This extension can create command sequence as one command and bind a key, or call it manually.
- create command sequence as one command and bind a key.
- call command sequence manually.
- set interval between each command execution.
There is simple usage that uses only keybindings.json and a usage that uses settings.json.
In keybindings.json, bind a key to extension.multiCommand.execute with passing a command sequence you want to execute as the argument.
For example:
{
"key": "alt+x",
"command": "extension.multiCommand.execute",
"args": {
"sequence": [
"cursorDown",
"cursorDown",
"cursorDown"
]
}
}This command sequence executes "cursorDown" command 3 times.
This usage is useful for reusing the defined command sequence in another command sequnce or executing the sequence manually.
In case using settings.json, the settings has 2 steps.
-
Create command sequence as one command in settings.json.
For example:"multiCommand.commands": [ { "command": "multiCommand.down3Lines", "sequence": [ "cursorDown", "cursorDown", "cursorDown" ] }, { "command": "multiCommand.swapChar", "interval": 30, "sequence": [ "cursorLeftSelect", "editor.action.clipboardCutAction", "cursorRight", "editor.action.clipboardPasteAction" ] } ]
First sequence is named "multiCommand.down3Lines" and executes "cursorDown" command 3 times.
Second sequence is named "multiCommand.swapChar". This sequence swaps cursor's left character and the right character. If a command is executed asynchronousely, you can set time interval between each command execution using "interval" configuration(milliseconds).
You can also use an object style that uses the command name as a key instead of an array.
"multiCommand.commands": { "multiCommand.down3Lines": { "sequence": [ "cursorDown", "cursorDown", "cursorDown" ] } }
This style is useful when you want to merge user settings and the workspace settings.
-
Bind a key to created command sequence in keybindings.json.
For example:{ "key": "F1", "command": "extension.multiCommand.execute", "args": { "command": "multiCommand.down3Lines" }, "when": "editorTextFocus" }, { "key": "F21", "command": "extension.multiCommand.execute", "args": { "command": "multiCommand.swapChar" }, "when": "editorTextFocus" }You can bind a key to the command directly.
For example:
{ "key": "F1", "command": "multiCommand.down3Lines", "when": "editorTextFocus" }, { "key": "F2", "command": "multiCommand.swapChar", "when": "editorTextFocus" }But when you use this key bind style, Visual Studio Code may warn about the command name. see: ryuta46#16
You can call a defined command sequence from command palette.
- Open command palette ( cmd + shift + p in mac).
- Choose "Multi command: Execute multi command."
- Choose one of command sequences you defined.
If you want to call a command sequence in shorter steps, bind a key to "extension.multiCommand.execute".
For example:
{
"key": "cmd+shift+m",
"command": "extension.multiCommand.execute"
}If you set label and description parameters in settings.json, they are displayed when you choose a command sequence.
Both parameters are optional.
For example:
"multiCommand.commands": [
{
"command": "multiCommand.down3Lines",
"label": "down3Lines",
"description": "down the cursor in 3 times",
"sequence": [
"cursorDown",
"cursorDown",
"cursorDown"
]
},If you set languages parameter in settings.json, the sequence is displayed only when a document of specified language is opened.
For example:
"multiCommand.commands": [
{
"command": "multiCommand.eslint",
"sequence": [
"eslint.executeAutofix",
],
"languages": ["javascript", "typescript"]
},
]multiCommand.eslint is displayed only when the opened document is JavaScript or TypeScript.
You can pass arguments to commands by defining a command sequence with args parameter.
For Example:
{
"command": "multiCommand.cutAndType",
"sequence": [
"editor.action.clipboardCutAction",
{ "command": "type", "args": { "text": "CUT !!" } }
]
}This sequence cut selected text and type "CUT !!".
You can also use some variables like ${userHome} or ${config:editor.fontSize} in arguments.
Because some commands substitute these kinds of variables in their extensions, variable substitution in multi-command extenstion is kind of experimental.
If you use variable substituion, set variableSubstitution to true in command setting.
For example:
"sequence": [
{
"command": "type",
"args": { "text": "Font size is ${config:editor.fontSize}" },
"variableSubstitution": true
}
],Current supported variables:
${userHome}${workspaceFolder}${workspaceFolderBasename}${file}${fileWorkspaceFolder}${relativeFile}${relativeFileDirname}${fileBasename}${fileBasenameNoExtension}${fileDirname}${fileExtname}${cwd}${lineNumber}${selectedText}${pathSeparator}${env:*}${config:*}
Contents of each variable are described in variables reference in VSCode. Note that all variables in the document is not supported in multi-command extension.
The above multiCommand.down3Lines sample also written as follows by using repeat field:
{
"command": "multiCommand.down3Lines",
"label": "down3Lines",
"description": "down the cursor in 3 times",
"sequence": [
{ "command": "cursorDown", "repeat": 3 }
],
}You can also repeat a sequence by using extension.multiCommand.execute or defined command in settings.json.
