A high-availability RabbitMQ deployment using Consul for Docker Swarm
- Hashicorp Consul, see YouMightNotNeedKubernetes/hashicorp-consul for deployment instructions.
For more information on Cluster and Cluster Formation, see https://www.rabbitmq.com/clustering.html, https://www.rabbitmq.com/cluster-formation.html
All data/state required for the operation of a RabbitMQ broker is replicated across all nodes. An exception to this are message queues, which by default reside on one node, though they are visible and reachable from all nodes. To replicate queues across nodes in a cluster, use a queue type that supports replication. This topic is covered in the Quorum Queues guide.
Some distributed systems have leader and follower nodes. This is generally not true for RabbitMQ. All nodes in a RabbitMQ cluster are equal peers: there are no special nodes in RabbitMQ core. This topic becomes more nuanced when quorum queues and plugins are taken into consideration but for most intents and purposes, all cluster nodes should be considered equal.
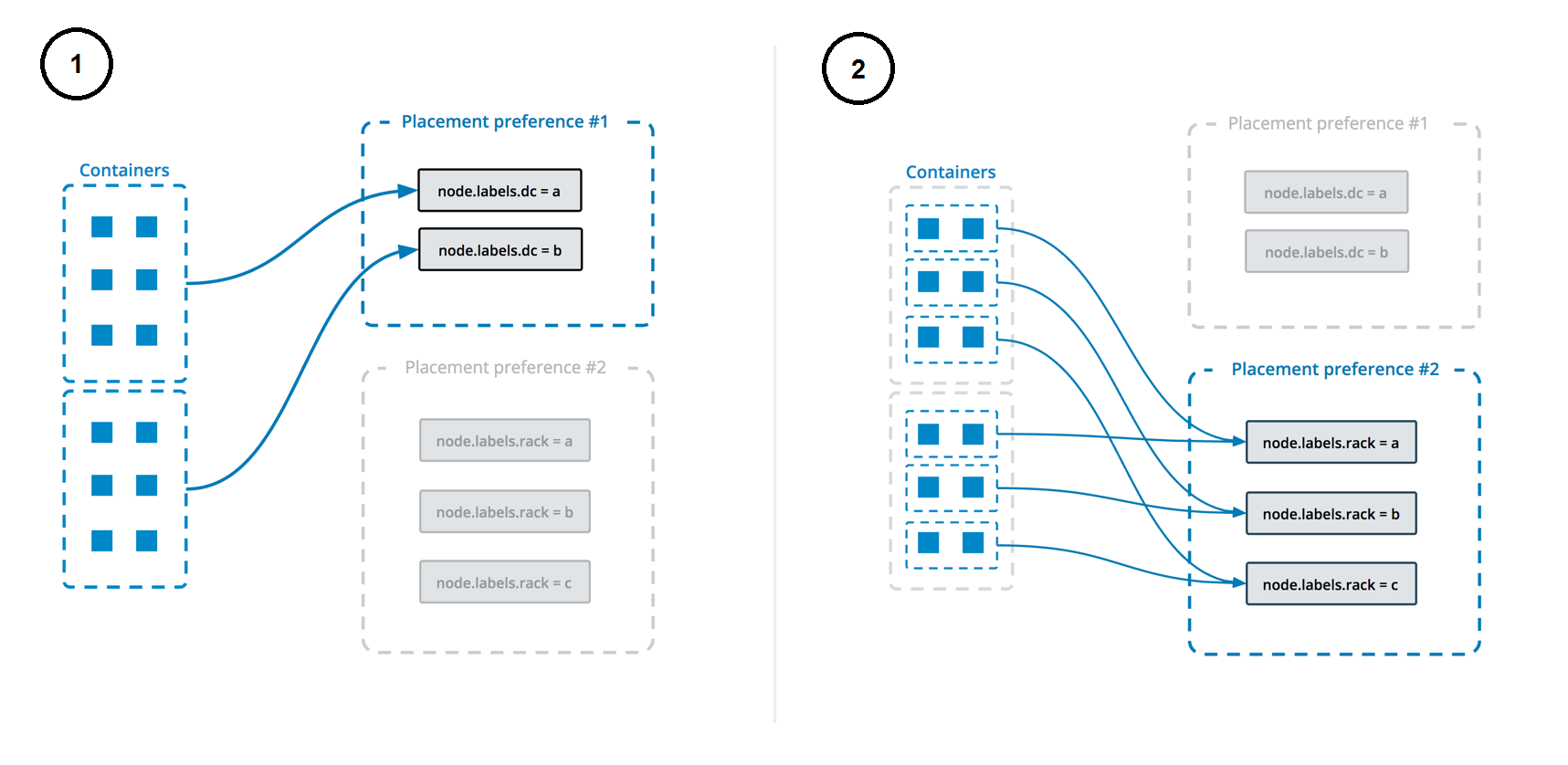
A node.labels.rabbitmq label is used to determine which nodes the service can be deployed on.
The deployment uses both placement constraints & preferences to ensure that the servers are spread evenly across the Docker Swarm manager nodes and only ALLOW one replica per node.
See https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/services/#control-service-placement for more information.
On the manager node, run the following command to list the nodes in the cluster.
docker node lsOn the manager node, run the following command to add the label to the node.
Repeat this step for each node you want to deploy the service to. Make sure that the number of node updated matches the number of replicas you want to deploy.
Example deploy service with 3 replicas:
docker node update --label-add rabbitmq=true <node-1>
docker node update --label-add rabbitmq=true <node-2>
docker node update --label-add rabbitmq=true <node-3>To deploy the stack, run the following command:
$ make deployTo destroy the stack, run the following command:
$ make destroy