A recommendation model that is small, powerful and efficient to train
DQRM paper in pdf format is now available

This repo is built based on the original DLRM repo, while the quantization code for embedding tables and linear layers is shared with HAWQ.
State-of-the-art click through rate recommendation model DLRM is intensively used in the industry environment. However, DLRM has gigantic embedding tables which cause great memory overhead during inference and training. Large embedding tables took up more than 99% of the total parameters in these models, and previous works have shown that these embedding tables are over-parameterized.
This project shows that large and over-parameterized embedding tables lead to severe overfitting and huge inefficiency in using the training data, as model overfits during second epoch of the training set. Then, the project shows that heavy quantization (uniform INT4 quantization) and quantization-aware training (QAT) can significantly reduce overfitting during training. The quantized model performance even edge against the original unquantized model on Criteo Kaggle Dataset.
However, naive QAT can lead to inefficiency for recommendation models, exacebating the memory bottleneck during training. We proposed two techniques to improve the naive QAT. Also, DLRM are usually large and trained under distributed environments, we combined quantization and sparsification together to compress the communication. We publish our project as Deep Quantized Recommendation System (DQRM), which is a recommendation system that is small, powerful, and efficient to train.
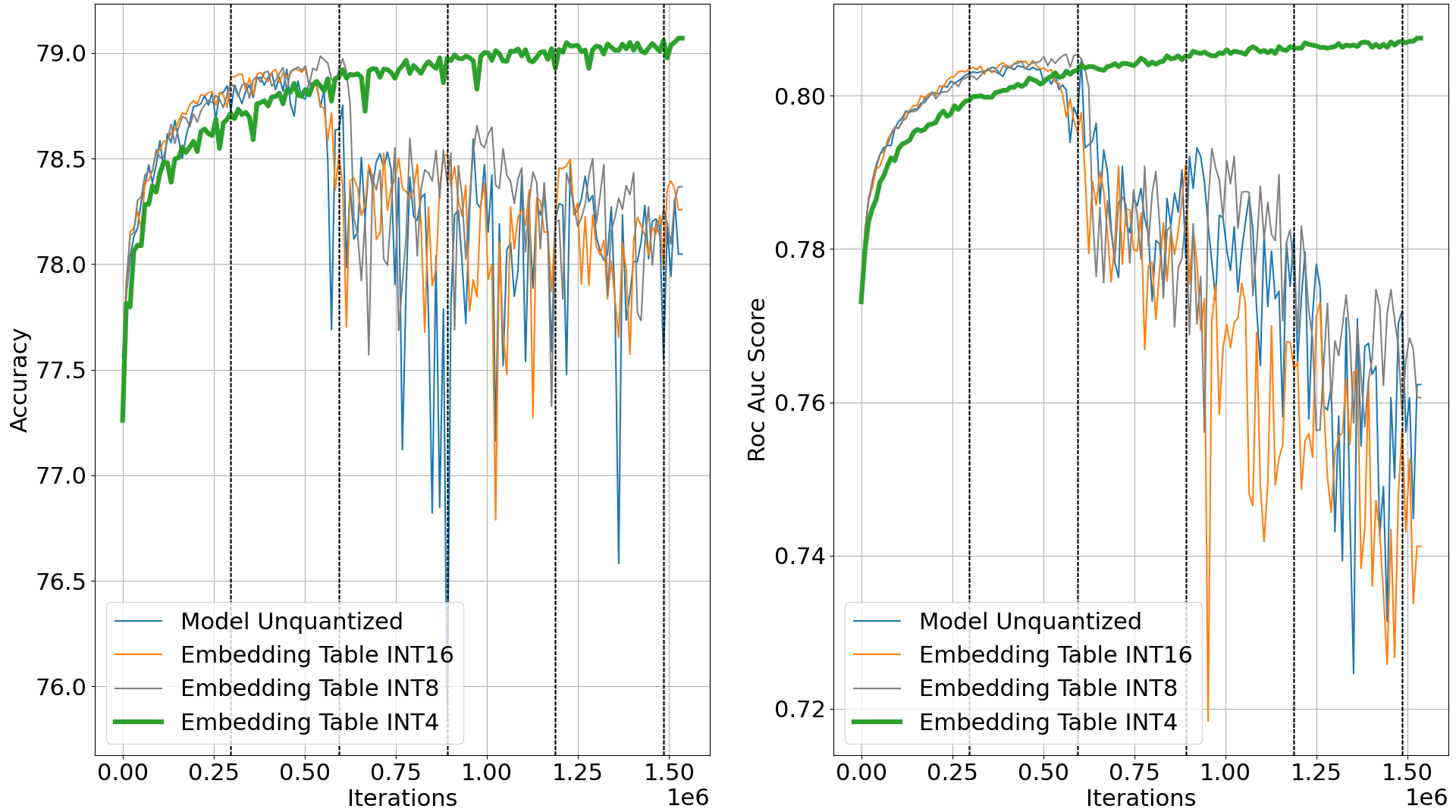
We found that low-precision quantization of embedding tables exhibits strong effect of overfitting reduction. As the results can be better exihit from the following diagrams. We present contrast between low-precision quantization (QAT) versus single-precision (normal training). Experiments conducted using one single Nvidia A5000 GPU.
