📄 Imagination Augmented Generation: Learning to Imagine Richer Context for Question Answering over Large Language Models 💡
🔔 Code • 📃 Paper • 🤗 Dataset • 🏠 Homepage
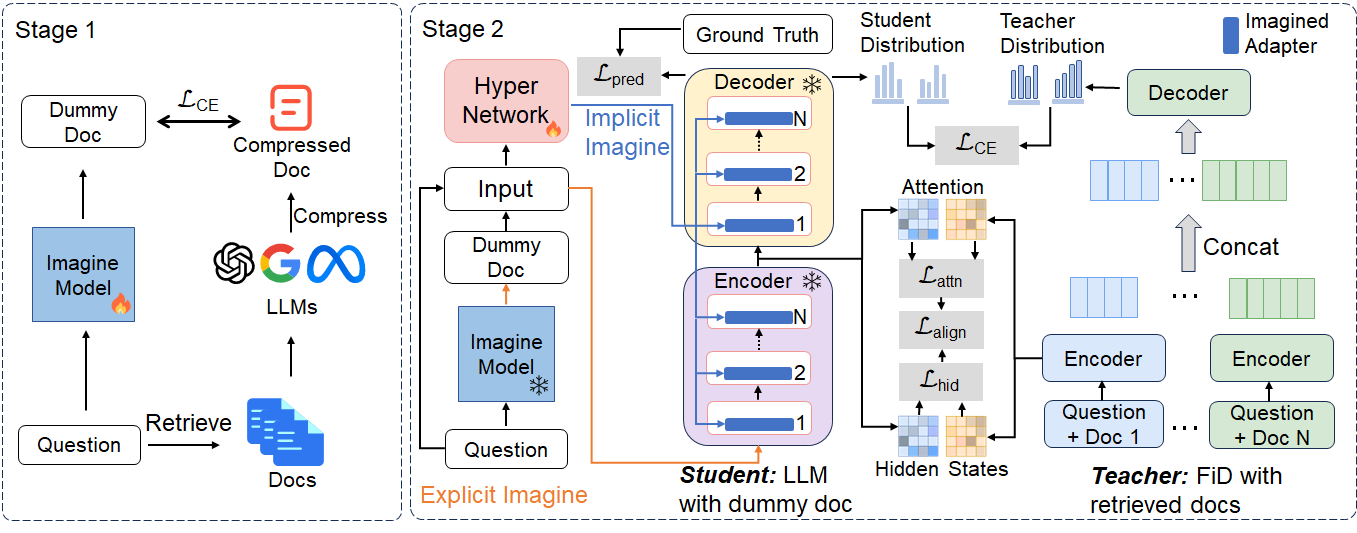
Imagination Augmented Generation (IAG) is a novel framework designed to enhance the knowledge utilization of Large Language Models (LLMs) for question answering tasks. IAG simulates the human capacity to compensate for knowledge deficits through imagination, without relying on external resources. This method is particularly useful for knowledge-intensive tasks where LLMs often lack the sufficient capability to handle independently. The architecture of the proposed ImcQA whithin IAG is shown in the following figure.
bash scripts/run.shPlease install the 1.13.1 versions of PyTorch (torch) by following the official installation instructions.
You can install the requirements with pip install --r requirements.txt.
You can refer to the Dockerfile for setting up the environment.
We tested the code with python==3.8, torch==1.13.1, accelerate==0.24.0, transformers==4.23.1, pytorch_lightning==1.6.3, and CUDA version 11.7.
To obtain the training and evaluation data, please refer to the official websites: [NQ/TriviaQA/WebQ].
Please put them into data folder.
To get the pretraining data of Imagine Model, you can refer to the data/compress.py and LongLLmlingua for compressed data.
main.py: train ImcQAtest.py: test ImcQAft_llama/: folder that conteins finetuning llama filesmodel/: folder that conteins model filesconfig/: folder that contains all config files
Training consists of two stage: a pretraning stage and the finetune stage. You can change the path of these arguments for your own system.
-
We use the FiD code from its official GitHub repository [link].
-
Download our trained FiD checkpoint at Huggingface Hub.
Refer to the scripts/image.sh for the training and evaluation commands. To reproduce the models from the paper, you can use:
deepspeed --include localhost:1,2,3,4 --master_port 52999 main.py \
--use_checkpoint \
--accelerator gpu \
--devices 4 \
--strategy ddp \
--seed 29 \
--precision bf16 \
--accumulate_grad_batches 4 \
--max_steps 40000 \
--lr 1e-4 \
--batch_size 8 \
--weight_decay 0.01 \
--text_maxlength 256 \
--answer_maxlength 256 \
--context_maxlength 256 \
--val_check_interval 0.5 \
--num_workers 5 \
--default_root_dir output \
--n_context 10 \
--warmup_ratio 0.08 \
--train_data data/$dataset/train.json \
--eval_data data/$dataset/dev.json \
--test_data data/$dataset/test.json \
--model_name t5-${size} \
--teacher_model ${teacher_model} \
--t_learning_rate 5e-05 \
--alpha_kd 0.4 \
--temperature 3.0 \
--save_top_k 1 \
--r ${lora_rank} \
--lora_rank ${lora_rank} \
${extra_args}You can also customize this for your own purposes by taking a closer look at the config files and main.py.
In this stage, we test Llama model with the following command in ft_llama:
deepspeed --include localhost:${gpus} --master_port ${random_port} hylora.py \
--train_name hyperlora \
--model_name_or_path models/llama2/13b \
--tokenizer_name /models/llama2/13b \
--train_files data/${dataset}/train.json \
--validation_files /data/${dataset}/eval.json \
--per_device_train_batch_size ${batch_size} \
--per_device_eval_batch_size ${batch_size} \
--use_fast_tokenizer true \
--output_dir ${output_model} \
--evaluation_strategy steps \
--max_eval_samples 800 \
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 8 \
--num_train_epochs 8 \
--warmup_steps 400 \
--load_in_bits 8 \
--lora_r 8 \
--lora_alpha 16 \
--target_modules q_proj,k_proj,v_proj,o_proj,down_proj,gate_proj,up_proj \
--logging_dir ${output_model}/logs \
--logging_strategy steps \
--logging_steps 10 \
--save_strategy steps \
--preprocessing_num_workers 8 \
--save_steps 200 \
--eval_steps 200 \
--save_total_limit 1 \
--seed 29 \
--disable_tqdm false \
--ddp_find_unused_parameters true \
--block_size ${block_size} \
--report_to tensorboard \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--ignore_data_skip true \
--ddp_timeout 18000000 \
--do_train \
--do_eval \If you are interested in more customized runs, you can use the script above as an example.
You can simply modify the config file or add additional command line arguments to finetune-lora.sh.
For zero-shot results, use:
bash ft_llama/test/eval.shIf you find our work useful in your research and would like to cite our project, please use the following citation: found this work useful, please consider giving this repository a star and citing our paper as follows:
@article{liao2024imagination,
title={Imagination Augmented Generation: Learning to Imagine Richer Context for Question Answering over Large Language Models},
author={Liao, Huanxuan and He, Shizhu and Xu, Yao and Zhang, Yuanzhe and Liu, Kang and Liu, Shengping and Zhao, Jun},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.15268},
year={2024}
}