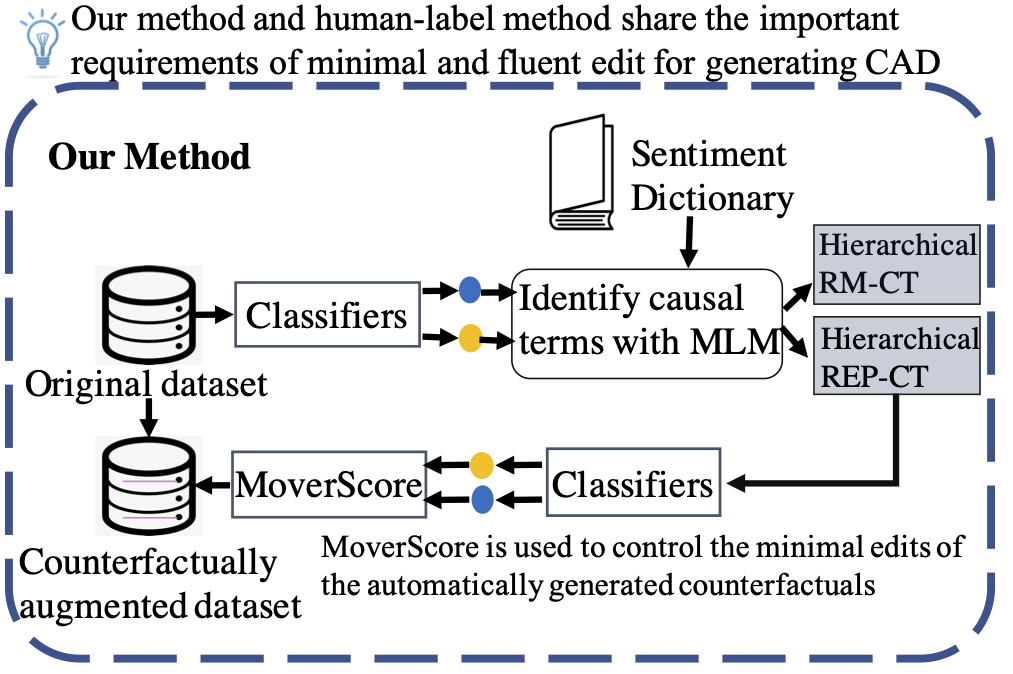
This is the code repositry for the ACL-IJCNLP 2021 paper: Exploring the Efficacy of Automatically Generated Counterfactuals for Sentiment Analysis
Authors: Linyi Yang, Jiazheng Li, Pádraig Cunningham, Yue Zhang, Barry Smyth and Ruihai Dong
While state-of-the-art NLP models have been achieving the excellent performance of a wide range of tasks in recent years, important questions are being raised about their robustness and their underlying sensitivity to systematic biases that may exist in their training and test data. Such issues come to be manifest in performance problems when faced with out-of-distribution data in the field. One recent solution has been to use counterfactually augmented datasets in order to reduce any reliance on spurious patterns that may exist in the original data. Producing high-quality augmented data can be costly and time-consuming as it usually needs to involve human feedback and crowdsourcing efforts. In this work, we propose an alternative by describing and evaluating an approach to automatically generating counterfactual data for the purpose of data augmentation and explanation. A comprehensive evaluation on several different datasets and using a variety of state-of-the-art benchmarks demonstrate how our approach can achieve significant improvements in model performance when compared to models training on the original data and even when compared to models trained with the benefit of human-generated augmented data.
Default project structure:
Counterfactuals-for-Sentiment-Analysis
├── README.md
├── Introduction.png
├── .gitignore
├── requirements.txt
├── run.sh
├── cfsa.py
├── cfsa
│ ├── cfsa.py
│ ├── cfsarep.py
│ ├── cfsarm.py
│ ├── constants.py
│ └── loader.py
├── mvscore
│ └── mvscore.py
├── sa_dictionary
│ ├── neg_proun.npy
│ ├── negative.txt
│ └── positive.txt
├── model
│ ├── best-checkpoint
│ │ └── ...
│ └── ...
└── outputs
└── ...
-
Install
condaandpipif you do not already have them. Create a new Python 3.7 env and activate.conda create --name cfsa python=3.7 conda activate cfsa
-
Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/lijiazheng99/Counterfactuals-for-Sentiment-Analysis.git -
Install required dependencies with
pip:pip install -r requirements.txt
Note: requires internet connection and GPU access.
-
Download a sample model from here (1.52 GB), unzip into the default language model folder
model/. -
Run the sample:
python cfsa.py --best_model model/best-checkpoint/ --tokenizer model/
| Arguments | Description |
|---|---|
--train_set |
Specify the path to the train set. Default value is a link to the default train set. |
--dict_path |
Specify the path to dictionaries. Default folder is sa_dictionary/ |
--model |
Setting for model type. This project is designed to take four types of configurations bert-base, bert-large, roberta and xlnet. The default value is bert-base. You can check out Hugging Face Transformers and edit constants.py to explore more models. |
--token_length |
Specify the token length for your current language model, default setting is 128. |
--best_model |
Path to the best checkpoint for your fine-tuned model. |
--tokenizer |
Path to the tokenizer of your fine-tuned model. |
--output_path |
Path to the output folder for store generated counterfactuals and logs. The default value is outputs/. |
--cuda |
(Not necessary) Specify the GPU, if you have multiple GPUs. |
--store_cfs |
(Not necessary) Stores unselected conterfactuals data. |
Please checkout these examples from Hugging Face Transformer, to fine-tune your custom models.
To be available soon.
Please consider to cite our work, thanks.
@inproceedings{yang-etal-2021-exploring,
title = "Exploring the Efficacy of Automatically Generated Counterfactuals for Sentiment Analysis",
author = "Yang, Linyi and
Li, Jiazheng and
Cunningham, Padraig and
Zhang, Yue and
Smyth, Barry and
Dong, Ruihai",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers)",
month = aug,
year = "2021",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-long.26",
pages = "306--316",
abstract = "While state-of-the-art NLP models have been achieving the excellent performance of a wide range of tasks in recent years, important questions are being raised about their robustness and their underlying sensitivity to systematic biases that may exist in their training and test data. Such issues come to be manifest in performance problems when faced with out-of-distribution data in the field. One recent solution has been to use counterfactually augmented datasets in order to reduce any reliance on spurious patterns that may exist in the original data. Producing high-quality augmented data can be costly and time-consuming as it usually needs to involve human feedback and crowdsourcing efforts. In this work, we propose an alternative by describing and evaluating an approach to automatically generating counterfactual data for the purpose of data augmentation and explanation. A comprehensive evaluation on several different datasets and using a variety of state-of-the-art benchmarks demonstrate how our approach can achieve significant improvements in model performance when compared to models training on the original data and even when compared to models trained with the benefit of human-generated augmented data.",
}