Amazon Virtual Private Cloud(Amazon VPC) is a service that lets you launch AWS resources in a logically isolated virtual network that you define. You have complete control over your virtual networking environment, including selection of your own IP address range, creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and network gateways. You can use both IPv4 and IPv6 for most resources in your virtual private cloud, helping to ensure secure and easy access to resources and applications.
Follow the official guide to install and configure profiles.
After the installation is complete, you can check the aws cli version:
aws --version
aws-cli/2.5.8 Python/3.9.11 Darwin/21.4.0 exe/x86_64 prompt/off
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code software tool that enables you to safely and predictably create, change, and improve infrastructure.
This is the official guide for terraform binary installation. Please visit this Install Terraform website and follow the instructions.
Or, you can manually get a specific version of terraform binary from the websiate. Move to the Downloads page and look for the appropriate package for your system. Download the selected zip archive package. Unzip and install terraform by navigating to a directory included in your system's PATH.
Or, you can use tfenv utility. It is very useful and easy solution to install and switch the multiple versions of terraform-cli.
First, install tfenv using brew.
brew install tfenv
Then, you can use tfenv in your workspace like below.
tfenv install <version>
tfenv use <version>
Also this tool is helpful to upgrade terraform v0.12. It is a major release focused on configuration language improvements and thus includes some changes that you'll need to consider when upgrading. But the version 0.11 and 0.12 are very different. So if some codes are written in older version and others are in 0.12 it would be great for us to have nice tool to support quick switching of version.
tfenv list
tfenv install latest
tfenv use <version>
module "vpc" {
source = "Young-ook/vpc/aws"
name = "network"
tags = { env = "test" }
}Run terraform:
terraform init
terraform apply
A default VPC is ready for you to use so that you don't have to create and configure your own VPC. A default VPC is suitable for getting started quickly, and for launching public instances such as a blog or simple website. You can modify the components of your default VPC as needed.
The following figure illustrates the key components that we set up for a default VPC
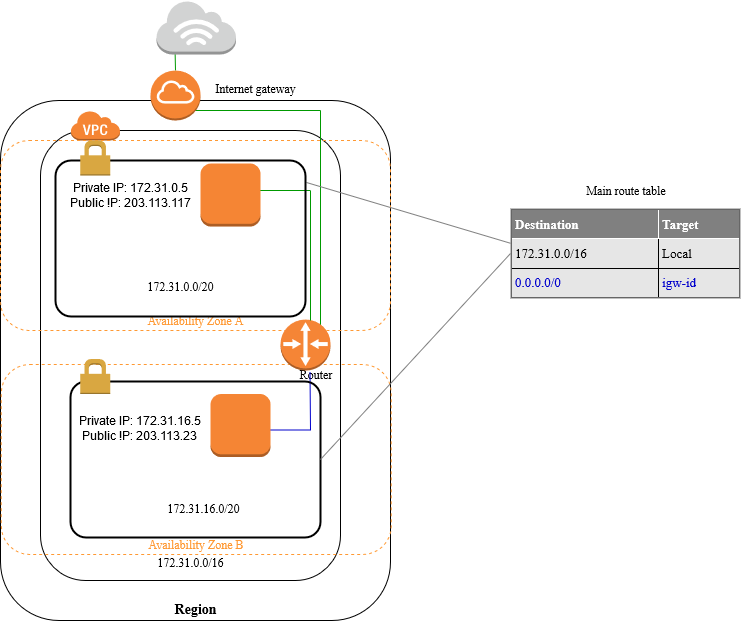
By default, a default subnet is a public subnet, because the main route table sends the subnet's traffic that is destined for the internet to the internet gateway. You can make a default subnet into a private subnet by removing the route from the destination 0.0.0.0/0 to the internet gateway. However, if you do this, no EC2 instance running in that subnet can access the internet.
What is public subnets? - public subnets connect directly to the Internet using an Internet Gateway. If you want your instances to have a public IP address and be directly reachable from the Internet, you must place them in a public subnet. In other word, internet-facing subnets.
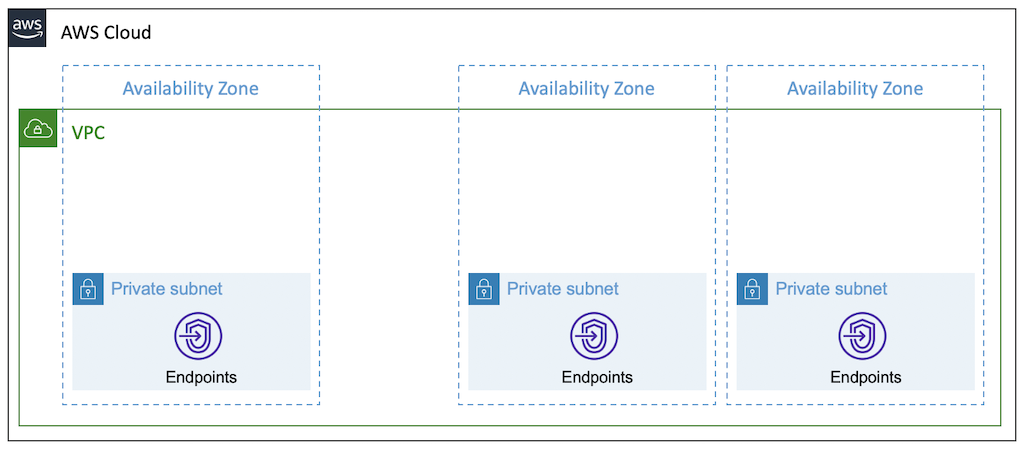
To get started using Amazon VPC, you can create a non-default VPC. You can create a custom VPC for your workloads using this module. Following is a supported network architecture you can create with this vpc module.
