VSCode setup to work with ROS 2 Humble in Ubuntu 22.04.
This configuration can be used to develop ROS components in
- C++
- Python
The configuration here provided can be used as follows:
- Copy the .vscode directory to the directory where you wish to work on
- Take the pieces of the configuration here provided to your already active directory
- clang
- clang-tidy
- clang-format
- gdb
- black
- RobbOwen.synthwave-vscode
- GitHub.copilot
- usernamehw.errorlens
- ms-iot.vscode-ros
- smilerobotics.urdf
- eamodio.gitlens
- mhutchie.git-graph
- redjue.git-commit-plugin
- yzhang.markdown-all-in-one
- DavidAnson.vscode-markdownlint
- ms-vscode-remote.remote-ssh
- ms-vscode.remote-explorer
- ms-vscode-remote.remote-containers
- ms-azuretools.vscode-docker
To install the recommended extensions do cat general_extensions.txt | xargs -I {} code --install-extension {}
- jeff-hykin.better-cpp-syntax
- josetr.cmake-language-support-vscode
- ms-vscode.cmake-tools
- ms-vscode.cpptools
- xaver.clang-format
- llvm-vs-code-extensions.vscode-clangd
- vadimcn.vscode-lldb
To install the recommended extensions do cat cpp_extensions.txt | xargs -I {} code --install-extension {}
- charliermarsh.ruff
- ms-python.python
- ms-python.vscode-pylance
- ms-toolsai.jupyter
- ms-toolsai.jupyter-keymap
- ms-toolsai.jupyter-renderers
- ms-toolsai.vscode-jupyter-cell-tags
To install the recommended extensions do cat python_extensions.txt | xargs -I {} code --install-extension {}
Here are the settings that you should have in VSCode to get the most out of it.
The complete settings can be found in .vscode/settings.json
{
"editor.tabSize": 2,
"editor.rulers": [100],
"ros.distro": "humble",
"search.exclude": {
"**/build": true,
"**/install": true,
"**/log": true
}
}These will do the following:
- Use 2 spaces whenever you press tab
- Add a visible ruler at 100 characters (encourage proper line length)
- Exclude directories for searching (Otherwise you get polluted results)
{
"C_Cpp.codeAnalysis.clangTidy.enabled": true,
"[cpp]": {
"editor.defaultFormatter": "xaver.clang-format"
}
}Regarding the settings for C++. They do the following:
-
Enable clang-format as the formatter for C++ files.
- You can format a file by either right click->Format document or
Ctrl+Shift+I - It is also possible for you to configure vscode to format every time you save. Simply add
"editor.formatOnSave": trueto yoursettings.json - Note: It requires a
.clang-formatconfig file
- You can format a file by either right click->Format document or
-
Enable clang-tidy code analysis. This ensures that clang-tidy is executed on the currently open file every time you save your changes.
- Note: It requires a
.clang-tidyconfig file, as well as acompile_commands.jsonfile.
- Note: It requires a
-
A
.vscode/c_cpp_properties.jsonfile is also required
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Linux",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**",
"/opt/ros/humble/include/**",
"/usr/include/**"
],
"defines": [],
"intelliSenseMode": "gcc-x64",
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/gcc",
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"compileCommands": "${workspaceFolder}/build/compile_commands.json"
}
],
"version": 4
}The configurations entered in the c_cpp_properties.json do the following:
- Path where to find for code definitions. This is consumed by Intellisense to better find includes in the source code.
- Specify the compiler used by intellisense (Language Server)
- Specify path to the compiler
- Version of C and C++ to be used
- Path to the
compile_commands.jsonfile.
"python.envFile": "${workspaceFolder}/.env",
"python.autoComplete.extraPaths": [
"/opt/ros/humble/lib/python3.10/site-packages/"
],
"python.analysis.extraPaths": [
"/opt/ros/humble/lib/python3.10/site-packages/"
],
"[python]": { // Only applies to python files
"editor.defaultFormatter": "charliermarsh.ruff", // Use Ruff as the default formatter
"editor.formatOnSave": true, // Automatically format on save
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll.ruff": "explicit", // Automatically fix fixable lint errors on save
"source.organizeImports.ruff": "explicit", // Automatically organize import statements on save
}
},These settings will do the following:
- Communicate Pylance where to get additional information for code analysis and auto completion
- Path to
.envfile where additional environmental variables can be entered - Code analysis mode (Info: stric is too pedantic)
- VsCode will use both Pylance and Ruff to lint your code every time you save
- Set
ruffas code formatter- You can format a file by either right click->Format document or
Ctrl+Shift+I - It is also possible for you to configure vscode to format every time you save. Simply add
"editor.formatOnSave": trueto yoursettings.json
- You can format a file by either right click->Format document or
These tasks can be used to work with a ROS 2 to compile and test the complete workspace or individual packages.
Note that it expects the following inputs to query the user for some more input data
{
"inputs": [
{
"id": "package",
"type": "promptString",
"description": "Package name",
"default": "demo_nodes_cpp"
}
]
}The complete tasks configurations can be found in .vscode/tasks.json
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "build workspace",
"detail": "Build ROS 2 workspace",
"type": "shell",
"command": "colcon build --symlink-install --cmake-args -DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=ON",
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
}
]
}Builds workspace as symlink-install and generates the compile_commands.json.
