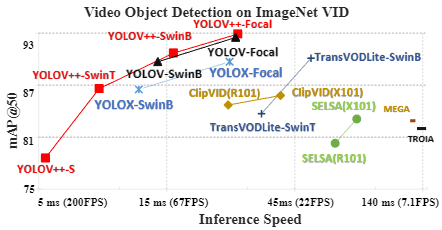
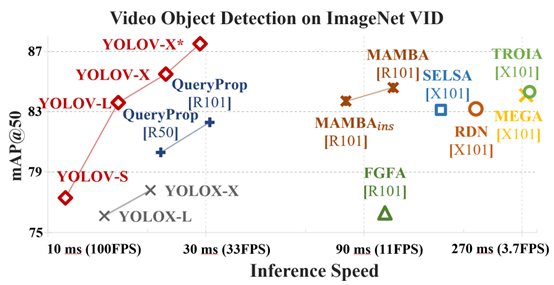
July. 30th, 2024: The pre-print version of the YOLOV++ paper is now available on Arxiv.May. 8th, 2024: We release code, log and weights for YOLOV++.April. 21th, 2024: Our enhanced model now achieves a 92.9 AP50(w.o post-processing) on the ImageNet VID dataset, thanks to a more robust backbone and algorithm improvements. It maintains a processing time of 26.5ms per image during batch inference on a 3090 GPU. Code release is forthcoming.
YOLOV series are high performance video object detector. Please refer to YOLOV and YOLOV++ on Arxiv for more details.
This repo is an implementation of PyTorch version YOLOV and YOLOV++ based on YOLOX.
| Model | size | mAP@50val |
Speed 2080Ti(batch size=1) (ms) |
Speed 3090(batch size=32) (ms) |
weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOX-s | 576 | 69.5 | 9.4 | 1.4 | |
| YOLOX-l | 576 | 76.1 | 14.8 | 4.2 | |
| YOLOX-x | 576 | 77.8 | 20.4 | - | |
| YOLOX-SwinTiny | 576 | 79.2 | 19.0 | 5.5 | |
| YOLOX-SwinBase | 576 | 86.5 | 24.9 | 11.8 | |
| YOLOX-FocalLarge | 576 | 89.7 | 42.2 | 25.7 | - |
| Model | size | mAP@50val |
Speed 3090(batch size=32) (ms) |
weights | logs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOV++ s | 576 | 78.7 | 5.3 | link | |
| YOLOV++ l | 576 | 84.2 | 7.6 | - | |
| YOLOV++ SwinTiny | 576 | 85.6 | 8.4 | link | |
| YOLOV++ SwinBase | 576 | 90.7 | 15.9 | link | |
| YOLOV++ FocalLarge | 576 | 92.9 | 27.6 | link | |
| YOLOV++ FocalLarge + Post | 576 | 93.2 | - | - |
| Model | size | mAP@50val |
Speed 2080Ti(batch size=1) (ms) |
weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOV-s | 576 | 77.3 | 11.3 | |
| YOLOV-l | 576 | 83.6 | 16.4 | |
| YOLOV-x | 576 | 85.5 | 22.7 | |
| YOLOV-x + post | 576 | 87.5 | - | - |
- Finish Swin-Transformer based experiments.
- Release updated code, model and log.
Installation
Install YOLOV from source.
git clone git@github.com:YuHengsss/YOLOV.git
cd YOLOVCreate conda env.
conda create -n yolov python=3.7
conda activate yolov
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip3 install -v -e .Demo
Step1. Download a pretrained weights.
Step2. Run yolov demos. For example:
python tools/vid_demo.py -f [path to your yolov exp files] -c [path to your yolov weights] --path /path/to/your/video --conf 0.25 --nms 0.5 --tsize 576 --save_result For online mode, exampled with yolov_l, you can run:
python tools/yolov_demo_online.py -f ./exp/yolov/yolov_l_online.py -c [path to your weights] --path /path/to/your/video --conf 0.25 --nms 0.5 --tsize 576 --save_result For yolox models, please use python tools/demo.py for inferencing.
