The main idea behind pseudo labels is to take full advantage of a pre-trained teacher network to teach a student network under lack of labeled data. A teacher network generates the so-called "pseudo labels" from large amounts of unlabeled data which a student network then learns from in a supervised manner. An issue with this approach, however, is that a teacher network is bound to make a few mistakes along the way by incorrectly labeling data and thus resulting in the student to learn the mistakes as well. Meta pseudo labels [1] tackles this challenge by updating the teacher based on the student's performance on labeled data. A student performing poorly on labeled data can serve as a signal for the teacher to improve and generate better labels. Meta Pseudo Labels can be utilized to improve the performance of any model when large amounts of unlabeled data are present.
| Ground Truth | Supervised | Meta Pseudo Labels |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
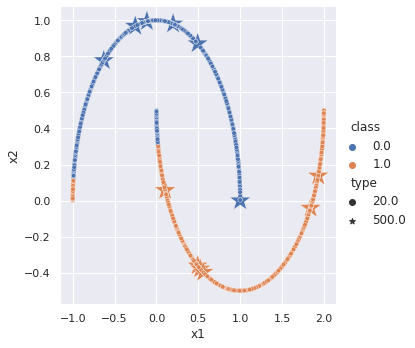 |
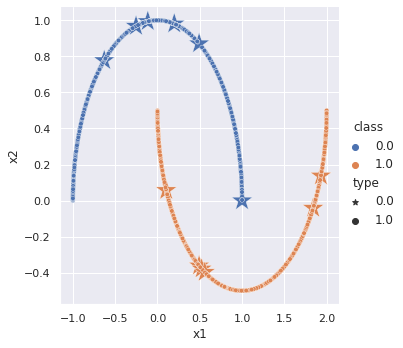
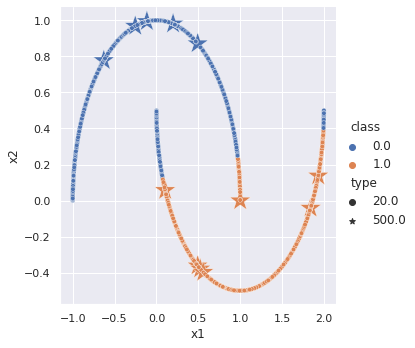
In the supervised learning scenario, a model is given 12 labeled data, 6 from each cluster, and asked to classify all the remaining data points. In the plot above, a model trained via supervised learning learns a simple linear decision boundary that even misclassifies one labeled data point. However, by leveraging meta pseudo labels, it is possible to train a network that is capable of generating nonlinear decision boundaries given the same amount of labeled data.
- More experimental results using larger datasets and models
[1] Pham, Hieu, Zihang Dai, Qizhe Xie, and Quoc V. Le. "Meta pseudo labels." In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 11557-11568. 2021.