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "build pedantic release",
"detail": "Build workspace with release info and with all warnings enabled",
"type": "shell",
"command": "colcon build --symlink-install --cmake-args '-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfo' '-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=On' -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic",
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
}
]
}Builds workspace as symlink-install with release info and all warnings enabled.
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "build single package",
"detail": "Build single ROS 2 package",
"type": "shell",
"command": "colcon build --symlink-install --packages-select ${input:package} --cmake-args '-DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=On'",
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
}
]
}Builds a single ROS package (prompt the user for the name) as symlink-install
and generates the compile_commands.json
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "debug workspace",
"detail": "Build ROS 2 workspace with debug symbols",
"type": "shell",
"command": "colcon build --symlink-install --cmake-args '-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug'",
"group": "build",
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
}
]
}Builds workspace as symlink-install with debug symbols
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "debug single package",
"detail": "Build single ROS 2 package with debug symbols",
"type": "shell",
"command": "colcon build --symlink-install --packages-select ${input:package} --cmake-args '-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug'",
"group": "build",
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
}
]
}Builds a single ROS package (prompt the user for the name) as symlink-install
with debug symbols
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "source-humble",
"detail": "Sources the current workspace with bash shell",
"type": "shell",
"command": "source ${workspaceFolder}/install/setup.bash && printenv > ${workspaceFolder}/local_humble_ws.env",
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"problemMatcher": "$gcc"
}
]
}Helper task that can be used for certain launch configurations to source the ROS workspace.
{
"tasks": [
{
"label": "test workspace",
"detail": "Run all unit tests and show results.",
"type": "shell",
"command": "colcon test && colcon test-result --all",
"group": {
"kind": "test",
"isDefault": true
}
}
]
}Runs colcon test and display the results file.
{
"label": "ament_cpplint current file",
"detail": "Lint the currently open file with cpplint.",
"type": "shell",
"command": "ament_cpplint ${relativeFile}",
"presentation": {
"panel": "dedicated",
"reveal": "silent",
"clear": true
},
"problemMatcher": [
{
"owner": "cpplint",
"source": " cpplint",
"fileLocation": "absolute",
"pattern": [
{
"regexp": "^(.+):(\\d+):\\s+(.+)\\[(.+)\\]$",
"file": 1,
"line": 2,
"message": 3,
"code": 4
}
]
}
]
}Runs ament_cpplint in the current open file and propagates the errors to VSCode
problem matcher.
{
"label": "ament_cppcheck current file",
"detail": "Run static code checker cppcheck on the currently opened file.",
"type": "shell",
"command": "ament_cppcheck ${relativeFile}",
"presentation": {
"panel": "dedicated",
"reveal": "silent",
"clear": true
},
"problemMatcher": [
{
"owner": "cppcheck",
"source": "cppcheck",
"pattern": [
{
"regexp": "^\\[(.+):(\\d+)\\]:\\s+(.+)$",
"file": 1,
"line": 2,
"message": 3
}
]
}
]
}Runs ament_cppcheck in the current open file and propagates the errors to VSCode
problem matcher.
The complete launch configurations can be found in .vscode/launch.json
{
"name": "ROS: Debug launch",
"type": "ros",
"request": "debug_launch",
"target": "${file}"
},Spawns a Python debugger in the current ROS 2 launch file.
{
"name": "Python: ROS 2 launch test",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"preLaunchTask": "source-humble",
"envFile": "${workspaceFolder}/local_humble_ws.env",
"program": "/opt/ros/humble/bin/launch_test",
"args": ["${file}"],
"console": "integratedTerminal"
}Spawns a Python debugger in the current ROS 2 launch test file that use unitttest
framework. This launch configuration uses the launch_test executable from ROS
and it takes care of sourcing the local workspace.
NOTE: When you want to debug a ROS 2 launch test that uses launch_pytest instead, you can either use vscode testing extension or add a main to your file and use Python Launch Configuration
- To attach to a running process, it is required to do the following.
