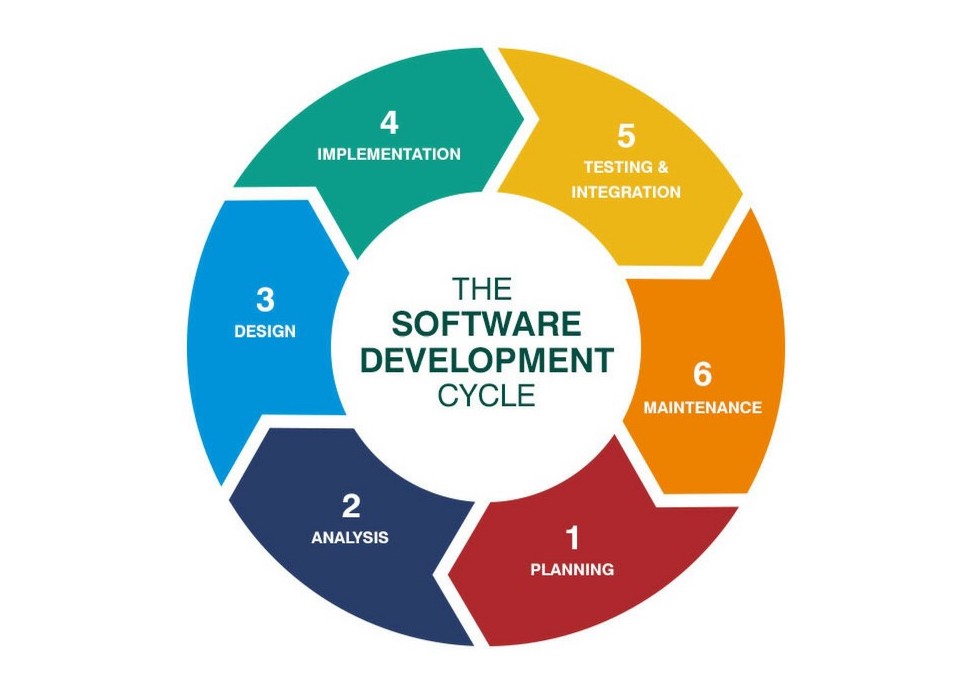
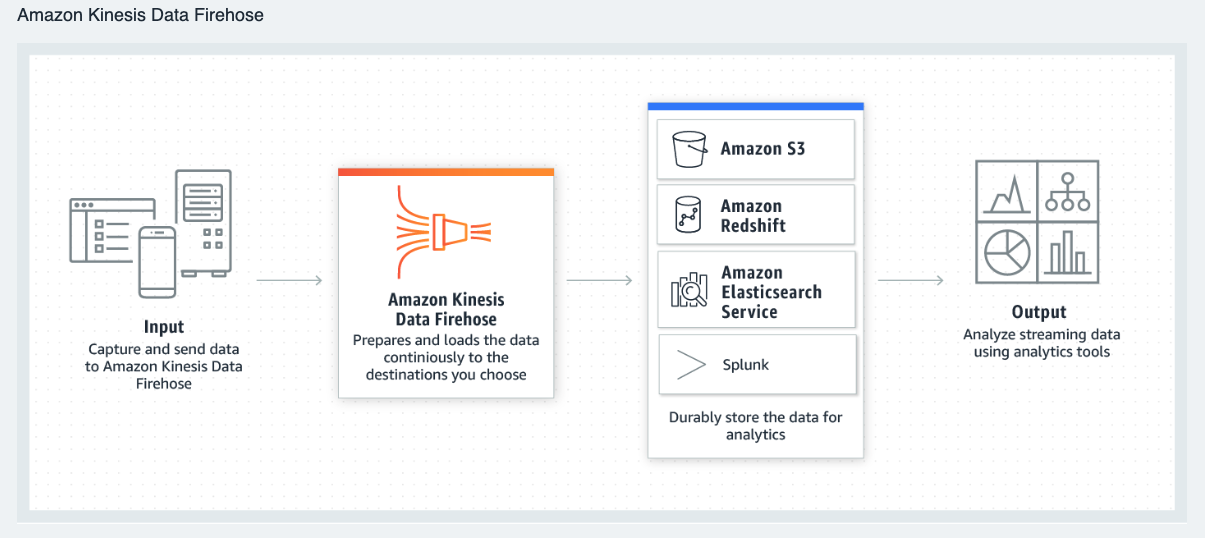
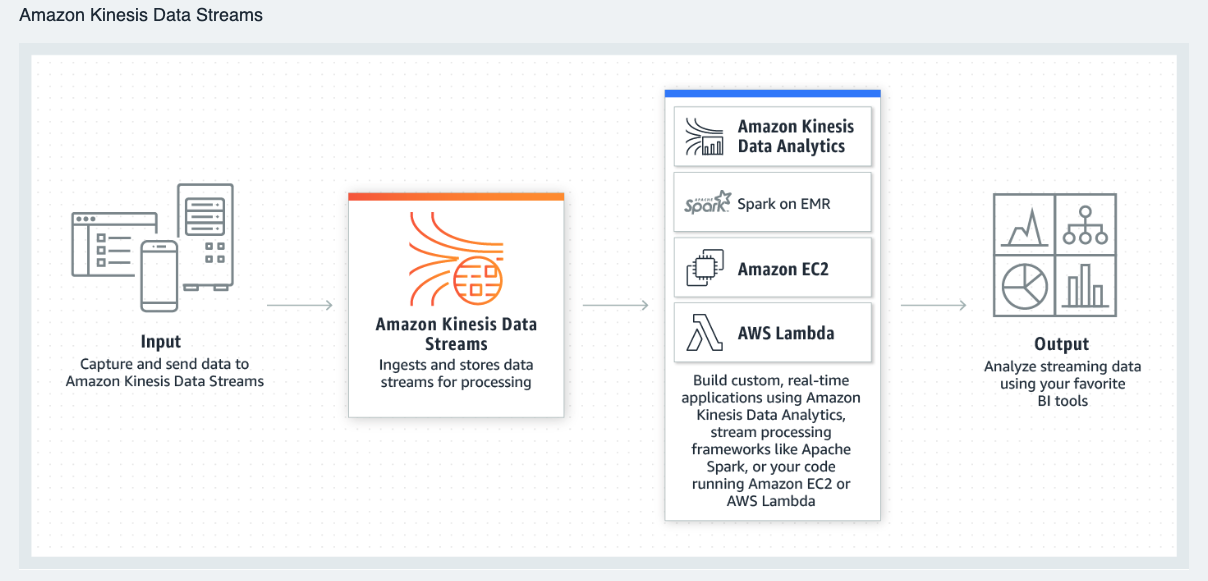
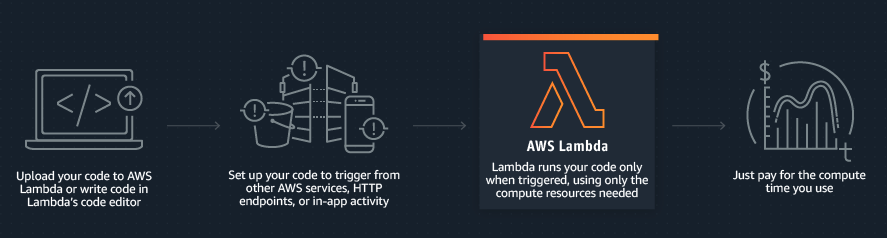
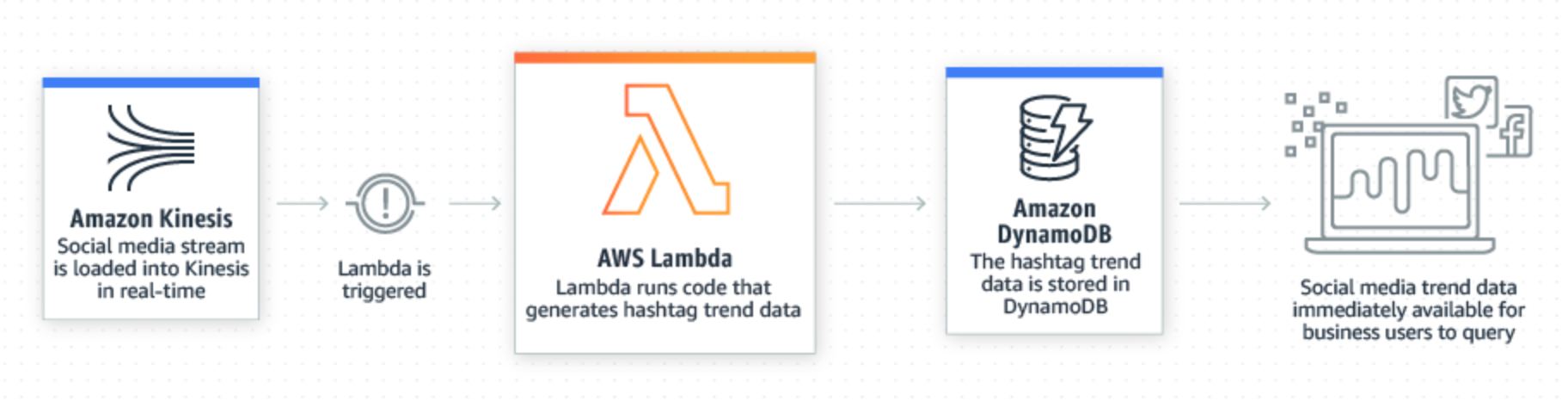
