Java 8 introduced a series of ground-breaking features for the language, that proved to be more than useful for the everyday life of Java developers.It improves application performance without any specific work or tuning.
- Lambda Expressions 😱
- Iterable For Each with Lambda Expression
- Passing multiple Statement Using Lambda Expression
- Comparator Using Lambda Expression
- Filtering Of Collection Data Using Lambda Expression
- Method References 😀
- Reference to a static method
- Reference to instance method
- Reference to constructor
- Functional Interfaces 😯
- Stream API's and Filter 😀
Now lets us see about Lambda Expression usage with below examples
Lets develop a Mobile from scratch based on Mobile Manufacturer & Designer & Tester needs.

As shown in the above image we have Mobile Manufacturer, Mobile Designer and Mobile Developer !
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to list out all the mobiles created already.
/**
* Get All Mobiles
*
* Iterable For Each with Lambda Expression
*
* @param developer
* @return
*/
public void getAllMobileName(MobileDeveloper developer) {
System.out.println("Iterable For Each Using Lambda Expression");
developer.getAllMobile().forEach(mobile->System.out.println(mobile.getMobileName()));
}
Now assume like Mobile Designer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to append Mobile Name and Color for a single mobile.
/**
* @author Yashwanth
*
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MobileDesigner {
public String appendMobileNameAndColor(String color);
}
/**
* Appending of Mobile Name And Color
*
* Passing multiple Statement Using Lambda Expression
*/
private static void appendingOfMobileNameAndColor(MobileDeveloper developer) {
System.out.println("Passing multiple Statement Using Lambda Expression");
String mobileName=developer.getAllMobile().get(0).getMobileName();
MobileDesigner designer = (color)->
{
return mobileName+" "+color;
};
System.out.println(designer.appendMobileNameAndColor("Black"));
}
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to list all mobiles names in ascending order.
/**
* Sorting Based on Mobile Name
*
* Comparator Using Lambda Expression
*
* @param developer
*/
private static void sortingOfMobileNames(MobileDeveloper developer) {
System.out.println("Comparator Using Lambda Expression");
List allMobile = developer.getAllMobile();
Collections.sort(allMobile, (firstMobile,secondMobile)->
{
return firstMobile.getMobileName().compareTo(secondMobile.getMobileName());
}
);
allMobile.forEach(mobile->System.out.println(mobile.getMobileName()));
}
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to list all mobiles names and prices based on their price greater than 600EU.
/**
* Filtering of Mobile Names Based on Price
*
* Filtering Of Collection Data Using Lambda Expression
*
* @param developer
*/
private void filterMobileNamesBasedOnPrice(MobileDeveloper developer) {
System.out.println("Filtering Using Lambda Expression");
Stream filterMobiles = developer.getAllMobile().stream().filter(mobile->mobile.getMobilePriceInEUR()>600);
filterMobiles.forEach(mobile->System.out.println("Mobile Name:"+mobile.getMobileName() +" " +"Mobile Price:"+mobile.getMobilePriceInEUR()));
}
Now lets us see about Method References usage with below examples
As shown in the above image we have Mobile Manufacturer, Mobile Designer, Mobile Tester and Mobile Developer !
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to list out all the mobiles based on status created already.
ContainingClass::staticMethodName
Here is my code :
/**
* Filtering of Mobile Names Based on Status
*
* Static Method Referencing
*
* @param developer
*/
public static void getAllMobileBasedOnStatus(Mobile mobile) {
if(mobile.getMobileStatus().equalsIgnoreCase("Available"))
{
System.out.println("Mobile Name:"+mobile.getMobileName()+" "+"Status:"+mobile.getMobileStatus());
}
}
Invoking of Static Method Reference
developer.getAllMobile().forEach(MobileDeveloper::getAllMobileBasedOnStatus);
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to list out all the mobiles based on battery capacity.
ContainingObject::InstanceMethodName
Here is my code :
/**
* Filtering of Mobile Names Based on Battery Capacity
*
* Static Method Referencing
*
* @param developer
*/
public void getAllMobileBasedOnBatteryCapacity(Mobile mobile) {
if(mobile.getMobileBatteryCapacity()>4100)
{
System.out.println("Mobile Name:"+mobile.getMobileName()+"|"+"Mobile Battery Capacity:"+mobile.getMobileBatteryCapacity());
}
}
Invoking of Instance Method Reference
developer.getAllMobile().forEach(developer::getAllMobileBasedOnBatteryCapacity);
Now assume like Mobile Tester comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to list out all the mobiles to test based on their status (Availability in Market).
className::new
Here is my code :
/**
* @author Yashwanth
*
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MobileTester {
public MobileTesters getCountOfTestedMobiles(MobileDeveloper developer);
}
/**
* @author Yashwanth
*
*/
public class MobileTesters {
/**
* Providing the count of tested mobiles
*/
public MobileTesters(MobileDeveloper developer) {
Stream filterMobiles = developer.getAllMobile().stream().filter(mobile->mobile.getMobileStatus().equalsIgnoreCase("Available"));
System.out.println("Tested Mobile Count:"+filterMobiles.count());
}
}
Invoking of Constructor
MobileTester tester=MobileTesters::new;
tester.getCountOfTestedMobiles(developer);
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to check for Huawei Enjoy 20 5G Mobile to increase the cost of the mobile.