sudo vim /etc/sysctl.d/10-ptrace.conf- Add (or change value to)
kernel.yama.ptrace_scope = 0
- For further details see vscode cpp debuging
- Also, remember to build the package you wish to debug with the debug symbols
--cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug
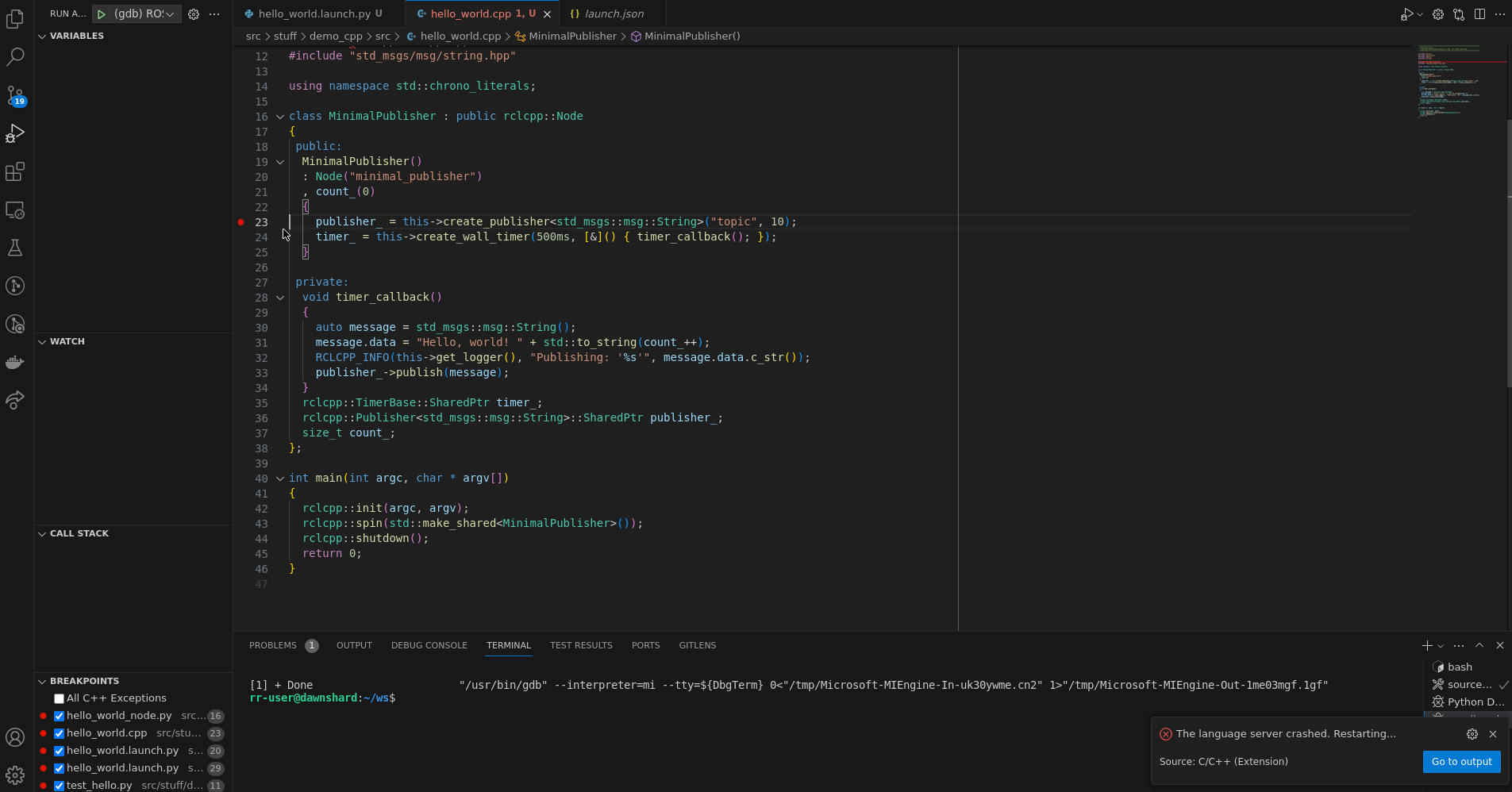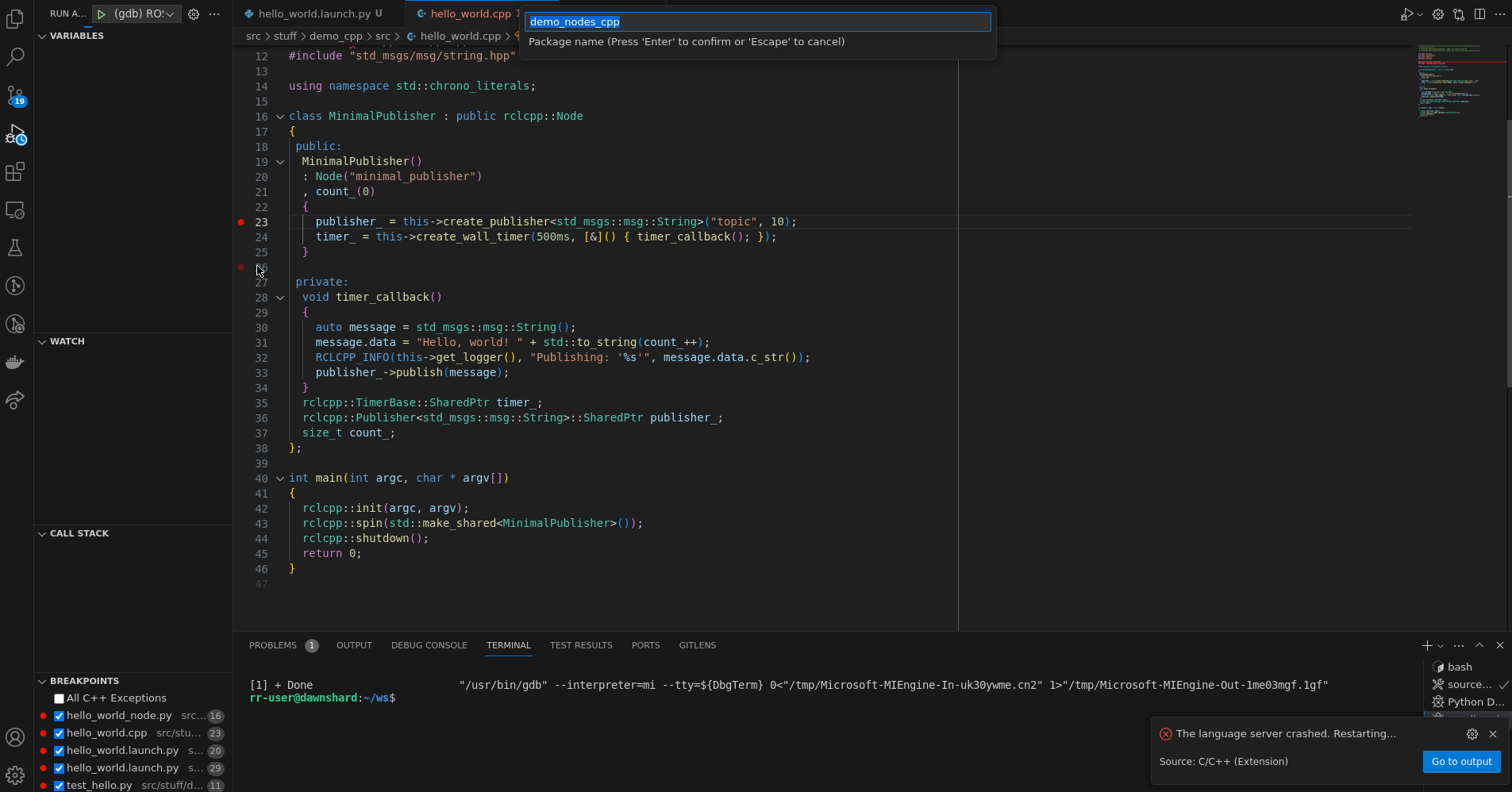