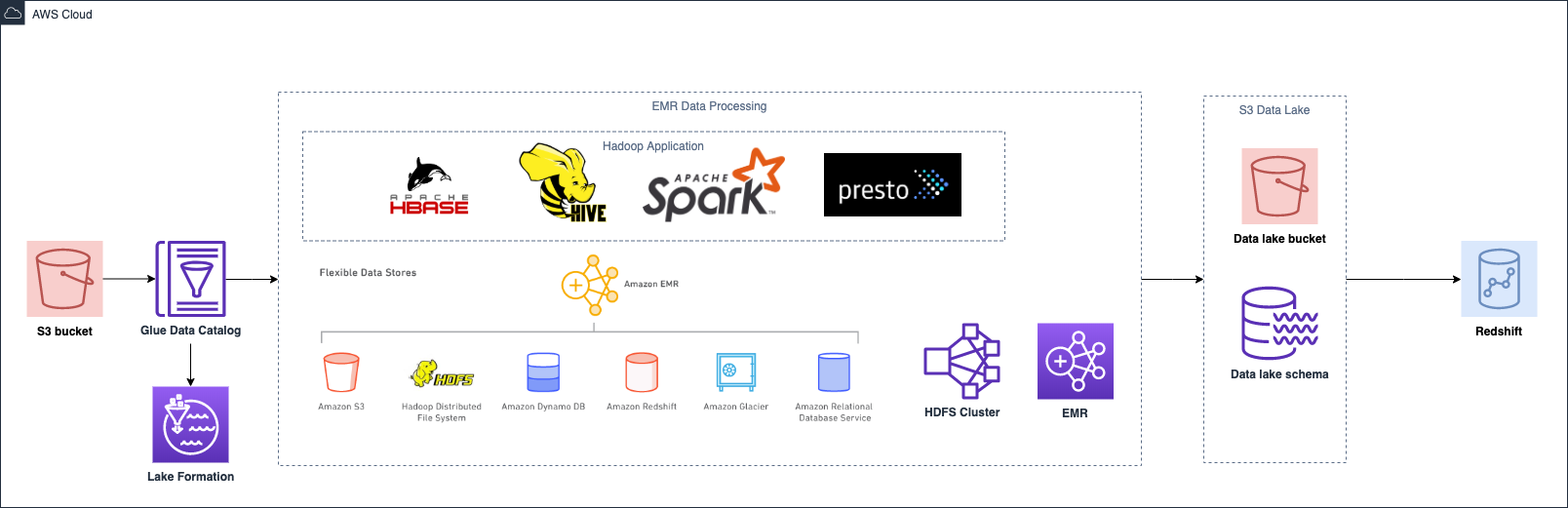
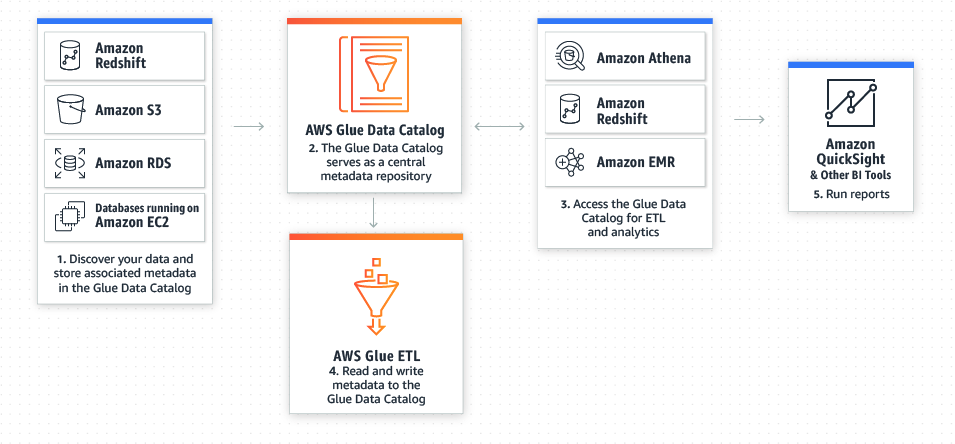
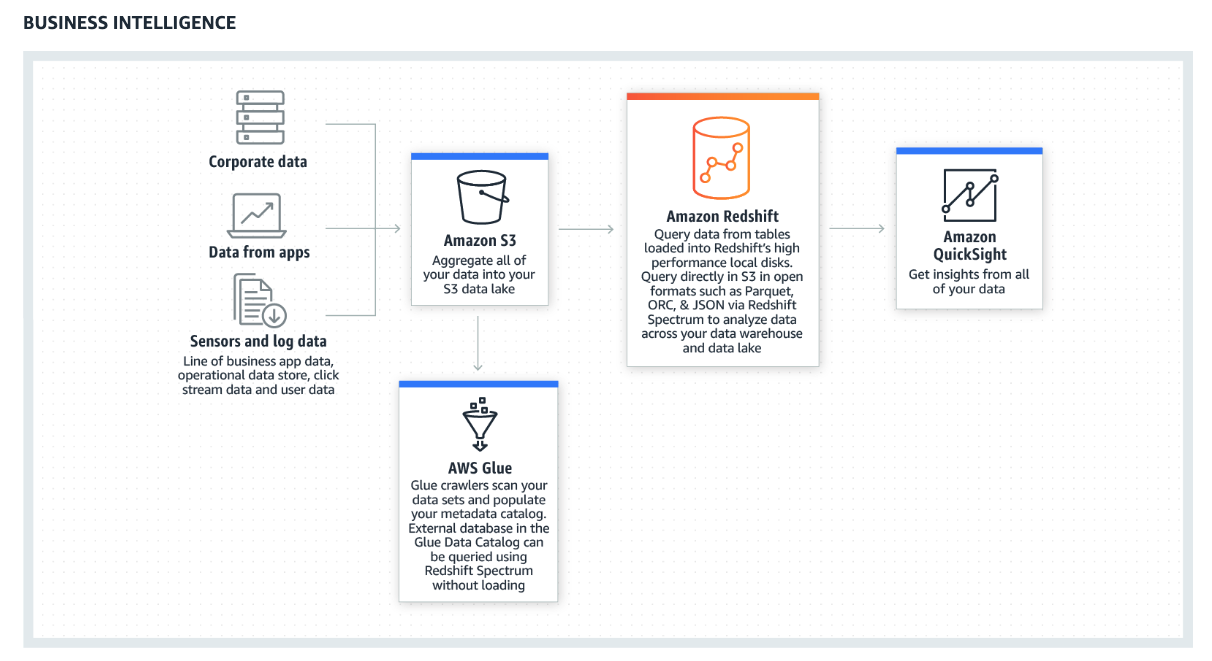
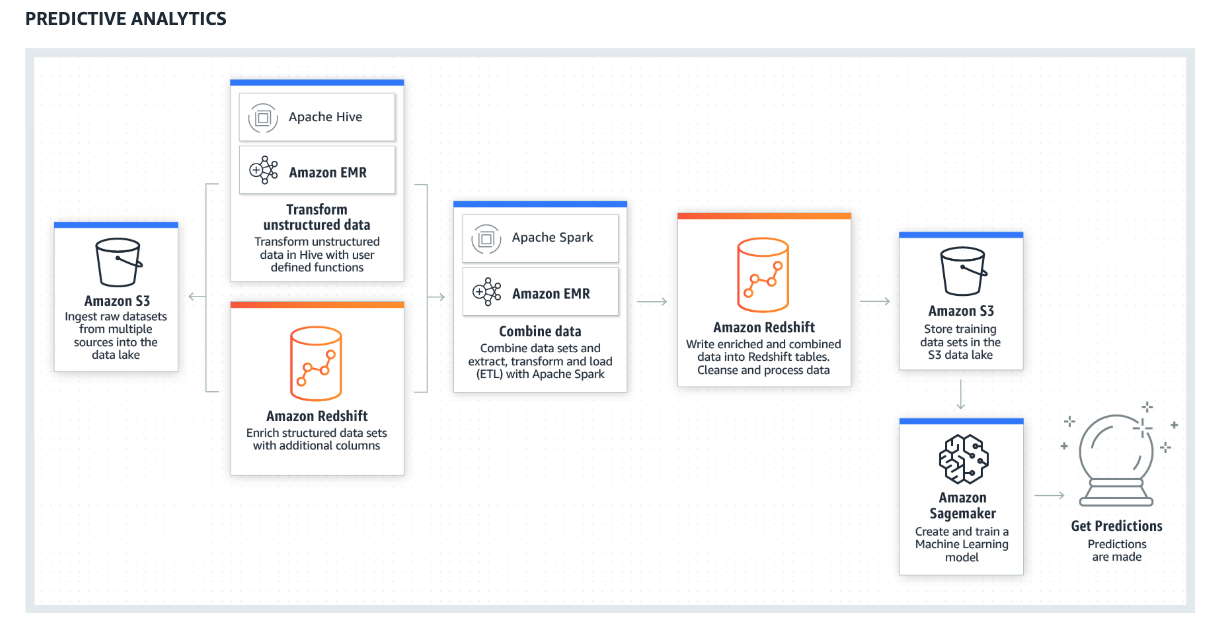
To solve the problem of data silos, many companies try to embrace