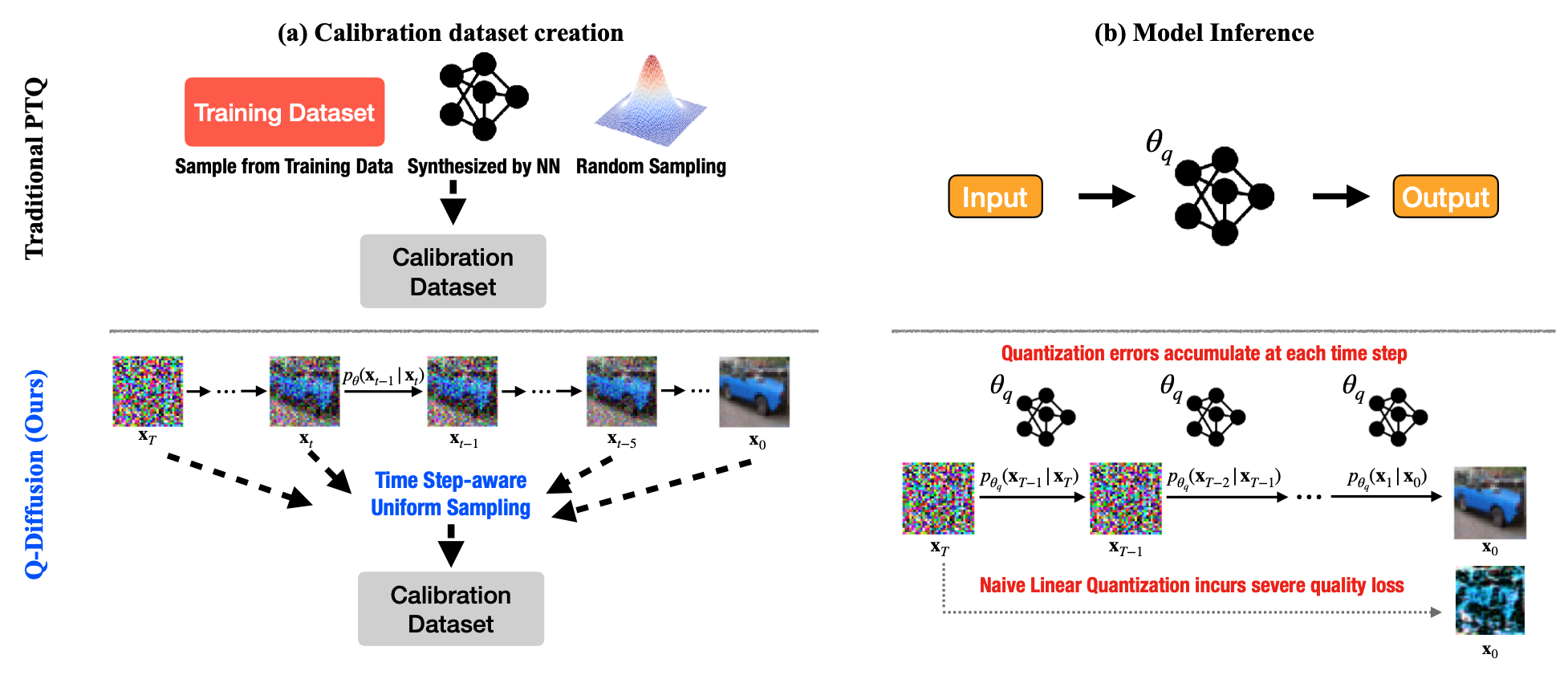
Diffusion models have achieved significant success in image synthesis by iteratively estimating noise using deep neural networks. However, the slow inference and the memory and computational intensity of the noise estimation model hinder the efficient implementation of diffusion models. Although post-training quantization (PTQ) is considered a go-to compression method for other tasks, it does not work seamlessly with diffusion models. We propose a novel PTQ method specifically designed for the unique multi-timestep pipeline and model architecture of diffusion models, which compresses the noise estimation network to accelerate the generation process. We identify the primary challenge of diffusion model quantization as the changing output distributions of noise estimation networks over multiple time steps and the bimodal activation distribution of the shortcut layers within the noise estimation network. We address these challenges with timestep-aware calibration and split shortcut quantization in this work.
Clone this repository, and then create and activate a suitable conda environment named qdiff by using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/Xiuyu-Li/q-diffusion.git
cd q-diffusion
conda env create -f environment.yml
conda activate qdiff-
For Latent Diffusion and Stable Diffusion experiments, first download relvant checkpoints following the instructions in the latent-diffusion and stable-diffusion repos from CompVis. We currently use
sd-v1-4.ckptfor Stable Diffusion. -
Download quantized checkpoints from the Google Drive [link]. The checkpoints quantized with 4/8-bit weights-only quantization are the same as the ones with 4/8-bit weights and 8-bit activations quantization.