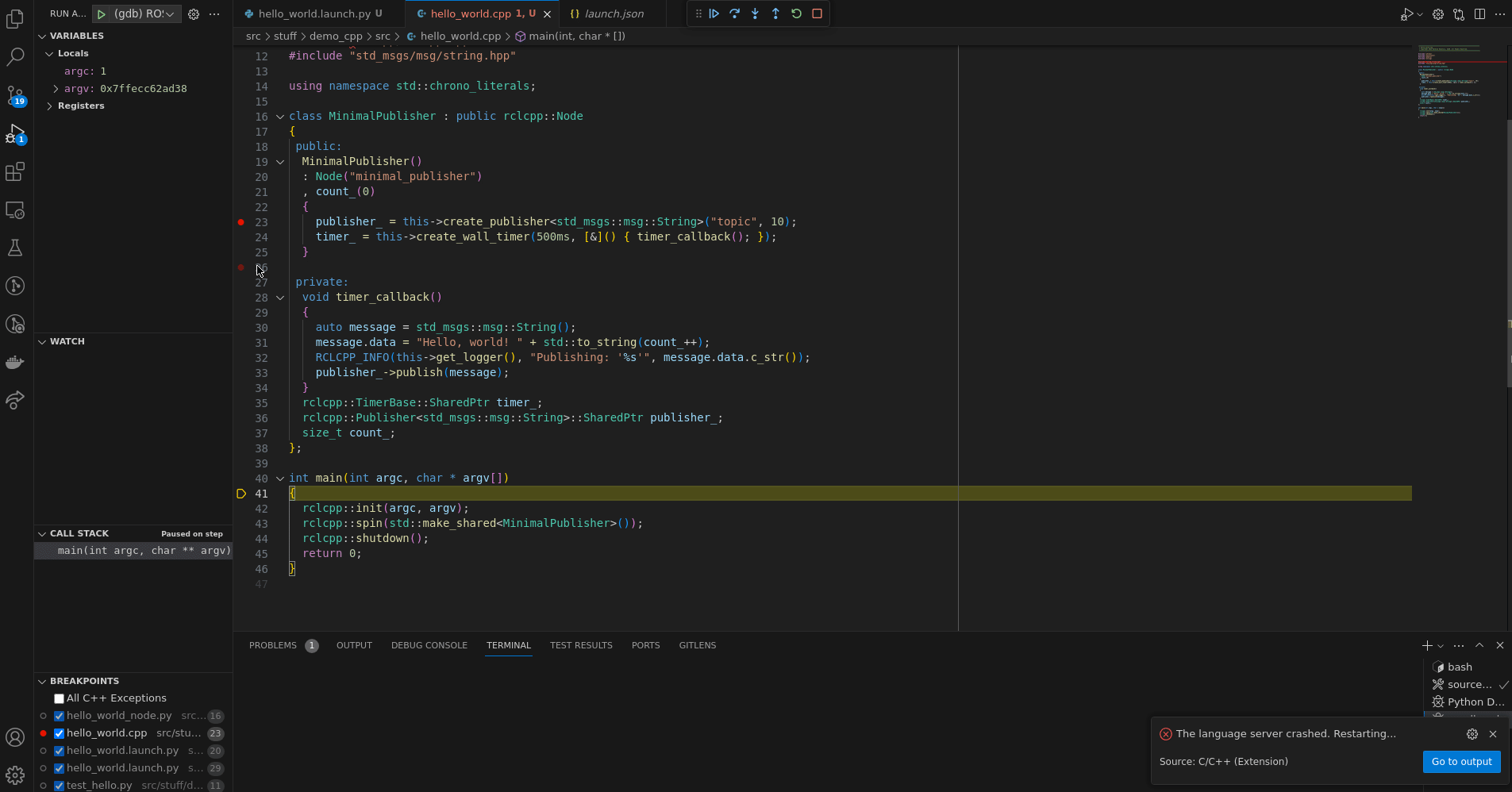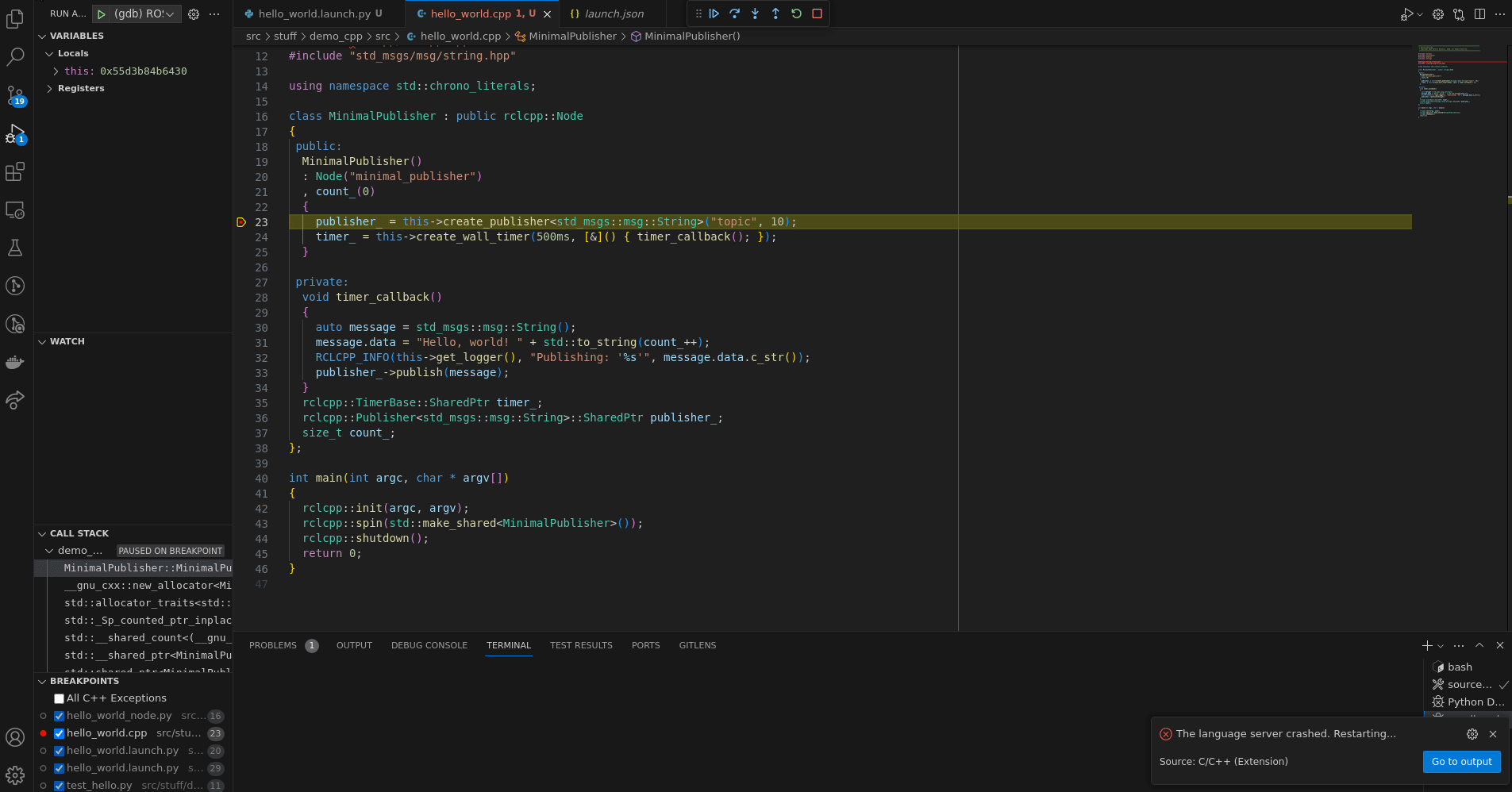
{
"name": "ROS 2 CPP Node",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/install/${input:package}/lib/${input:package}/${input:program}",
"args": [],
"preLaunchTask": "source-humble",
"envFile": "${workspaceFolder}/local_humble_ws.env",