the beneficial data solution to develop their data platform. AWS is one of the essential components for the company to build a prominent data platform that provides scalable and reliable approaches for the customer. Nevertheless, a few pieces of concept need to be established before design your architecture on AWS to make architectural trade-offs as your plans evolve.
The passage will elucidate how to combine AWS Well-Architected Framework concept with data platform design
Building an application is not difficult
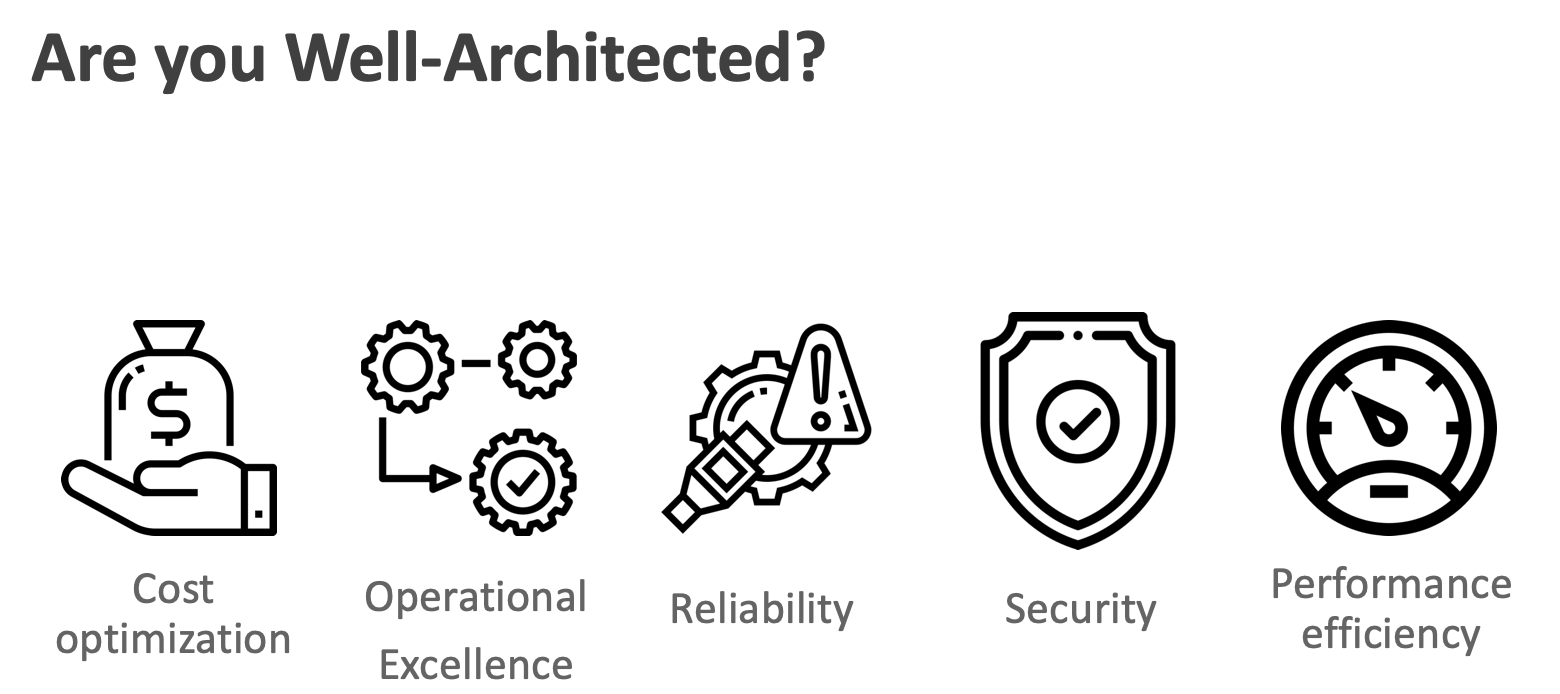
When you reviewing the system, can you answer the question: "Are you Well-Architected?"