Below are experiments of DQRM weight quantization results. Please note that all of the statistics reported here are all run under the distributed data parallelism. As mentioned in the paper, accuracies are consistently lower than running on the single node or machine settings. We report single machine accuracies in the paper section 3 for better evaluation of weight quantization performance from DQRM. Please refer to the paper for official results, statistics shown here are for reference.
Following the observations, we further quantize the MLP layers into INT4. The entire model is then quantized into INT4 uniformly.
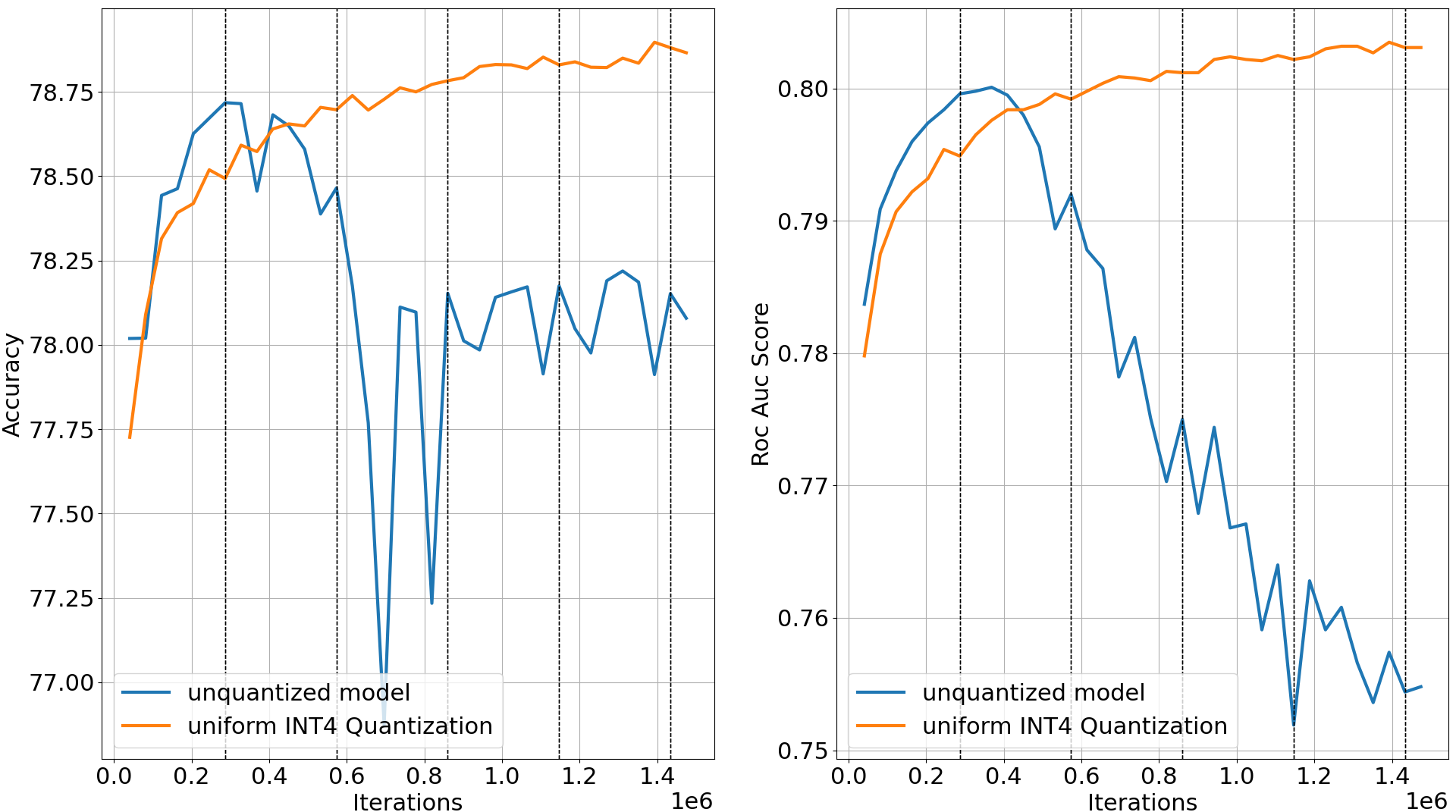
Heavily quantized models outperforms the original models by better overcoming overfitting (Criteo Kaggle Dataset)
| Settings | Model bit width | Training loss | Testing Accuracy | Testing ROC AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | FP32 | 0.303685 | 78.718% | 0.8001 |
| DQRM | INT4 | 0.436685 | 78.897% | 0.8035 |
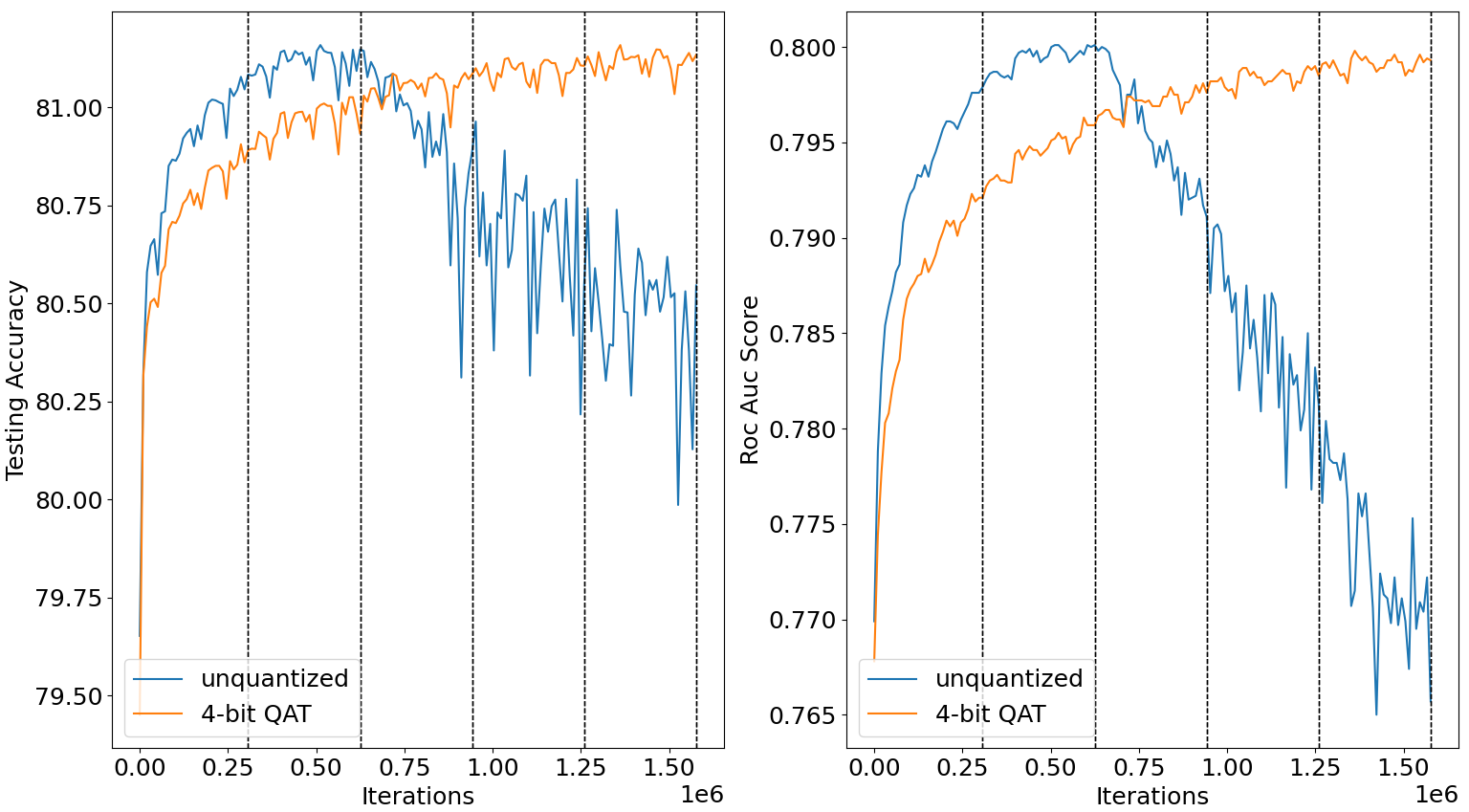
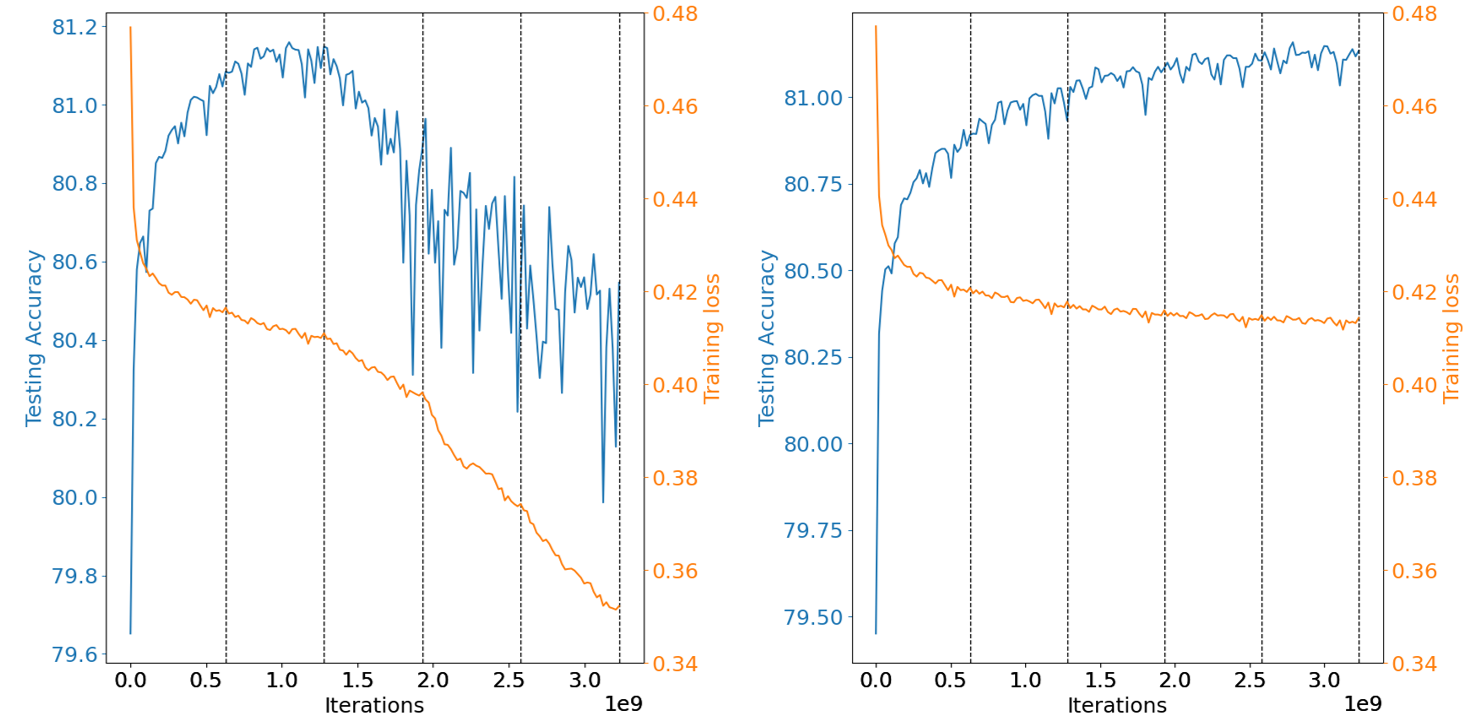
Heavily quantized models outperforms the original models by better overcoming overfitting (Criteo Terabyte Dataset)