/**
* Check For Huawai Enjoy Mobile
*
*/
@Override
public void checkForHuaweiEnjoyMobile(Predicate< Mobile > mobileCondition) {
System.out.println("Functional Interface - Predicate");
for(Mobile mob:getAllMobile())
{
if(mobileCondition.test(mob))
{
System.out.println("Predict returns "+mobileCondition.test(mob));
increaseTheCostOfMobile();
break;
}
else
{
//If Mobile Doesn't Exist - Return False
System.out.println("Predict returns "+mobileCondition.test(mob));
}
}
System.out.println();
}
Invoking of Predicate
//Predicate - Provides True or False based on the Argument[Takes A Input] -> return (boolean)
Predicate< Mobile > mobileConditionPredOne = mobile->mobile.getMobileName().equals("Huawei Enjoy 20 5G");
developer.checkForHuaweiEnjoyMobile(mobileConditionPredOne);
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to check for Huawei Enjoy 20 5G Mobile and Price equals 6000.
/**
* Check For Huawai Enjoy Mobile Name and Price Matching or Not
*
* @param mobileConditionPredTwo
*/
public void checkForHuaweiEnjoyMobileAndPrice(BiPredicate< Mobile, Mobile > mobileCondition) {
System.out.println("Functional Interface - BiPredicate");
for(Mobile mob:getAllMobile())
{
if(mobileCondition.test(mob, mob))
{
System.out.println("BiPredicate returns "+mobileCondition.test(mob, mob));
getAllDetailsOfMobile(mob);
break;
}
else
{
//If Mobile Doesn't Exist - Return False
System.out.println("BiPredicate returns "+mobileCondition.test(mob, mob));
}
}
System.out.println();
}
Invoking of BiPredicate
//BiPredicate - Provides True or False based on the Argument[Takes Two Input] -> return (boolean)
BiPredicate< Mobile, Mobile > mobileConditionPredTwo=(mobileName,mobilePrice)->mobileName.getMobileName().equals("Huawei Enjoy 20 5G") && mobilePrice.getMobilePriceInEUR()==6000;
developer.checkForHuaweiEnjoyMobileAndPrice(mobileConditionPredTwo);
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to list all mobile names with battery capacity.
public void getAllMobileNameWithBatteryCapacity(Consumer< Mobile > mobilesConsumer,List mobileList)
{
System.out.println("Functional Interface - Consumer");
getAllMobile().stream().forEach(mobile->mobilesConsumer.accept(mobile));
System.out.println();
}
Invoking of Consumer
//Consumer - Performs an Operations by taking single input - Doesn't return anything (void)
Consumer< Mobile > mobileConsumer=(mob)->System.out.println("Mobile Name:"+mob.getMobileName(
)+"|"+"Mobile Battery Capacity:"+mob.getMobileBatteryCapacity());
developer.getAllMobileNameWithBatteryCapacity(mobileConsumer, developer.getAllMobile());
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to list all mobile names with increased battery capacity.
/**
* Get All Mobile Names With Increased Battery Capacity with 10
*
* @param mobileBiConsumer
* @param allMobile
*/
public void getAllMobileNameWithIncreasedBatteryCapacity(BiConsumer< Mobile, Long > mobileBiConsumer,
List allMobile) {
System.out.println("Functional Interface - BiConsumer");
Long increasedBat=Long.parseLong("10");
getAllMobile().stream().forEach(mobile->
{
mobile.setMobileBatteryCapacity(mobile.getMobileBatteryCapacity()+increasedBat);
mobileBiConsumer.accept(mobile,increasedBat);
});
System.out.println();
}
Invoking of BiConsumer
//BiConsumer - Performs an Operations by taking two input - Doesn't return anything (void)
BiConsumer< Mobile, Long > mobileBiConsumer=(mob,mobBattery)->System.out.println(mob.getMobileName()+"|"+mob.getMobileBatteryCapacity());
developer.getAllMobileNameWithIncreasedBatteryCapacity(mobileBiConsumer, developer.getAllMobile());
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to check of mobiles for their price greater than 1K.