Reproduce our results on VID
Step1. Download datasets and weights:
Download ILSVRC2015 DET and ILSVRC2015 VID dataset from IMAGENET and organise them as follows:
path to your datasets/ILSVRC2015/
path to your datasets/ILSVRC/Download our COCO-style annotations for training, FGFA version training annotation and video sequences. Then, put them in these two directories:
YOLOV/annotations/vid_train_coco.json
YOLOV/annotations/ILSVRC_FGFA_COCO.json
YOLOV/yolox/data/dataset/train_seq.npyChange the data_dir in exp files to [path to your datasets] and Download our weights.
Step2. Generate predictions and convert them to IMDB style for evaluation.
python tools/val_to_imdb.py -f exps/yolov/yolov_x.py -c path to your weights/yolov_x.pth --fp16 --output_dir ./yolov_x.pklEvaluation process:
python tools/REPPM.py --repp_cfg ./tools/yolo_repp_cfg.json --predictions_file ./yolov_x.pkl --evaluate --annotations_filename ./annotations/annotations_val_ILSVRC.txt --path_dataset [path to your dataset] --store_imdb --store_coco (--post)(--post) indicates involving post-processing method. Then you will get:
{'mAP_total': 0.8758871720817065, 'mAP_slow': 0.9059275666099181, 'mAP_medium': 0.8691557352372217, 'mAP_fast': 0.7459511040452989}Training example
python tools/vid_train.py -f exps/yolov/yolov_s.py -c weights/yoloxs_vid.pth --fp16Roughly testing
python tools/vid_eval.py -f exps/yolov/yolov_s.py -c weights/yolov_s.pth --tnum 500 --fp16tnum indicates testing sequence number.
Details
Training base detector
The train_coco.json is a COCO format annotation file. When trainig the base detector on your own dataset, try to convert the annotation to COCO format.
Training YOLOV Series
The train_seq.npy and val_seq.npy files are numpy arrays of lists. They can be loaded using the following command:
numpy.load('./yolox/data/datasets/train_seq.npy',allow_pickle=True)Each list contains the paths to all images in a video. The specific annotations(xml annotation in VID dataset) are loaded via these image paths, refer to
YOLOV/yolox/data/datasets/vid.py
Line 125 in f5a57dd
Details
-
Finetuing the base detector(YOLOX) on your custom dataset with COCO format annotation. You need to modify the YOLOX experiment file. For instance, the experiment file for the Imagenet VID dataset is modified as this example. Initialized weights with COCO pretraining is essential for the performance, you can find these coco pretrained weights in YOLOX official repo (YOLOX-S~YOLOX-X) and this huggingface repo (YOLOX-SwinTiny and SwinBase).
-
Construct your dataset in the COCO format. Here is a template for the dataset structure (sourced from OVIS):
{ "info" : info, "videos" : [video], "annotations" : [annotation] or None, "categories" : [category], } video{ "id" : int, "width" : int, "height" : int, "length" : int, "file_names" : [file_name], } annotation{ "id" : int, "video_id" : int, "category_id" : int, "areas" : [float or None], "bboxes" : [[x,y,width,height] or None], "iscrowd" : 0 or 1, } category{ "id" : int, "name" : str, "supercategory" : str, }After preparing the COCO format dataset, we provide code which converts the COCO format annotation for video object detection. You can construct your experiment file for YOLOV such as YOLOVs_OVIS. For YOLOV++, please refer example in exps/customed_example/v++_SwinTiny_example.py, please config the OVIS in the get_data_loader and get_eval_loader according to your own dataset. Remember to change the category information in the evaluator.
-
Initialize the YOLOV or YOLOV++ with finetuned weights obtained by Step 1. You may adjust the hyperparameters such as proposal numbers according to your dataset for getting better performance:
python tools/vid_train.py -f exps/customed_example/v++_SwinTiny_example.py -c [path to your weights] --fp16
Note that the batch size when training video detector is determined by the lframe and gframe, refer to this line. You can adjust the batch size according to your GPU memory. However, a very small batch size (<4) may lead to poor performance.
Expand
If YOLOV series are helpful for your research, please cite the following paper:
@article{shi2024yolovpp,
title={Practical Video Object Detection via Feature Selection and Aggregation},
author={Yuheng Shi and Tong Zhang and Xiaojie Guo},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.19650},
year={2024},
}
@article{shi2022yolov,
title={YOLOV: Making Still Image Object Detectors Great at Video Object Detection},
author={Shi, Yuheng and Wang, Naiyan and Guo, Xiaojie},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.09686},
year={2022}
}