-
Then use the following commands to run inference scripts with quantized checkpoints:
# CIFAR-10 (DDIM)
# 4/8-bit weights-only
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ddim.py --config configs/cifar10.yml --use_pretrained --timesteps 100 --eta 0 --skip_type quad --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_mode qdiff --split --resume -l <output_path> --cali_ckpt <quantized_ckpt_path>
# 4/8-bit weights, 8-bit activations
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ddim.py --config configs/cifar10.yml --use_pretrained --timesteps 100 --eta 0 --skip_type quad --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_mode qdiff --quant_act --act_bit 8 --a_sym --split --resume -l <output_path> --cali_ckpt <quantized_ckpt_path>
# LSUN Bedroom (LDM-4)
# 4/8-bit weights-only
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ldm.py -r models/ldm/lsun_beds256/model.ckpt -n 20 --batch_size 10 -c 200 -e 1.0 --seed 41 --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --resume -l <output_path> --cali_ckpt <quantized_ckpt_path>
# 4/8-bit weights, 8-bit activations
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ldm.py -r models/ldm/lsun_beds256/model.ckpt -n 20 --batch_size 10 -c 200 -e 1.0 --seed 41 --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_act --act_bit 8 --a_sym --resume -l <output_path> --cali_ckpt <quantized_ckpt_path>
# LSUN Church (LDM-8)
# 4/8-bit weights-only
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ldm.py -r models/ldm/lsun_churches256/model.ckpt -n 20 --batch_size 10 -c 400 -e 0.0 --seed 41 --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --resume -l <output_path> --cali_ckpt <quantized_ckpt_path>
# 4/8-bit weights, 8-bit activations
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ldm.py -r models/ldm/lsun_churches256/model.ckpt -n 20 --batch_size 10 -c 400 -e 0.0 --seed 41 --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_act --act_bit 8 --resume -l <output_path> --cali_ckpt <quantized_ckpt_path>
# Stable Diffusion
# 4/8-bit weights-only
python scripts/txt2img.py --prompt <prompt. e.g. "a puppy wearing a hat"> --plms --cond --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_mode qdiff --no_grad_ckpt --split --n_samples 5 --resume --outdir <output_path> --cali_ckpt <quantized_ckpt_path>
# 4/8-bit weights, 8-bit activations (with 16-bit for attention matrices after softmax)
python scripts/txt2img.py --prompt <prompt. e.g. "a puppy wearing a hat"> --plms --cond --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_mode qdiff --no_grad_ckpt --split --n_samples 5 --resume --quant_act --act_bit 8 --sm_abit 16 --outdir <output_path> --cali_ckpt <quantized_ckpt_path>To conduct the calibration process, you must first generate the corresponding calibration datasets. We provide some example calibration datasets here. These datasets contain around 1000-2000 samples of intermediate outputs at each time step, which are much more than sufficient for calibration purposes. We will soon upload smaller subsets that meet the minimum requirements for calibration. In the meantime, you may consider generating the calibration datasets yourself by following the procedures described in the paper.
To reproduce the calibrated checkpoints, you can use the following commands:
# CIFAR-10 (DDIM)
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ddim.py --config configs/cifar10.yml --use_pretrained --timesteps 100 --eta 0 --skip_type quad --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_mode qdiff --cali_st 20 --cali_batch_size 32 --cali_n 256 --quant_act --act_bit 8 --a_sym --split --cali_data_path <cali_data_path> -l <output_path>
# LSUN Bedroom (LDM-4)
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ldm.py -r models/ldm/lsun_beds256/model.ckpt -n 50000 --batch_size 10 -c 200 -e 1.0 --seed 40 --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_mode qdiff --cali_st 20 --cali_batch_size 32 --cali_n 256 --quant_act --act_bit 8 --a_sym --a_min_max --running_stat --cali_data_path <cali_data_path> -l <output_path>
# LSUN Church (LDM-8)
python scripts/sample_diffusion_ldm.py -r models/ldm/lsun_churches256/model.ckpt -n 50000 --batch_size 10 -c 400 -e 0.0 --seed 40 --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_mode qdiff --cali_st 20 --cali_batch_size 32 --cali_n 256 --quant_act --act_bit 8 --cali_data_path <cali_data_path> -l <output_path>
# Stable Diffusion
python scripts/txt2img.py --prompt "a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse" --plms --cond --ptq --weight_bit <4 or 8> --quant_mode qdiff --quant_act --act_bit 8 --cali_st 25 --cali_batch_size 8 --cali_n 128 --no_grad_ckpt --split --running_stat --sm_abit 16 --cali_data_path <cali_data_path> --outdir <output_path>Note that using different hyperparameters for calibration may result in slightly different performance.
If you find this work useful in your research, please consider citing our paper:
@InProceedings{li2023qdiffusion,
author={Li, Xiuyu and Liu, Yijiang and Lian, Long and Yang, Huanrui and Dong, Zhen and Kang, Daniel and Zhang, Shanghang and Keutzer, Kurt},
title={Q-Diffusion: Quantizing Diffusion Models},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
month={October},
year={2023},
pages={17535-17545}
}Our code was developed based on ddim, latent-diffusion and stable-diffusion. We referred to BRECQ for the blockwise calibration implementation.
We thank DeepSpeed for model sizes and BOPS measurement and torch-fidelity for IS and FID computation.