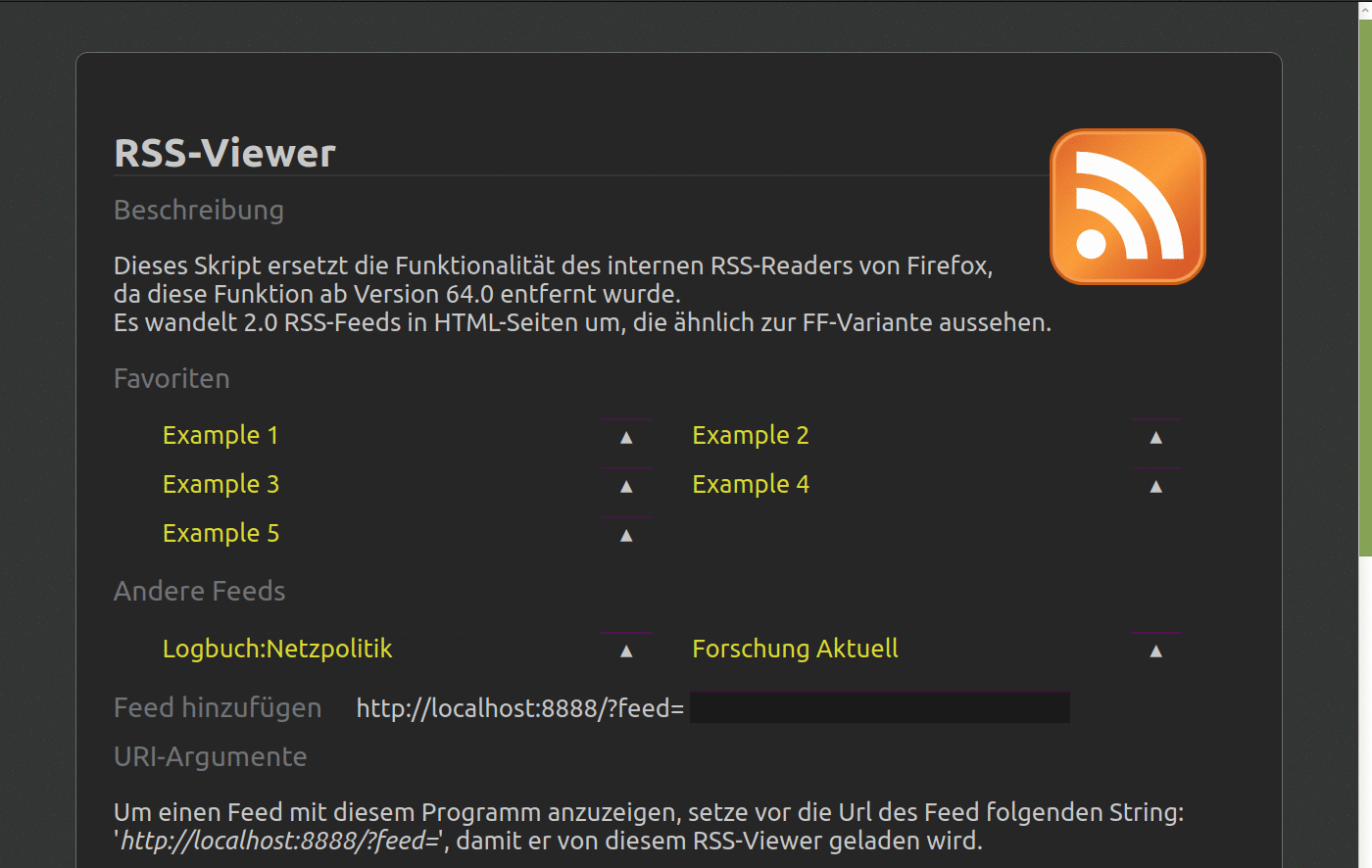
Background daemon to convert RSS Feeds into HTML pages. Presentation of data is similar to Firefox's variant.
The usage of the web interface can be protected by a list of users/passwords. Authenticated users can trigger commands for media files of a RSS feed, e.g. for downloading it. See Adding action handlers to feeds for instruction how to add own commands.
Python >= 3.8 List of required packages: See pyproject.toml
python3 -m pip install {PATH to *.whl-file}
or with virtual environment
apt install python3-venv
python3 -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
python3 -m pip install {PATH to *.whl-file}
git clone "{This repo}"
cd rss2html
poetry install
poetry run python3 -m rss2html
Call python3 -m rss2html and visit http://localhost:8888
Take a look into the Setup section to see how you could
configure the program.
If you want install the program as background daemon,
call make install_service. If you installed rss2html by *.whl-file
you probably need to adapt rss_server.service.
- Install program and its dependencies.
- The settings are defined in rss2html/default_settings.py.
