Norfair is a customizable lightweight Python library for real-time multi-object tracking.
Using Norfair, you can add tracking capabilities to any detector with just a few lines of code.
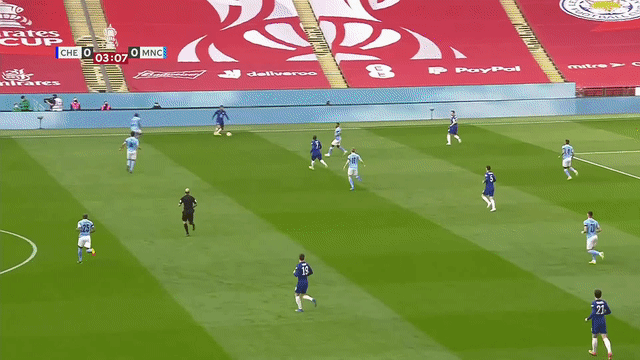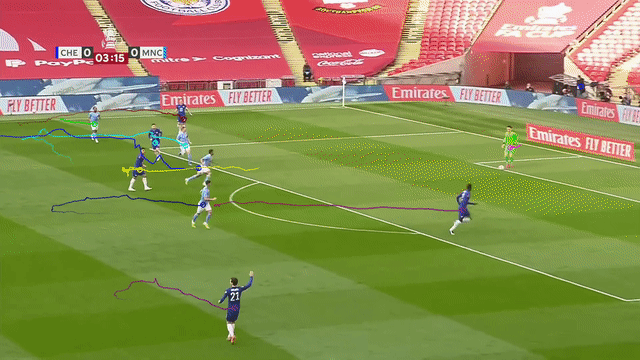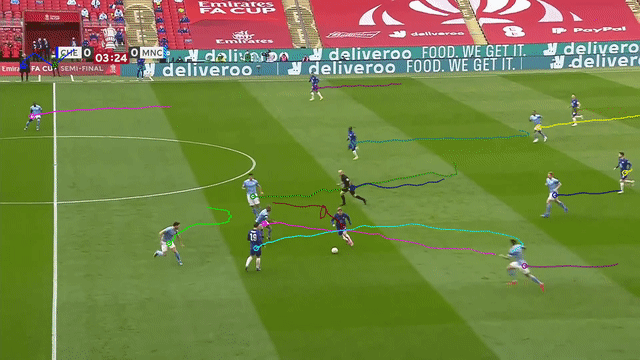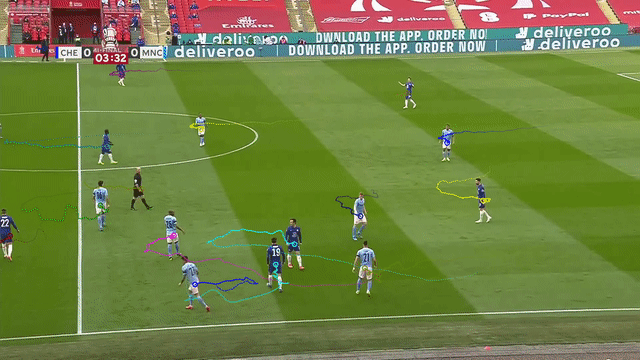
| Tracking players with moving camera | Tracking 3D objects |
|---|---|
 |
 |
-
Any detector expressing its detections as a series of
(x, y)coordinates can be used with Norfair. This includes detectors performing tasks such as object or keypoint detection (see examples). -
Modular. It can easily be inserted into complex video processing pipelines to add tracking to existing projects. At the same time, it is possible to build a video inference loop from scratch using just Norfair and a detector.
-
Supports moving camera, re-identification with appearance embeddings, and n-dimensional object tracking (see Advanced features).
-
Norfair provides several predefined distance functions to compare tracked objects and detections. The distance functions can also be defined by the user, enabling the implementation of different tracking strategies.
-
Fast. The only thing bounding inference speed will be the detection network feeding detections to Norfair.
Norfair is built, used and maintained by Tryolabs.
Norfair currently supports Python 3.6+.
