you can also check: https://zlab.umassmed.edu/CIpipe/ or http://www.calyx.biz/cipipe.html
#CIpipe - CRISPR Indel pipe ###Apr22, 2016 (Nov07, 2016), Yingxiang Li
- Introduction
- Installation
- Usage
- [Workflow Charts](#Workflow Charts)
- [Annotation of example.input.tab](#Annotation of example.input.tab)
- [Test Cases](#Test Cases)
- Thanks
CRISPR-Cas9 is a powerful tool for sequence-specific genome editing. The Cas protein cuts genomic DNA at locations complementary to a single guide RNA. Insertions and deletions (indels) often result when the cuts are repaired. Currently, there is no easy-to-use computational pipeline to determine the locations, identities, and frequencies of the indels. We have developed a pipeline, named CIpipe (CRISPR Indel pipeline), to identify indels in high-throughput DNA sequencing data and provide the statistical characterization of these indels.
Installation ------CIpipe can only run on Mac OS or Linux OS.
You need python 2.7.10, R 3.2.2, bwa 0.7.5a, fastqc v0.11.2, samtools 1.3, java 1.7.0_95 first.
After installation of pip, type in your terminal:
(sudo) pip install CIpipe (--upgrade)| parameter | introduction |
|---|---|
| -h, --help | show this help message and exit |
| -V, --version | show program's version number and exit |
| -R REFERENCE, --reference REFERENCE | sample reference file, fasta format. (eg: my_ref.fa) |
| -D DATA, --data DATA | sample data directory, fastq-ONLY. one file for single end, two files for paired end. (eg: my_data/) |
| -O OUTPUT, --output | OUTPUT output directory, will be created if not exists. (eg: my_output/) |
| -F, --refresh | whether to refresh all processes. default: OFF, -RE will turn ON. |
| -N NAME, --name NAME | sample name, default is name of output directory. (eg: my_sample) |
| -RK RANK, --rank RANK | sample rank. (eg: 1) |
| -CA CUTADAPTA, --cutadapta CUTADAPTA | cut 3' adapter with cutadapt, default: none. |
| -CG CUTADAPTG, --cutadaptg CUTADAPTG | cut 5' adapter with cutadapt, default: none. |
| -S SEED, --seed SEED | the minimum seed length in BWA, default: 19. |
| -M, --markdup | whether to mark and remove duplicate by Picard. default: OFF, -M will turn ON. |
| -U, --unlimited | whether to set no read depth limit in mpileup by SAMtools. default: ON, -U will turn OFF. |
| -G, --gatk | whether to search for indel by GATK. default: OFF, -G will turn ON. |
| -P PVALUE, --pvalue | PVALUE minimal p value, default: 0.05. |
| -B BASEQUALITY, --basequality BASEQUALITY | minimal base quality, default: 30. |
| -A VARFREQ, --varfreq VARFREQ | minimal variant frequency, default: 0.0001. |
| -VO, --vcf | whether to output VarScan in VCF format. default: OFF, -VI will turn ON. |
| -VI, --indel | whether to search for indel by VarScan. default: ON, -VI will turn OFF. |
| -VR, --readcount | whether to search for read counts by VarScan. default: ON, -VR will turn OFF. |
| -VS, --snp | whether to search for SNP by VarScan. default: OFF, -VS will turn ON. |
| -VC, --consensus | whether to search for consensus call by VarScan. default: OFF, -VC will turn ON. |
| -T TARGET, --target TARGET | CRISPR target position. indel in target range will be picked out, mutiple targets separated by ',', default: 'none'. (eg: gene1:100,gene2:200) |
| -US UPSTREAM, --upstream UPSTREAM | up stream distance from CRISPR target position, default: 20. |
| -DS DOWNSTREAM, --downstream DOWNSTREAM | down stream distance from CRISPR target position, default: 10. |
| -Q RESULTFREQ, --resultfreq RESULTFREQ | to select the results above appointed frequency, default: 0.05. |
###For multiple samples and advanced analysis. Synopsis
CIpipe -E
CIpipe -I test.input.taboptional arguments:
| parameter | introduction |
|---|---|
| -E, --example | whether to create example input data. modify the example.input.tab to fit your data. default: OFF, -E will turn ON. |
| -I INPUT, --input INPUT | information table of all input data. all settings should be in it. (eg. example.input.tab) |
###For a single samples analysis (basic).