The AWS Well-Architected Framework is based on five pillars — operational excellence, security, reliability, performance efficiency, and cost optimization
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Operational Excellence | The ability to run and monitor systems to deliver business value and to continually improve supporting processes and procedures. |
| Security | The ability to protect information, systems, and assets while delivering business value through risk assessments and mitigation strategies. |
| Reliability | The ability of a system to recover from infrastructure or service disruptions dynamically acquire computing resources to meet demand, and mitigate disruptions such as misconfigurations or transient network issues. |
| Performance Efficiency | The ability to use computing resources efficiently to meet system requirements, and to maintain that efficiency as demand changes and technologies evolve. |
| Cost Optimization | The ability to run systems to deliver business value at the lowest price point. |
Eliminate guessing about your infrastructure capacity needs. When you make a capacity decision before you deploy a system, you might end up sitting on expensive idle resources or dealing with the performance implications of limited capacity. With cloud computing, these problems can go away. You can use as much or as little capacity as you need, and scale up and down automatically.
In the cloud, you can create a production-scale test environment on demand, complete your testing, and then decommission the resources. Because you only pay for the test environment when it's running, you can simulate your live environment for a fraction of the cost of testing on premises.
Automation allows you to create and replicate your systems at low cost and avoid the expense of manual effort. You can track changes to your automation, audit the impact, and revert to previous parameters when necessary.
Allow for evolutionary architectures. In a traditional environment, architectural decisions are often implemented as static, one-time events, with a few major versions of a system during its lifetime. As a business and its context continue to change, these initial decisions might hinder the system's ability to deliver changing business requirements. In the cloud, the capability to automate and test on demand lowers the risk of impact from design changes. This allows systems to evolve over time so that businesses can take advantage of innovations as a standard practice.
In the cloud you can collect data on how your architectural choices affect the behavior of your workload. This lets you make fact-based decisions on how to improve your workload. Your cloud infrastructure is code, so you can use that data to inform your architecture choices and improvements over time.
Test how your architecture and processes perform by regularly scheduling game days to simulate events in production. This will help you understand where improvements can be made and can help develop organizational experience in dealing with events.
-
Perform operations as code
In the cloud, you can apply the same engineering discipline that you use for application code to your entire environment. You can define your entire workload (applications, infrastructure) as code and update it with code. You can implement your operations procedures as code and automate their execution by triggering them in response to events. By performing operations as code, you limit human error and enable consistent responses to events.
-
Annotate documentation
In an on-premises environment, documentation is created by hand, used by people, and hard to keep in sync with the pace of change. In the cloud, you can automate the creation of annotated documentation after every build (or automatically annotate hand-crafted documentation). Annotated documentation can be used by people and systems. Use annotations as an input to your operations code.
-
Make frequent, small, reversible changes
Design workloads to allow components to be updated regularly. Make changes in small increments that can be reversed if they fail (without affecting customers when possible).
-
Refine operations procedures frequently
As you use operations procedures, look for opportunities to improve them. As you evolve your workload, evolve your procedures appropriately. Set up regular game days to review and validate that all procedures are effective and that teams are familiar with them.