Original model training loss falls as the model suffers overfitting, comparing with uniform INT4 Quantization-aware Training (QAT)
| Settings | Model bit width | Training loss | Testing Accuracy | Testing ROC AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseline | FP32 | 0.347071 | 81.165% | 0.8004 |
| DQRM | INT4 | 0.412979 | 81.159% | 0.7998 |
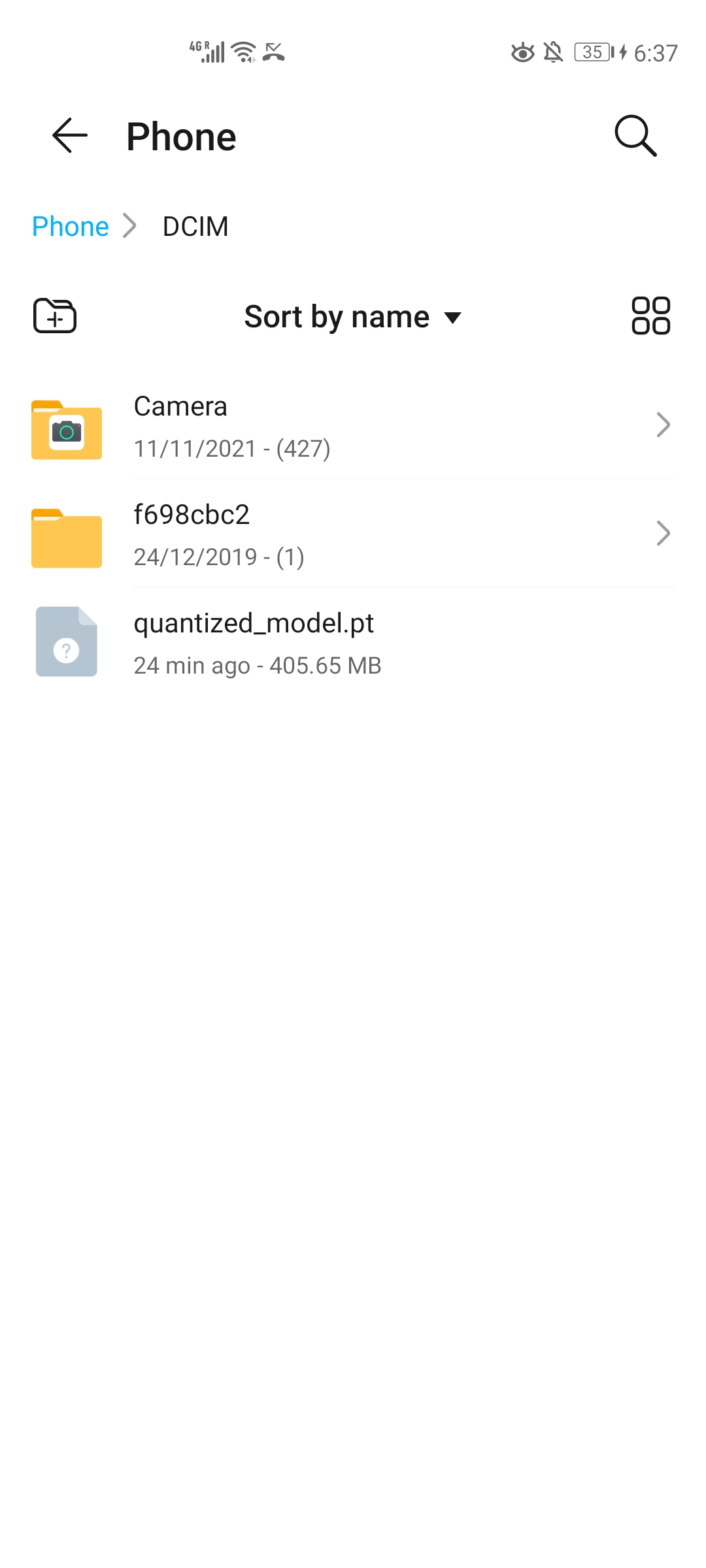
We include a demo of DQRM exported to an Android phone. From the below figures, the tested DQRM model size is 405.65 MB. As a reference, the DLRM Kaggle model size is 2.16 GB. The model size is not strictly 8$\times$ compression because of the following two reasons: 1) Embedding tables can be quantized into INT4, but the embedding vectors have to be bit-packed together into INT8 format to fully benefit from the INT4 low precision. However, bitpacking on PyTorch is tricky and PyTorch 4-bit packing is not fully optimized in terms of performance. 2) PyTorch doesn't support MLP layers to be quantized into bitwidth below INT8. Therefore, MLP layers, although quantized into INT4, still need to be stored as INT8 numbers. Still, we believe this is a first step towards deploying large recommendation models to edge devices so as to alleviate the heavy cloud AI inference pressure.
