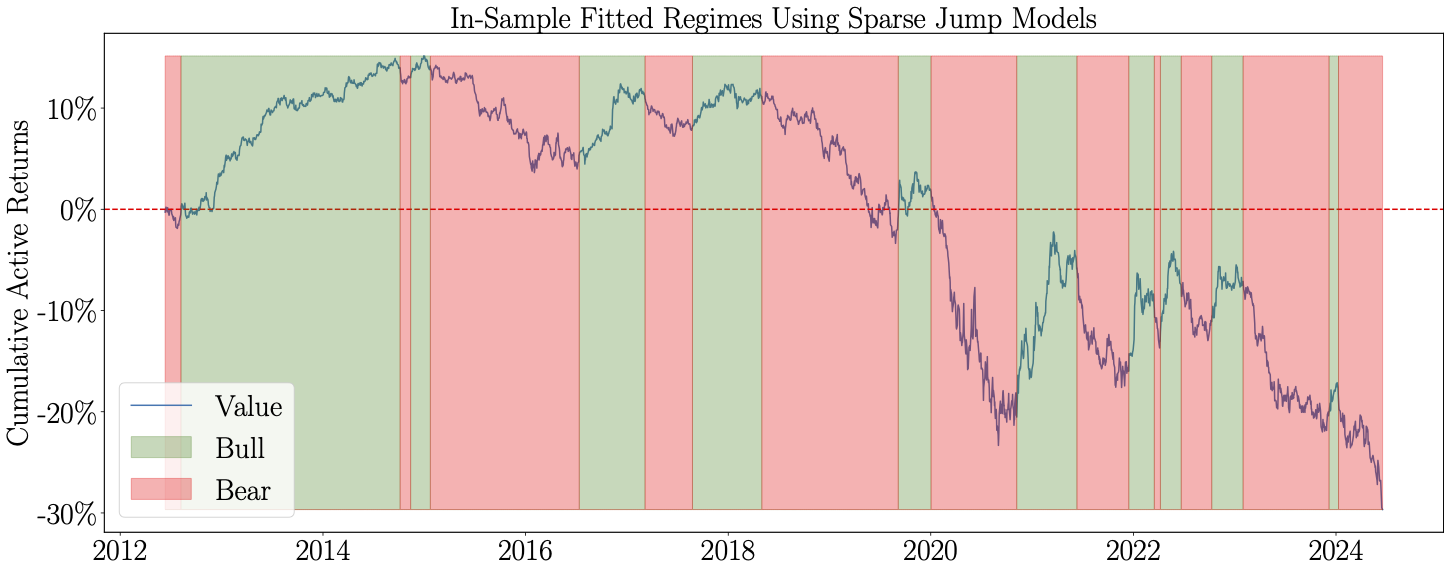
Note: An explanation of the application of JMs to the value factor in this figure can be found in the Examples section.
jumpmodels is a Python library offering a collection of statistical jump models (JMs), an unsupervised algorithm designed for regime identification in time series data.
It includes implementations of the original discrete JM, the continuous JM (CJM), and the sparse JM (SJM) with feature selection.
The library follows a scikit-learn-style API and supports pandas DataFrames for both input and output.
To install the package, use the following pip command:
pip install jumpmodelsjumpmodels requires the following dependencies:
- Python
(>=3.8) numpypandasscipyscikit-learnmatplotlib
All dependencies will be installed automatically with the package. While version sensitivity is minimal, an environment.yaml file is provided to ensure reproducibility.
To run the example notebook, you will also need the following additional dependencies:
yfinancejupyterlab
You can install these along with the package by running:
pip install jumpmodels[example]You can import the two core classes, JumpModel and SparseJumpModel, as follows:
from jumpmodels.jump import JumpModel # JM & CJM class
from jumpmodels.sparse_jump import SparseJumpModel # Sparse JM classWe follow a scikit-learn-style API, with class methods such as .fit(), .predict(), .predict_proba(), and .set_params() for model fitting, state and probability prediction, and resetting model parameters.
Specifically designed for time series applications, we also provide .predict_online() and .predict_proba_online() methods for online prediction.
A comprehensive demonstration of the core functionality is available in the examples/Nasdaq/example.ipynb notebook, which includes an analysis of the Nasdaq-100 Index using data from Yahoo Finance (fully public source).
The figure on top features an application of the sparse JM, showing the in-sample identified bull and bear market regimes for the value factor index based on its daily active returns relative to the market. Further details can be found in Shu and Mulvey (2024), as listed in the References section.