For the minimal version, install as:
pip install norfairTo make Norfair install the dependencies to support more features, install as:
pip install norfair[video] # Adds several video helper features running on OpenCV
pip install norfair[metrics] # Supports running MOT metrics evaluation
pip install norfair[metrics,video] # Everything includedIf the needed dependencies are already present in the system, installing the minimal version of Norfair is enough for enabling the extra features. This is particularly useful for embedded devices, where installing compiled dependencies can be difficult, but they can sometimes come preinstalled with the system.
Official reference available here.
We provide several examples of how Norfair can be used to add tracking capabilities to different detectors, and also showcase more advanced features.
Note: for ease of reproducibility, we provide Dockerfiles for all the demos. Even though Norfair does not need a GPU, the default configuration of most demos requires a GPU to be able to run the detectors. For this, make sure you install NVIDIA Container Toolkit so that your GPU can be shared with Docker.
It is possible to run several demos with a CPU, but you will have to modify the scripts or tinker with the installation of their dependencies.
Most tracking demos are showcased with vehicles and pedestrians, but the detectors are generally trained with many more classes from the COCO dataset.
- YOLOv7: tracking object centroids or bounding boxes.
- YOLOv5: tracking object centroids or bounding boxes.
- YOLOv4: tracking object centroids.
- Detectron2: tracking object centroids.
- AlphaPose: tracking human keypoints (pose estimation) and inserting Norfair into a complex existing pipeline using.
- OpenPose: tracking human keypoints.
- Tracking objects with YOLOPv2, a model for traffic object detection, drivable road area segmentation, and lane line detection.
- Speed up pose estimation by extrapolating detections using OpenPose.
- Track both bounding boxes and human keypoints (multi-class), unifying the detections from a YOLO model and OpenPose.
- Re-identification (ReID) of tracked objects using appearance embeddings. This is a good starting point for scenarios with a lot of occlusion, in which the Kalman filter alone would struggle.
- Accurately track objects even if the camera is moving, by estimating camera motion potentially accounting for pan, tilt, rotation, movement in any direction, and zoom.
- Track points in 3D, using MediaPipe Objectron.
- Tracking of small objects, using SAHI: Slicing Aided Hyper Inference.
- Kalman filter and distance function profiling using TRT pose estimator.
- Computation of MOT17 scores using motmetrics4norfair.
Norfair works by estimating the future position of each point based on its past positions. It then tries to match these estimated positions with newly detected points provided by the detector. For this matching to occur, Norfair can rely on any distance function. There are some predefined distances already integrated in Norfair, and the users can also define their own custom distances. Therefore, each object tracker can be made as simple or as complex as needed.
As an example we use Detectron2 to get the single point detections to use with this distance function. We just use the centroids of the bounding boxes it produces around cars as our detections, and get the following results.
On the left you can see the points we get from Detectron2, and on the right how Norfair tracks them assigning a unique identifier through time. Even a straightforward distance function like this one can work when the tracking needed is simple.
Norfair also provides several useful tools for creating a video inference loop. Here is what the full code for creating the previous example looks like, including the code needed to set up Detectron2:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from detectron2.config import get_cfg
from detectron2.engine import DefaultPredictor
from norfair import Detection, Tracker, Video, draw_tracked_objects
# Set up Detectron2 object detector
cfg = get_cfg()
cfg.merge_from_file("demos/faster_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml")
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST = 0.5
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = "detectron2://COCO-InstanceSegmentation/mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x/137849600/model_final_f10217.pkl"
detector = DefaultPredictor(cfg)
# Norfair
video = Video(input_path="video.mp4")
tracker = Tracker(distance_function="euclidean", distance_threshold=20)
for frame in video:
detections = detector(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
detections = [Detection(p) for p in detections['instances'].pred_boxes.get_centers().cpu().numpy()]
tracked_objects = tracker.update(detections=detections)
draw_tracked_objects(frame, tracked_objects)
video.write(frame)The video and drawing tools use OpenCV frames, so they are compatible with most Python video code available online. The point tracking is based on SORT generalized to detections consisting of a dynamically changing number of points per detection.