-
Anticipate failure
Perform “pre-mortem” exercises to identify potential sources of failure so that they can be removed or mitigated. Test your failure scenarios and validate your understanding of their impact. Test your response procedures to ensure that they are effective, and that teams are familiar with their execution. Setup regular game days to test workloads and team responses to simulated events.
-
Learn from all operational failures
Drive improvement through lessons learned from all operational events and failures. Share what is learned across teams and through the entire organization.
-
Essential
- CloudFormation
- enables you to provision resources in an orderly and consistent fashion from your development through production environments
- CloudFormation
-
Prepare
- AWS Config
- AWS Config and AWS Config rules can be used to create standards for workloads
- AWS Config
-
Operate
- CloudWatch
- monitor the operational health of a workload
- CloudWatch
-
Evolve
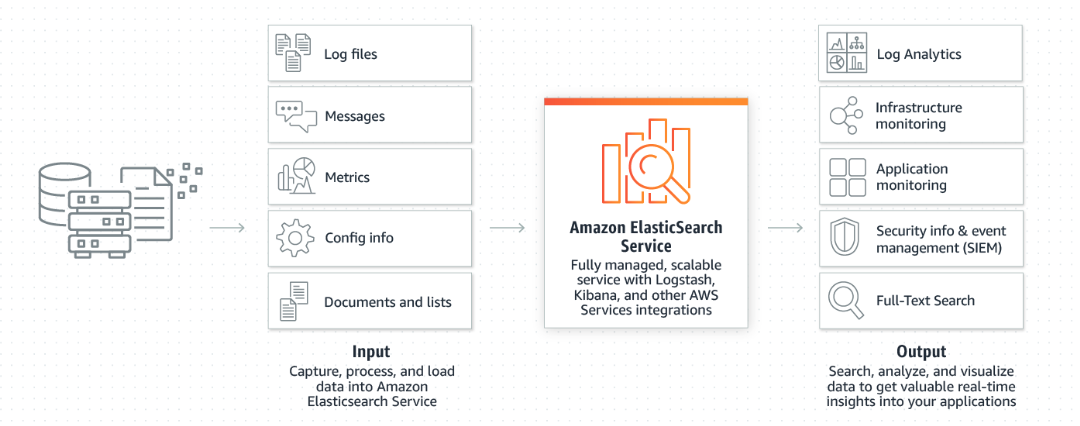
- Amazon Elasticsearch Service (ES)
- analyze your log data to gain actionable insights quickly and securely
- Amazon Elasticsearch Service (ES)
-
Implement a strong identity foundation
Implement the principle of least privilege and enforce separation of duties with appropriate authorization for each interaction with your AWS resources. Centralize privilege management and reduce or even eliminate reliance on long-term credentials.
-
Enable traceability
Monitor, alert, and audit actions and changes to your environment in real time. Integrate logs and metrics with systems to automatically respond and take action.
-
Apply security at all layers
Rather than just focusing on protection of a single outer layer, apply a defense-in-depth approach with other security controls. Apply to all layers (e.g., edge network, VPC, subnet, load balancer, every instance, operating system, and application).
-
Automate security best practices
Automated software-based security mechanisms improve your ability to securely scale more rapidly and cost effectively. Create secure architectures, including the implementation of controls that are defined and managed as code in version-controlled templates.
-
Protect data in transit and at rest
Classify your data into sensitivity levels and use mechanisms, such as encryption, tokenization, and access control where appropriate.
-
Keep people away from data
Create mechanisms and tools to reduce or eliminate the need for direct access or manual processing of data. This reduces the risk of loss or modification and human error when handling sensitive data.