A VPC that is made from this module consists of different thress subnets that instances can be placed into. There is the description of three subnet types:
Isolated - isolated subnets do not route from or to the Internet, and as such do not require NAT gateways. They can only connect to or be connected to from other instances in the same VPC.
Private - instances in private subnets are not directly routable from the Internet, and connect out to the Internet via a NAT gateway. Be aware that you will be charged for NAT gateways.
Public - public subnets connect directly to the Internet using an Internet Gateway. If you want your instances to have a public IP address and be directly reachable from the Internet, you must place them in a public subnet.
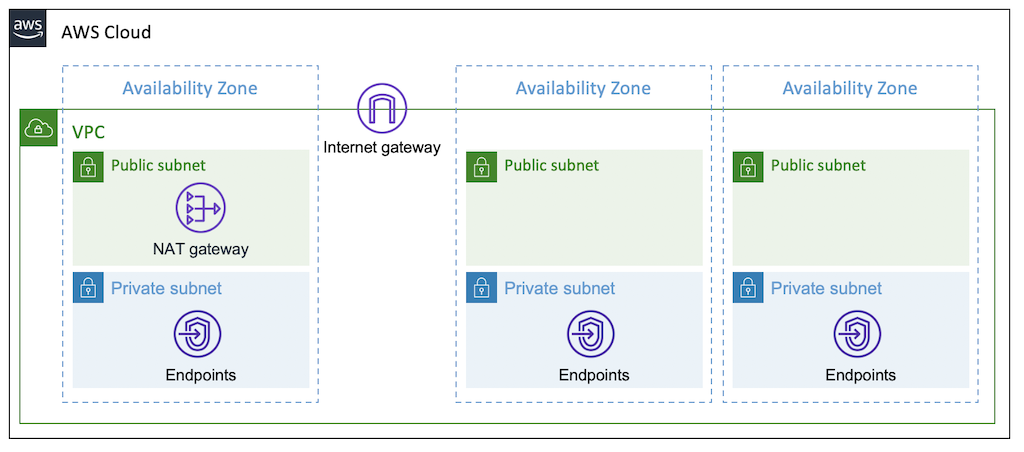
The following diagram shows how to deploy a vpc with a single shared NAT gateway across the availability zones. This is a cost-effective method, but it has the weakness of causing communication problems when something goes wrong with the availability zone where the NAT gateway is located. This is good choice for development environments.
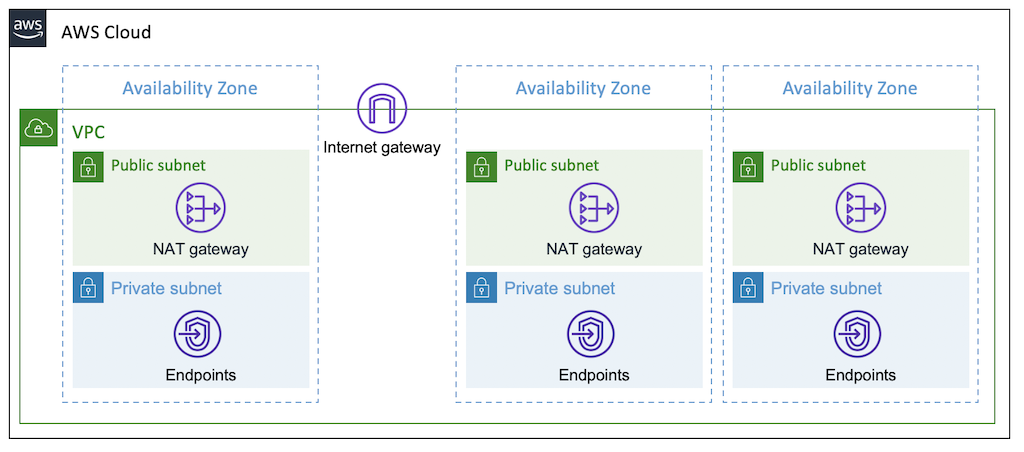
For high availability of communication between resources (instances) inside and outside your VPC, you should deploy a NAT gateway at least per Availability Zone. It is recommended to apply this configuration for production environments. By default, a NAT gateway is created in every public subnet for maximum availability.