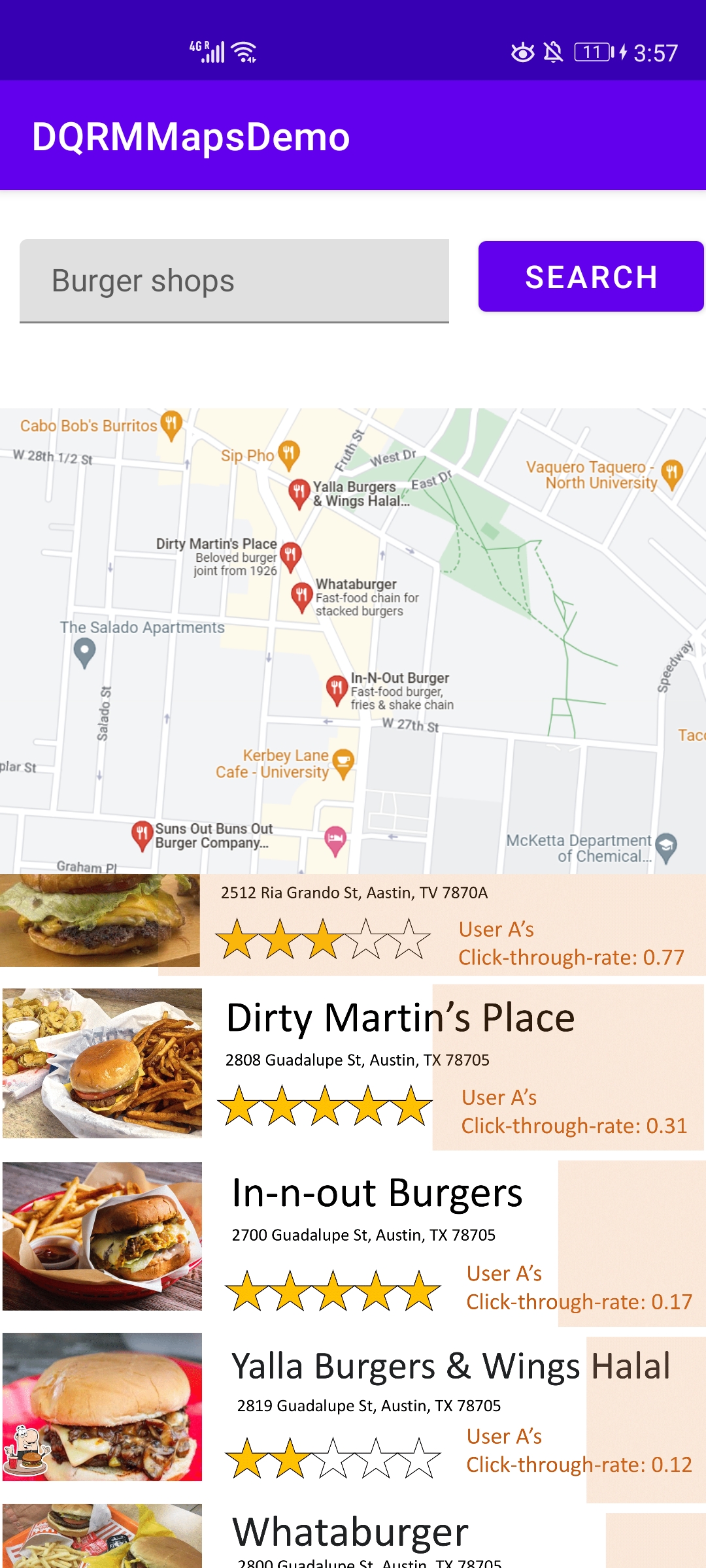
Also, we built an demo map mobile app to illustrate one possible use of the quantized recommendation model on edge.
- Running on GPUs and the Criteo Kaggle Dataset
bash -x ./bash_scripts/Kaggle/run_dlrm_kaggle_gpu_four.sh
- Running on CPU clusters and the Criteo Terabyte Dataset
bash -x ./bash_scripts/Terabytes/run_dlrm_tb_cpu.sh
pytorch-nightly (11/10/20)
scikit-learn
numpy
onnx (optional)
pydot (optional)
torchviz (optional)
mpi (optional for distributed backend)