"stopAtEntry": true,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
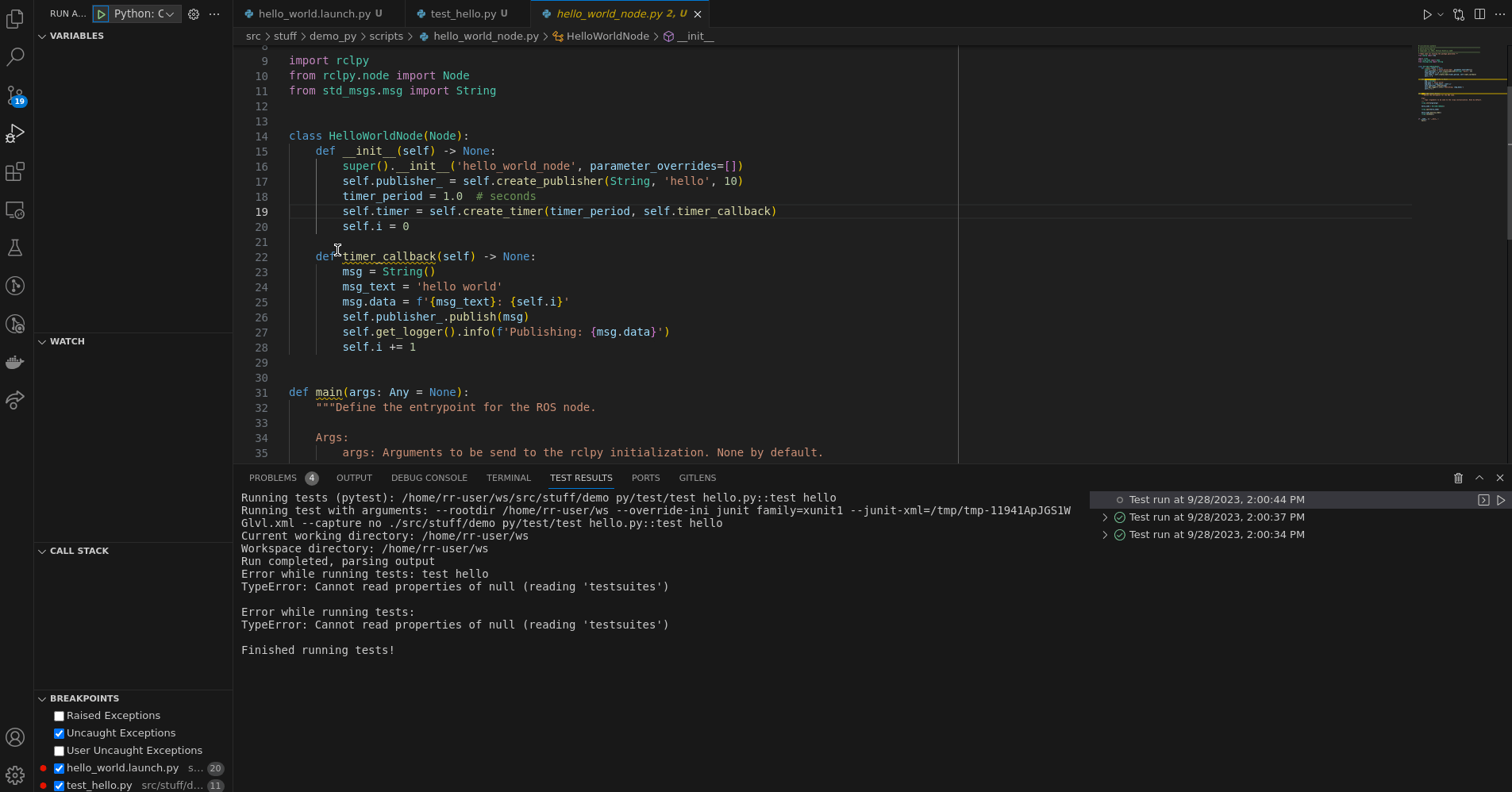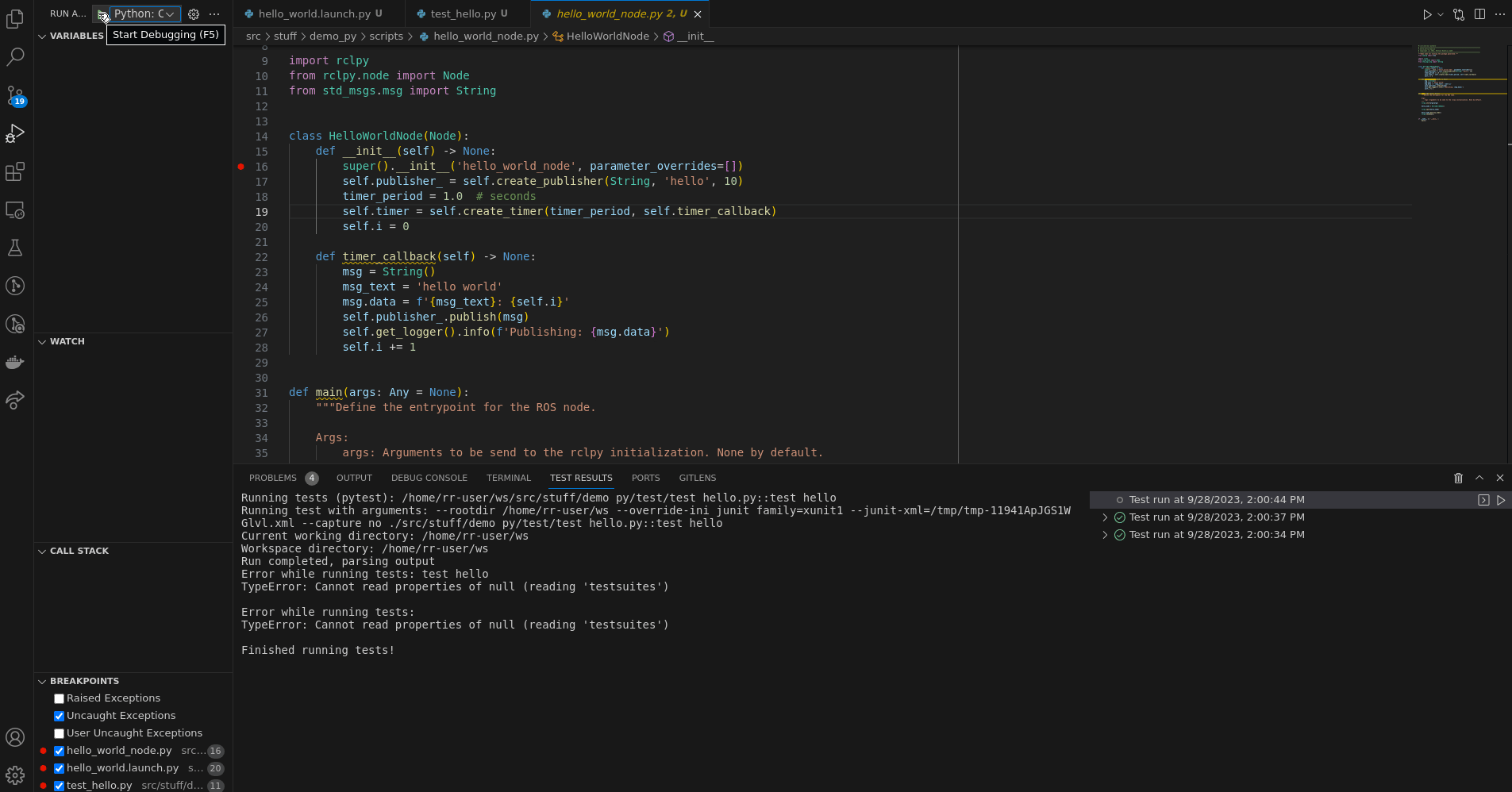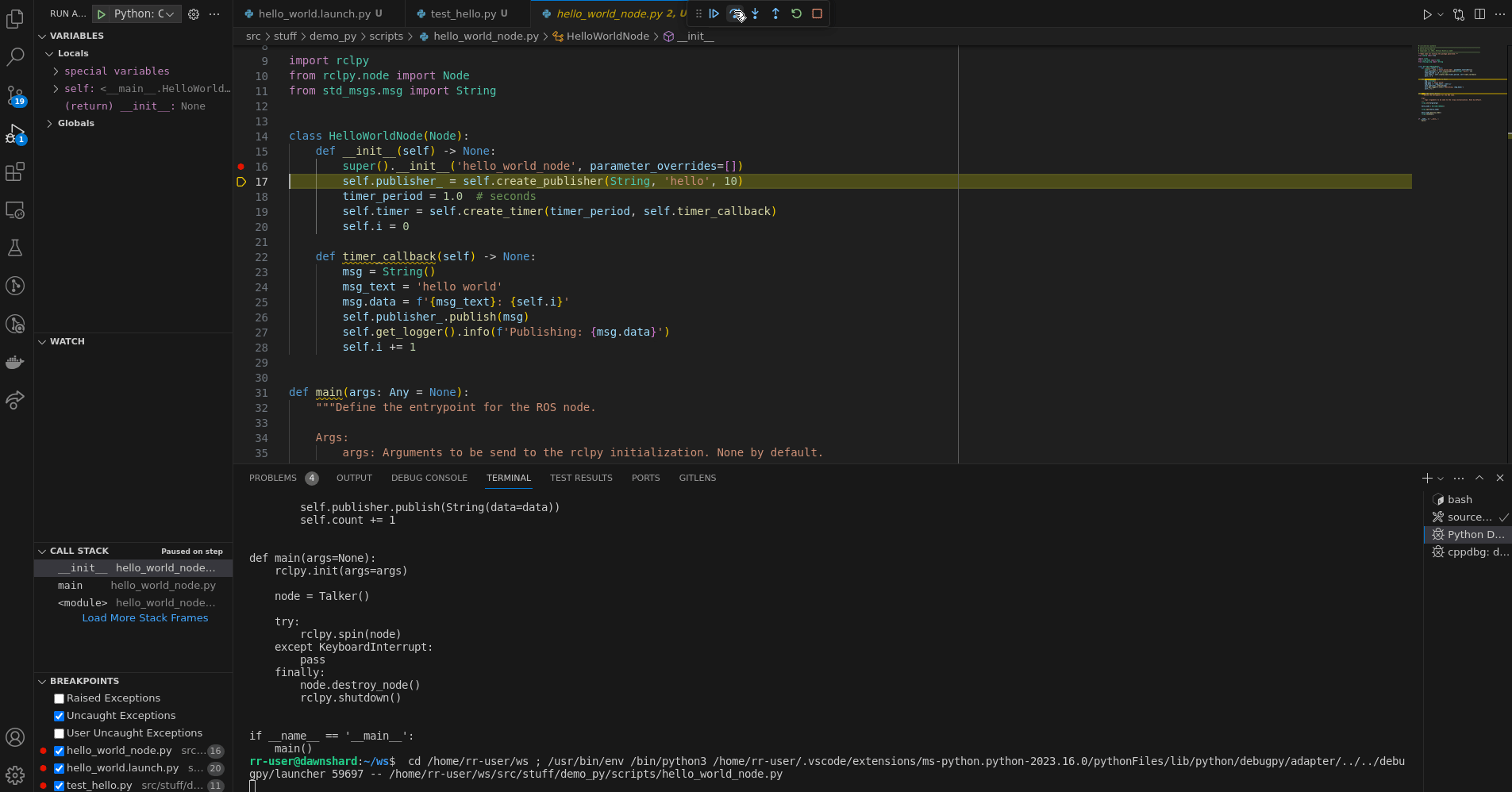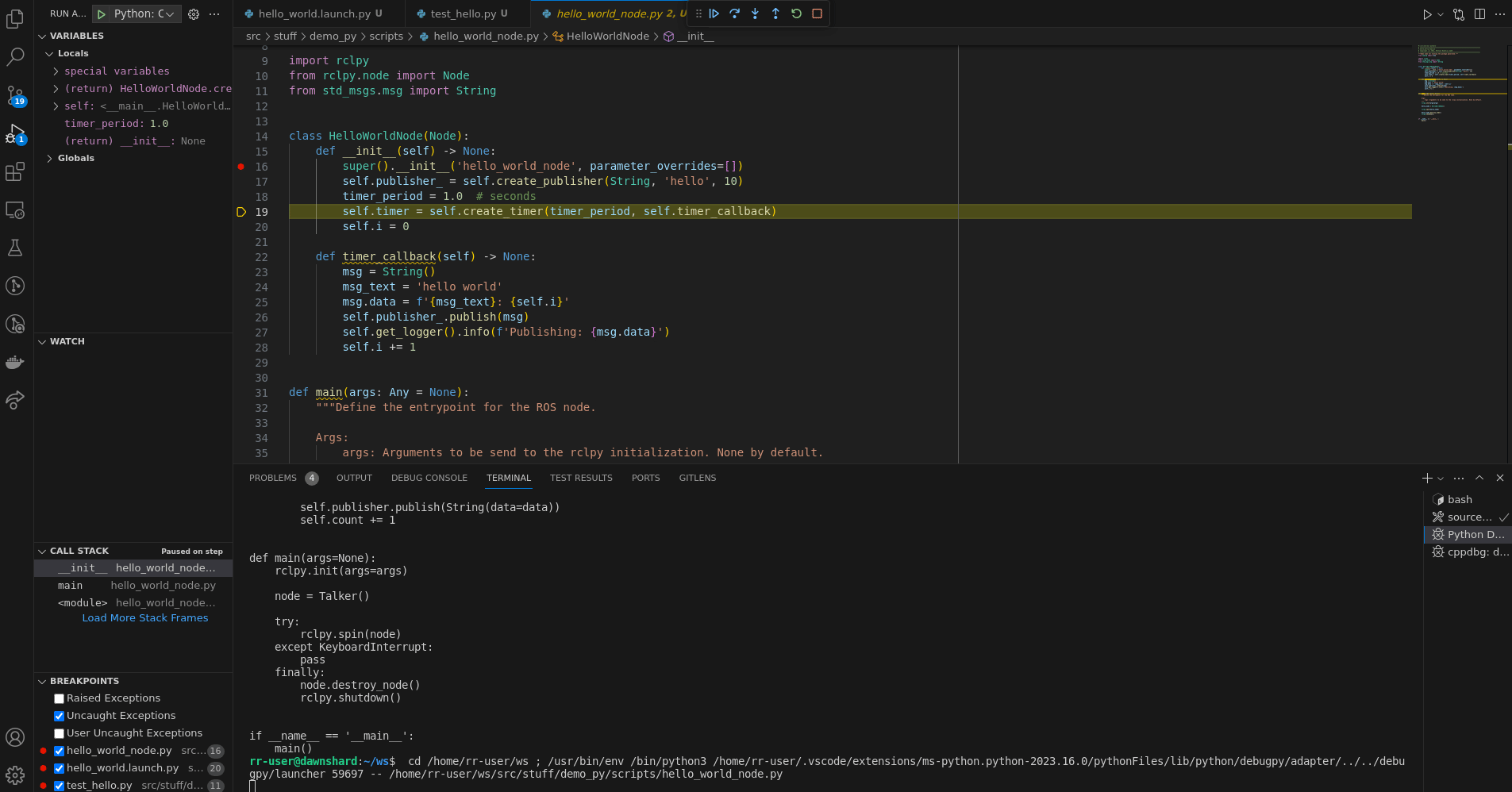
},Spawns a ROS 2 node using cppdbg with the current workspace sourced. It asks
the user for the ROS package and the ROS node that should be spawned.
{
"name": "ROS: Attach",
"type": "ros",
"request": "attach"
},Prompt the user to select the Node type as well as the Process to which the debugger should be attached to. Note: It requires having ptrace properly configure.
{
"name": "Python: Current File",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${file}",
"console": "integratedTerminal"
},Spawns debugpy in the current file and stop at any given breakpoints.
{
"name": "Python: ROS 2 current file",
"type": "python",
"preLaunchTask": "source-humble",
"envFile": "${workspaceFolder}/local_humble_ws.env",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${file}",
"console": "integratedTerminal"
},Very similar to the configuration before, but it loads the ROS 2 workspace environment beforehand.
- For using a vscode development container:
I recommend the following resources:
- athackst/vscode_ros2_workspace: Template repository
- erickkramer/vscode_ros2_workspace (template): Extension of the previous repository with the addition of ssh credential injection and the extensions enlisted above