###For a single samples analysis (complete).
###For multiple samples and advanced analysis. (basic).
###For multiple samples and advanced analysis. (complete).
Annotation of example.input.tab ------ Type: ```Bash CIpipe -E``` to create an `example.input.tab`. Then modify it to fit your real data.
The full data is: PRJNA283020. Here I only get the top 20,000 lines of each fastq file.
-
Download the data:
SRR2007490,SRR2007491,SRR207493. (12.5MB, 12.4MB, 11.8MB) -
Download the reference:
refer.zip(LSL_1008bp.fa, iGFP_448bp.fa). (2KB) -
For a single sample analysis (name: test1):
- Extract
refer.ziptorefer/. - Extract
SRR2007490todata/SRR2007490/. - After the installation of CIpipe, in the terminal, type:
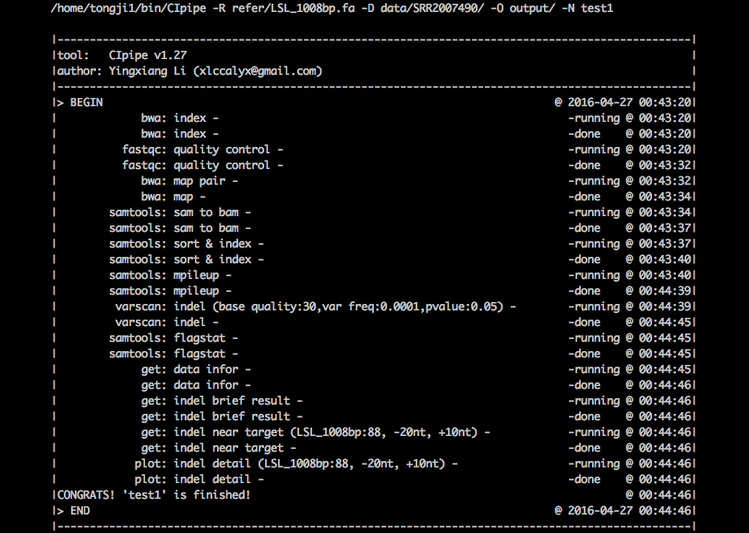
Bash CIpipe -R refer/LSL_1008bp.fa -D data/SRR2007490/ -O output/ -N test1 - CIpipe will show the progress on your terminal screen like this:
- The files in output/test1/result folder include:
test1.data.infor.txt(the map and data information)-
test1.indel.brief.tab(the brief indel result fromVarScan/test1.indel.tab) test1.indel.potential.LSL_1008bp:88.tab(the indel target position range result. if user didn't point out the cut position, CIpipe will assume that the position with the max varfreq was the cut position and add a 'potential' in the file name.)test1.indel.potential.LSL_1008bp:88.pdf(the indel target position region detail plot. it's ordered by positions and from small to large and indel types from deletion to insertion)test1.indel.potential.LSL_1008bp:88.sort.pdf(the indel target position detail plot. it's ordered by variant frequency from high to low.)
- Extract
-
For multiple samples and advanced analysis:
-
Extract
refer.ziptorefer/. -
Extract
SRR2007490,SRR2007491,SRR207493todata/SRR2007490/,data/SRR2007491/,data/SRR2007493/. -
In the terminal, type:
Bash CIpipe more -Eexmaple.input.tabwill be generated in the current working directory like this: -
Open
example.input.taband modify it totest2.input.tabas follows: -
In the terminal, type:
Bash CIpipe -I input/test2.input.tab -
CIpipe will show the progress on your terminal screen like this:
-
In result folder of each sample, there are such files (example:
LSL2):LSL2.data.infor.txt(the map and data information)LSL2.indel.brief.tab(the brief indel result)LSL2.indel.LSL_1008bp:88.tab(the indels only in target region, if user pointed out the cut position, there will be no 'potential' in the file name.)LSL2.indel.LSL_1008bp:88.pdf(the indel target position region detail plot)LSL2.indel.LSL_1008bp:88.sort.pdf(the indel target position region detail plot)
-
In the result folder of batch (test2.result/), there are such files:
test2.indel.iGFP_448bp.mat(indels across all iGFP samples)test2.indel.LSL_1008bp.mat(indels across all LSL samples)
-
-
You can change all kinds of parameters to filter the results. For example, you can change the p value to 0.01 to get a stricter indels result table; change base quality to 15 to get more potential indels.