{
"sequence": [
{
"command": "extension.multiCommand.execute",
"args": {
"sequence": [
"editor.action.commentLine",
"cursorDown"
]
},
"repeat": 5
}
],
}This sequence add line comment to next 5 lines.
A sequence can be branched by the result of whether or not a given command terminated with an error. This feature is useful when you are not sure if an extension is installed or not. You can use an alternative command if the extension is not installed.
For example:
{
"sequence": [
"eslint.executeAutofix || editor.action.formatDocument"
]
}Only when eslint.executeAutofix finished with an error like command not found, editor.action.formatDocument is invoked.
Note that there must be at least one space on each side of the || operator.
For more complex command like passing arguments, use onFail field.
"sequence": [
{
"command": "A",
"onFail": [
"B",
{
"command": "C",
"args": { "arg": "argumentForC" }
},
]
}
]Only when command A finished with an error, command B and command C with arguments are invoked.
-
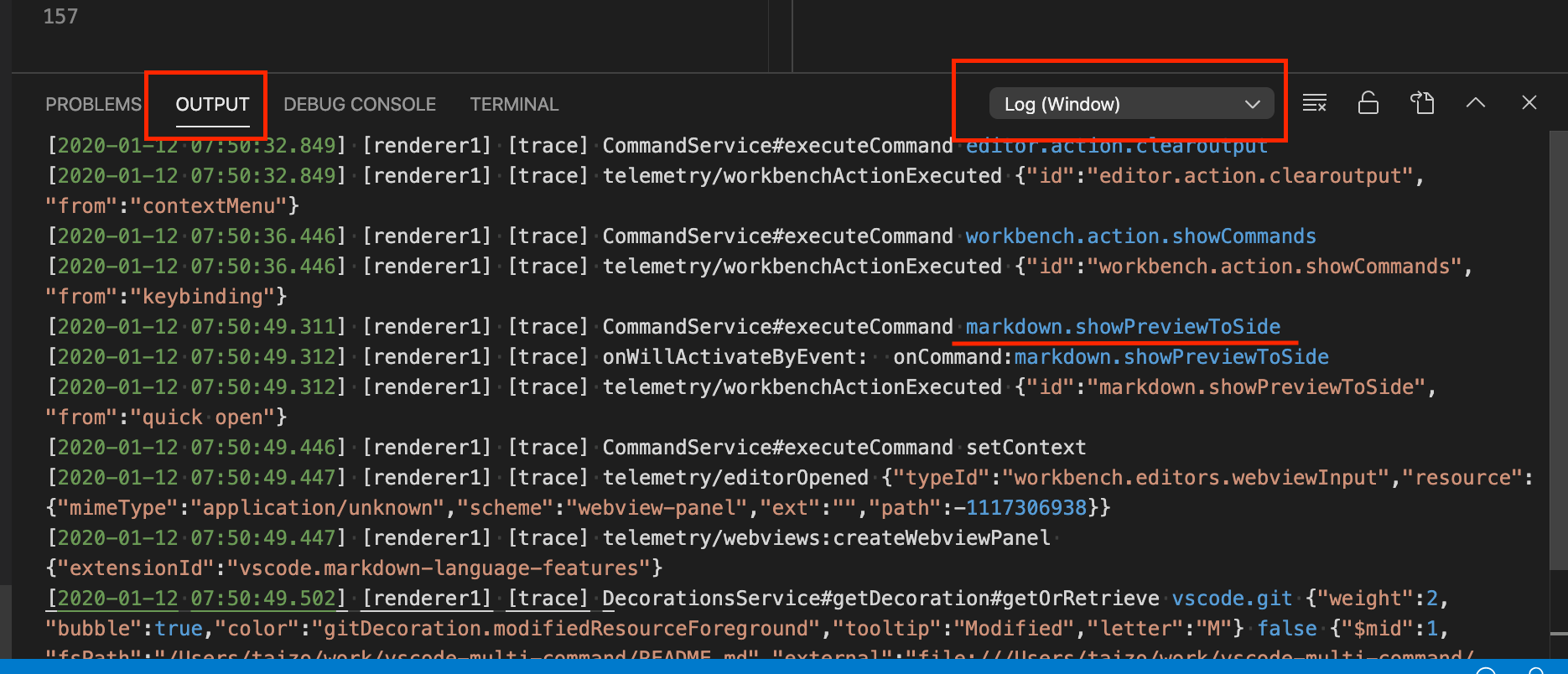
Execute "Developer: Set Log Level..." and select "trace" in the command palette.
-
Execute command of you want to know the name.
-
You can see the name in output panel for Log(Window) process( you can set the process for output in the rightside of the output panel).
You can use shell commands in a command sequence by using Command Runner extension together.
With Command Runner extension, you can write a command sequence with shell commands as:
{
"command": "multiCommand.checkoutDevelop",
"sequence": [
{
"command": "command-runner.run",
"args": { "command": "git checkout develop" }
},
"git.sync"
]
}See the Command Runner document for details on how to use the extension.