Trying out the latest state-of-the-art detectors normally requires running repositories that weren't intended to be easy to use. These tend to be repositories associated with a research paper describing a novel new way of doing detection, and they are therefore intended to be run as a one-off evaluation script to get some result metric to publish on a particular research paper. This explains why they tend to not be easy to run as inference scripts, or why extracting the core model to use in another standalone script isn't always trivial.
Norfair was born out of the need to quickly add a simple layer of tracking over a wide range of newly released SOTA detectors. It was designed to seamlessly be plugged into a complex, highly coupled code base, with minimum effort. Norfair provides a series of modular but compatible tools, which you can pick and choose to use in your project.
Norfair's contribution to Python's object tracker library repertoire is its ability to work with any object detector by being able to work with a variable number of points per detection, and the ability for the user to heavily customize the tracker by creating their own distance function.
If you are looking for a tracker, here are some other projects worth noting:
- OpenCV includes several tracking solutions like KCF Tracker and MedianFlow Tracker which are run by making the user select a part of the frame to track, and then letting the tracker follow that area. They tend not to be run on top of a detector and are not very robust.
- dlib includes a correlation single object tracker. You have to create your own multiple object tracker on top of it yourself if you want to track multiple objects with it.
- AlphaPose just released a new version of their human pose tracker. This tracker is tightly integrated into their code base, and to the task of tracking human poses.
- SORT and Deep SORT are similar to this repo in that they use Kalman filters (and a deep embedding for Deep SORT), but they are hardcoded to a fixed distance function and to tracking boxes. Norfair also adds some filtering when matching tracked objects with detections, and changes the Hungarian Algorithm for its own distance minimizer. Both these repos are also released under the GPL license, which might be an issue for some individuals or companies because the source code of derivative works needs to be published.
MOT17 and MOT20 results obtained using motmetrics4norfair demo script on the train split. We used detections obtained with ByteTrack's YOLOX object detection model.
| MOT17 Train | IDF1 IDP IDR | Rcll | Prcn | MOTA MOTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOT17-02 | 61.3% 63.6% 59.0% | 86.8% | 93.5% | 79.9% 14.8% |
| MOT17-04 | 93.3% 93.6% 93.0% | 98.6% | 99.3% | 97.9% 07.9% |
| MOT17-05 | 77.8% 77.7% 77.8% | 85.9% | 85.8% | 71.2% 14.7% |
| MOT17-09 | 65.0% 67.4% 62.9% | 90.3% | 96.8% | 86.8% 12.2% |
| MOT17-10 | 70.2% 72.5% 68.1% | 87.3% | 93.0% | 80.1% 18.7% |
| MOT17-11 | 80.2% 80.5% 80.0% | 93.0% | 93.6% | 86.4% 11.3% |
| MOT17-13 | 79.0% 79.6% 78.4% | 90.6% | 92.0% | 82.4% 16.6% |
| OVERALL | 80.6% 81.8% 79.6% | 92.9% | 95.5% | 88.1% 11.9% |
| MOT20 Train | IDF1 IDP IDR | Rcll | Prcn | MOTA MOTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOT20-01 | 85.9% 88.1% 83.8% | 93.4% | 98.2% | 91.5% 12.6% |
| MOT20-02 | 72.8% 74.6% 71.0% | 93.2% | 97.9% | 91.0% 12.7% |
| MOT20-03 | 93.0% 94.1% 92.0% | 96.1% | 98.3% | 94.4% 13.7% |
| MOT20-05 | 87.9% 88.9% 87.0% | 96.0% | 98.1% | 94.1% 13.0% |
| OVERALL | 87.3% 88.4% 86.2% | 95.6% | 98.1% | 93.7% 13.2% |
Tryolabs can provide commercial support, implement new features in Norfair or build video analytics tools for solving your challenging problems. Norfair powers several video analytics applications, such as the face mask detection tool.
If you are interested, please contact us.
For citations in academic publications, please export your desired citation format (BibTeX or other) from Zenodo.
Copyright © 2022, Tryolabs. Released under the BSD 3-Clause.








