Python is a modern, robust, high level programming language. It is very easy to pick up even if you are completely new to programming.
Mac OS X and Linux comes pre installed with python. Windows users can download
To install IPython run,
pip install ipython[all]
This will install all the necessary dependencies for the notebook, qtconsole, tests etc.
Installing all the necessary libraries might prove troublesome. Anaconda and Canopy comes pre packaged with all the necessary python libraries and also IPython.
Anaconda is completely free and includes more than 300 python packages. Both python 2.7 and 3.9 options are available.
From the terminal
ipython notebook
In Anaconda, Open the respective terminals and execute the above.
These are read-only versions. However you can "Run ▶" all the codes online by clicking here →
You can 
Go here if you aren't here already and click the "⭐ Star" button in the top right corner. You will be asked to create a GitHub account if you don't already have one.
-
Go here if you aren't here already.
-
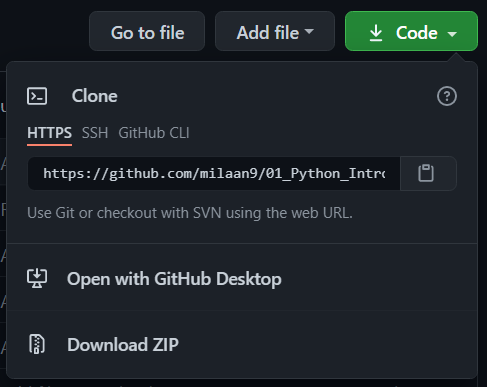
Click the big green "Clone or download" button in the top right of the page, then click "Download ZIP".
-
Extract the ZIP and open it. Unfortunately I don't have any more specific instructions because how exactly this is done depends on which operating system you run.
-
Launch ipython notebook from the folder which contains the notebooks. Open each one of them
Kernel > Restart & Clear Output
This will clear all the outputs and now you can understand each statement and learn interactively.
If you have git and you know how to use it, you can also clone the repository instead of downloading a zip and extracting it. An advantage with doing it this way is that you don't need to download the whole tutorial again to get the latest version of it, all you need to do is to pull with git and run ipython notebook again.
I'm Dr. Milaan Parmar and I have written this tutorial. If you think you can add/correct/edit and enhance this tutorial you are most welcome🙏
See github's contributors page for details.
If you have trouble with this tutorial please tell me about it by Create an issue on GitHub  and I'll make this tutorial better. This is probably the best choice if you had trouble following the tutorial, and something in it should be explained better. You will be asked to create a GitHub account if you don't already have one.
and I'll make this tutorial better. This is probably the best choice if you had trouble following the tutorial, and something in it should be explained better. You will be asked to create a GitHub account if you don't already have one.
If you like this tutorial, please give it a ⭐ star.
You may use this tutorial freely at your own risk. See LICENSE.