If you want override values create settings.py and place your changes there:
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
HOST = "localhost" # Empty string "" will allow access from everywhere.
PORT = 8888
# […]
Place this file into $HOME/.config/rss2html (Linux) or %APPDATA%/rss2html (Windows) or this folder.
-
Start service, e.g.:
python3 -m rss2html [--daemon] -
Visit localhost:8888/?feed=[your feed url] to view a feed.
The content presentation is similar to Firefox's <= 63.x. The feed will be stored in the history of visited feeds. -
(Optional) Combine Firefox's 'Open with'-dialog
for RSS-feeds with the scripts/rss_reader script.
This will open the feed content in a new browser tab.(Linux) The list of applications in the 'Open With'-dialog depends from the entries in /usr/share/applications.
To extend this dialog with 'rss_reader':
5.1 Copy scripts/rss_reader.desktop into above folder and
5.2 Copy scripts/rss_reader into /usr/local/bin (or edit the path in 'rss_reader.desktop') -
(Optional) Enable SSL encryption Write ssl key and crt path into settings.py variables
SSL_KEY_PATHandSSL_CRT_PATH. You can also generate both files bymake sslto test it locally. Then start programm with--sslflag.
The favorite feeds can be managed over the files favorites.py and, if multiple users are defined, favorites_{username}.py.
#!/usr/bin/python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from rss2html.feed import Feed
FAVORITES = [
Feed("example",
"http://www.deutschlandfunk.de/podcast-das-war-der-tag.803.de.podcast",
"Example Feed"),
]
Place the file(s) into $HOME/.config/rss2html (Linux) or
%APPDATA%/rss2html (Windows) or this folder.
These files will also be created/changed by actions taken on the web interface.
poetry, lessc, babel
python3 -m pip install poetry
apt install python3-babel node-less
git clone "{This repo}"
cd rss2html
poetry install
[comment]: # The classical way without venv/poetry: [comment]: # python3 -m pip install --target "site-packages" -U -r requirements.txt [comment]: # PYTHONPATH=src:site-packages python3 -m rss2html
make run or make run_443
Note that first call of run_443 creates a copy of the python binary and
allowing this copy the usage of lower port numbers by
/usr/bin/sudo /sbin/setcap CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE=+eip "./python3_443"
Use this during development only. You could also use
AmbientCapabilities=CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE in a Systemd service file.
Creates new package in dist:
poetry build
- Add language code in Makefile to
SUPPORTED_LANGSvariable. - Run
make babel_compile
- Run
make babel_prepare babel_updateto update *.pot- and *.po-files - Edit ./locale/{LANG CODE}/LC_MESSAGES/messages.po
- Run
make babel_compile
Two actions are predefined: Download file and play file locally. If you want define more actions you can extend your local settings file.
Extend your settings.py by
from rss2html.default_settings import ACTIONS
def can_action_name(feed, url, settings):
# Return True if your action should be possible for this url
# Can be used to restrict action on domain name, etc.
return True
def action_name(feed, url, settings):
# Add your stuff here
return True
ACTIONS.update({
"my_action" : {
"handler": action_name,
"check": can_action_name,
"title": "Description",
"icon": "icons/gnome_download.png",
},
})
If you want call a shell command but no python function you can use following variant:
from rss2html.default_settings import ACTIONS
from rss2html import actions
lexample = ["notify-send", "RSS VIEWER", "{url}"]
ACTIONS.update({
"play_ssh" : {
"handler": actions.factory__local_cmd(lexample),
"check": lambda feed, url, settings: True,
"title": _('Local example cmd'),
"icon": "icons/gnome_term.png",
},
})
This sections shows how you can trigger a command on an other host by invoking a script over SSH. This needs the generation of a new SSH Key and a binding of the script with this key. The allowed commands are defined in scripts/rss2html.sh on the remote machine.
Hint: Step 1-3 can be executed by scripts/install_ssh.sh
-
Create new key for rss2html:
ssh-keygen -f ~/.ssh/rss2html -P "" -
Copy scripts/rss2html_ssh.sh.example to rss2html.sh and add your commands into the script. The keyword (here: PLAY) should match with the value in step 2. Copy the script onto your target system.
-
Add following line in ~/.ssh/authorized_keys on your remote system. The command-prefix restricts the accesses on this single script.
command="{absolute path}/rss2html_ssh.sh" {Content of ~/.ssh/rss2html.pub} -
Extend your settings.py to propagate commands to web interface by
from rss2html.default_settings import ACTIONS
from rss2html import actions
ssh_args = ("user@machine", "PLAY '{url}'", "~/.ssh/rss2html")
ACTIONS.update({
"play_ssh" : {
"handler": actions.factory__ssh_cmd(*ssh_args),
"check": actions.can_play,
"title": _('SSH Play'),
"icon": "icons/gnome_term.png",
},
})
# ... Other