Below are articles related to the methodology and applications of JMs. If any of them assist your research, please cite the corresponding paper.
- Continuous Statistical Jump Models (CJM): Aydınhan, A. O., Kolm, P. N., Mulvey, J. M., and Shu, Y. (2024). Identifying patterns in financial markets: Extending the statistical jump model for regime identification. Annals of Operations Research. To appear. [journal] [SSRN]
@article{Aydinhan2024CJM,
title = {Identifying patterns in financial markets: extending the statistical jump model for regime identification},
author = {Afşar Onat Aydınhan and Petter N. Kolm and John M. Mulvey and Yizhan Shu},
journal = {Annals of Operations Research},
year = {2024},
note = {To appear},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-024-06035-z},
}- (Original) Statistical Jump Models: Nystrup, P., Lindström, E., and Madsen, H. (2020a). Learning hidden Markov models with persistent states by penalizing jumps. Expert Systems with Applications, 150:113307. [journal] [OpenAccess]
@article{Nystrup2020JM,
title = {Learning hidden {Markov} models with persistent states by penalizing jumps},
author = {Peter Nystrup and Erik Lindstr{\"o}m and Henrik Madsen},
journal = {Expert Systems with Applications},
year = {2020},
pages = {113307},
volume = {150},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113307},
}- Sparse Jump Models: Nystrup, P., Kolm, P. N., and Lindström, E. (2021). Feature selection in jump models. Expert Systems with Applications, 184:115558. [journal] [SSRN]
@article{nystrup2021SJM,
title = {Feature selection in jump models},
author = {Peter Nystrup and Petter N. Kolm and Erik Lindstr{\"o}m},
journal = {Expert Systems with Applications},
volume = {184},
pages = {115558},
year = {2021},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115558},
}- Online Inference for JMs: Nystrup, P., Kolm, P. N., and Lindström, E. (2020b). Greedy online classification of persistent market states using realized intraday volatility features. The Journal of Financial Data Science, 2(3):25–39. [journal] [OpenAccess]
@article{Nystrup2020onlineJM,
title = {Greedy Online Classification of Persistent Market States Using Realized Intraday Volatility Features},
author = {Peter Nystrup and Petter N. Kolm and Erik Lindstr{\"o}m},
journal = {The Journal of Financial Data Science}
year = {2020},
volume = {2},
number = {3},
pages = {25--39},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.3905/jfds.2020.2.3.025},
}- Downside Risk Recution: Shu, Y., Yu, C., and Mulvey, J. M. (2024a). Downside risk reduction using regime-switching signals: A statistical jump model approach. Journal of Asset Management. To appear. [journal] [SSRN]
@article{Shu2024downside,
title = {Downside Risk Reduction Using Regime-Switching Signals: A Statistical Jump Model Approach},
author = {Shu, Yizhan and Yu, Chenyu and Mulvey, John M.},
journal = {Journal of Asset Management},
year = {2024},
note = {To appear},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1057/s41260-024-00376-x},
}- Dynamic Asset Allocation: Shu, Y., Yu, C., and Mulvey, J. M. (2024b). Dynamic asset allocation with asset-specific regime forecasts. Annals of Operations Research. To appear. [journal] [SSRN]
@article{Shu2024DAA,
title = {Dynamic Asset Allocation with Asset-Specific Regime Forecasts},
author = {Shu, Yizhan and Yu, Chenyu and Mulvey, John M.},
journal = {Annals of Operations Research},
year = {2024},
note = {To appear},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-024-06266-0},
}- Dynamic Factor Allocation: Shu, Y. and Mulvey, J. M. (2024). Dynamic Factor Allocation Leveraging Regime-Switching Signals. [SSRN]
@article{Shu2024factor,
title = {Dynamic Factor Allocation Leveraging Regime-Switching Signals},
author = {Shu, Yizhan and Mulvey, John M.},
journal = {SSRN},
year = {2024},
}Pull requests and open issues are welcome. I am happy to discuss any related questions.
This library builds upon the open-source code accompanying Nystrup et al. (2021).
The GitHub Repo by Federico P. Cortese implements the generalized information criteria (GIC) for high-dimensional SJMs, detailed in Cortese, F. P., Kolm, P. N., and Lindström, E. (2024). Generalized information criteria for high-dimensional sparse statistical jump models [SSRN].
The structure of this README file is inspired by the format used in cvxpylayers.
Our library carries an Apache 2.0 license.