/**
* Check For Mobile Price Greater Than 1000K
*
* @param mobileFunction
* @param mobilePriceCheck
*/
public void checkMobilePriceGreaterThan1K(List allMobile,
Function< Mobile, Boolean > mobilePriceCheck) {
System.out.println("Functional Interface - Function");
allMobile.stream().forEach(mob->System.out.println("Mobile Name:"+mob.getMobileName()+"---->"+
"Mobile Price:"+mob.getMobilePriceInEUR()+"---->"+mobilePriceCheck.apply(mob)));
System.out.println();
}
Invoking of Function
//Function - Performs an Operation with single input and provides expected result Function T-Input & R-Result
Function< Mobile,Boolean > mobilePriceCheck=(mob)->mob.getMobilePriceInEUR()>1000;
developer.checkMobilePriceGreaterThan1K(developer.getAllMobile(),mobilePriceCheck);
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to check of mobiles for their price less than 5K and Status(Availability).
**
* Check For Mobile Price Greater Than 5000K & Status - Availability
*
* @param allMobile
* @param mobilePriceAndStatusCheck
*/
public void checkMobilePriceLessThan5kAndStatus(List allMobile,
BiFunction< Mobile, Mobile, Boolean > mobilePriceAndStatusCheck) {
System.out.println("Functional Interface - BiFunction");
allMobile.stream().forEach(mob->System.out.println("Mobile Name:"+mob.getMobileName()+"---->"+
"Mobile Price:"+mob.getMobilePriceInEUR()+"---->"+"Mobile Status:"+mob.getMobileStatus()+"---->"+mobilePriceAndStatusCheck.apply(mob,mob)));
System.out.println();
}
Invoking of BiFunction
//BiFunction - Performs an Operation with multiple input and provides expected result Function T-Input & R-Result
BiFunction< Mobile, Mobile, Boolean > mobilePriceAndStatusCheck=(mobPrice,mobStatus)->mobPrice.getMobilePriceInEUR()<5000 && mobStatus.getMobileStatus().equalsIgnoreCase("Available");
developer.checkMobilePriceLessThan5kAndStatus(developer.getAllMobile(),mobilePriceAndStatusCheck);
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to get Developer Name.
/**
* Returns Developer Name
*
* @return
*/
public static String getDeveloperName()
{
System.out.println("Functional Interface - Supplier");
return "Developer::>Yashwanth";
}
Invoking of Supplier
//Suppiler - Returns a value without any input
Supplier< String > mobiles=()->MobileDeveloper.getDeveloperName();
System.out.println(mobiles.get());
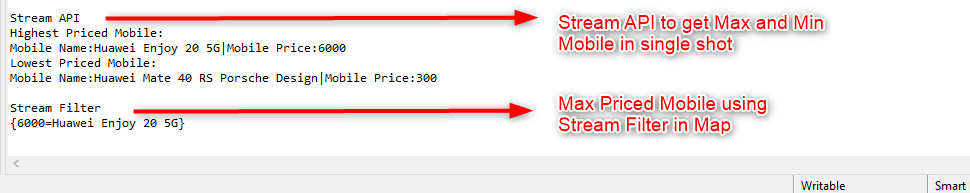
Now assume like Mobile Manufacturer comes to Mobile Developer and asks the Developer to get top 1 maximum and minimum priced mobile name and price alone.
/**
* Get Max and Min Price Mobile Details
*
* @param allMobile
*/
private void getMaxAndMinPriceMobileDetail(List allMobile) {
Mobile maxPricedMobile = allMobile.stream().max((firstMob,secondMob)->firstMob.getMobilePriceInEUR() > secondMob.getMobilePriceInEUR() ?1:-1 ).get();
System.out.println("Highest Priced Mobile:");
System.out.println("Mobile Name:"+maxPricedMobile.getMobileName()+"|"+"Mobile Price:"+maxPricedMobile.getMobilePriceInEUR());
Mobile minPricedMobile = allMobile.stream().max((firstMobile,secondMobile)->firstMobile.getMobilePriceInEUR() < secondMobile.getMobilePriceInEUR() ?1:-1 ).get();
System.out.println("Lowest Priced Mobile:");
System.out.println("Mobile Name:"+minPricedMobile.getMobileName()+"|"+"Mobile Price:"+minPricedMobile.getMobilePriceInEUR());
System.out.println();
}
Invoking of Stream API method
/**
* Get Max and Min Price Mobile
*/
@Override
public void getMaxPriceAndMinPriceMobile(MobileDeveloper developer) {
getMaxAndMinPriceMobileDetail(developer.getAllMobile());
}
In the other hand, if you wanna filter see the mobile prices greater than 5000EU in map means
/**
* Get Mobile Price & Name in Map
*
* @param developer
*/
public void getMaxMobliePriceAndNameInMap(MobileDeveloper developer) {
Map productPriceMap =developer.getAllMobile().stream().filter(mob->mob.getMobilePriceInEUR()>5000).collect(Collectors.toMap(mob->mob.mobilePriceInEUR, mob->mob.mobileName));
System.out.println(productPriceMap);
}
“Thanks for watching. If you liked this page, make sure to subscribe for more!”
First, solve the problem. Then, write the code.
😀