-
Prepare for security events
Prepare for an incident by having an incident management process that aligns to your organizational requirements. Run incident response simulations and use tools with automation to increase your speed for detection, investigation, and recovery
-
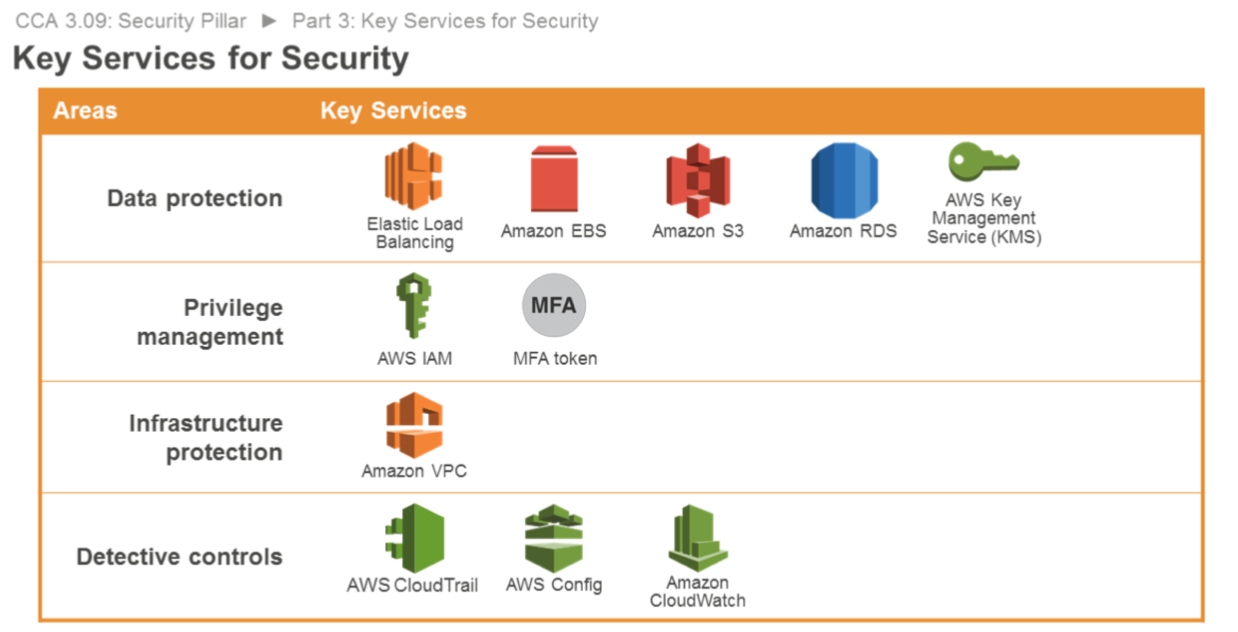
Data Protection
Services such as ELB, Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS), Amazon S3, and Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) include encryption capabilities to protect your data in transit and at rest. Amazon Macie automatically discovers, classifies and protects sensitive data, while AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) makes it easy for you to create and control keys used for encryption.
- ELB
- EBS
- S3
- RDS
- KMS
-
Identity and Access Management
IAM enables you to securely control access to AWS services and resources. MFA adds an additional layer of protection on user access. AWS Organizations lets you centrally manage and enforce policies for multiple AWS accounts.
- IAM
- MFA
-
Infrastructure Protection
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) enables you to launch AWS resources into a virtual network that you've defined. Amazon CloudFront is a global content delivery network that securely delivers data, videos, applications, and APIs to your viewers which integrates with AWS Shield for DDoS mitigation. AWS WAF is a web application firewall that is deployed on either Amazon CloudFront or Application Load Balancer to help protect your web applications from common web exploits.
- VPC
-
Detective Control
AWS CloudTrail records AWS API calls, AWS Config provides a detailed inventory of your AWS resources and configuration. Amazon GuardDuty is a managed threat detection service that continuously monitors for malicious or unauthorized behavior. Amazon CloudWatch is a monitoring service for AWS resources which can trigger CloudWatch Events to automate security responses.
- CloudWatch
- CloudTrail
-
Incident Response
IAM should be used to grant appropriate authorization to incident response teams and response tools. AWS CloudFormation can be used to create a trusted environment or clean room for conducting investigations. Amazon CloudWatch Events allows you to create rules that trigger automated responses including AWS Lambda.
- CloudWatch Events
- Lambda
-
Test recovery procedures
In an on-premises environment, testing is often conducted to prove the system works in a particular scenario. Testing is not typically used to validate recovery strategies. In the cloud, you can test how your system fails, and you can validate your recovery procedures. You can use automation to simulate different failures or to recreate scenarios that led to failures before. This exposes failure pathways that you can test and rectify before a real failure scenario, reducing the risk of components failing that have not been tested before.
-
Automatically recover from failure
By monitoring a system for key performance indicators (KPIs), you can trigger automation when a threshold is breached. This allows for automatic notification and tracking of failures, and for automated recovery processes that work around or repair the failure. With more sophisticated automation, it's possible to anticipate and remediate failures before they occur.
-
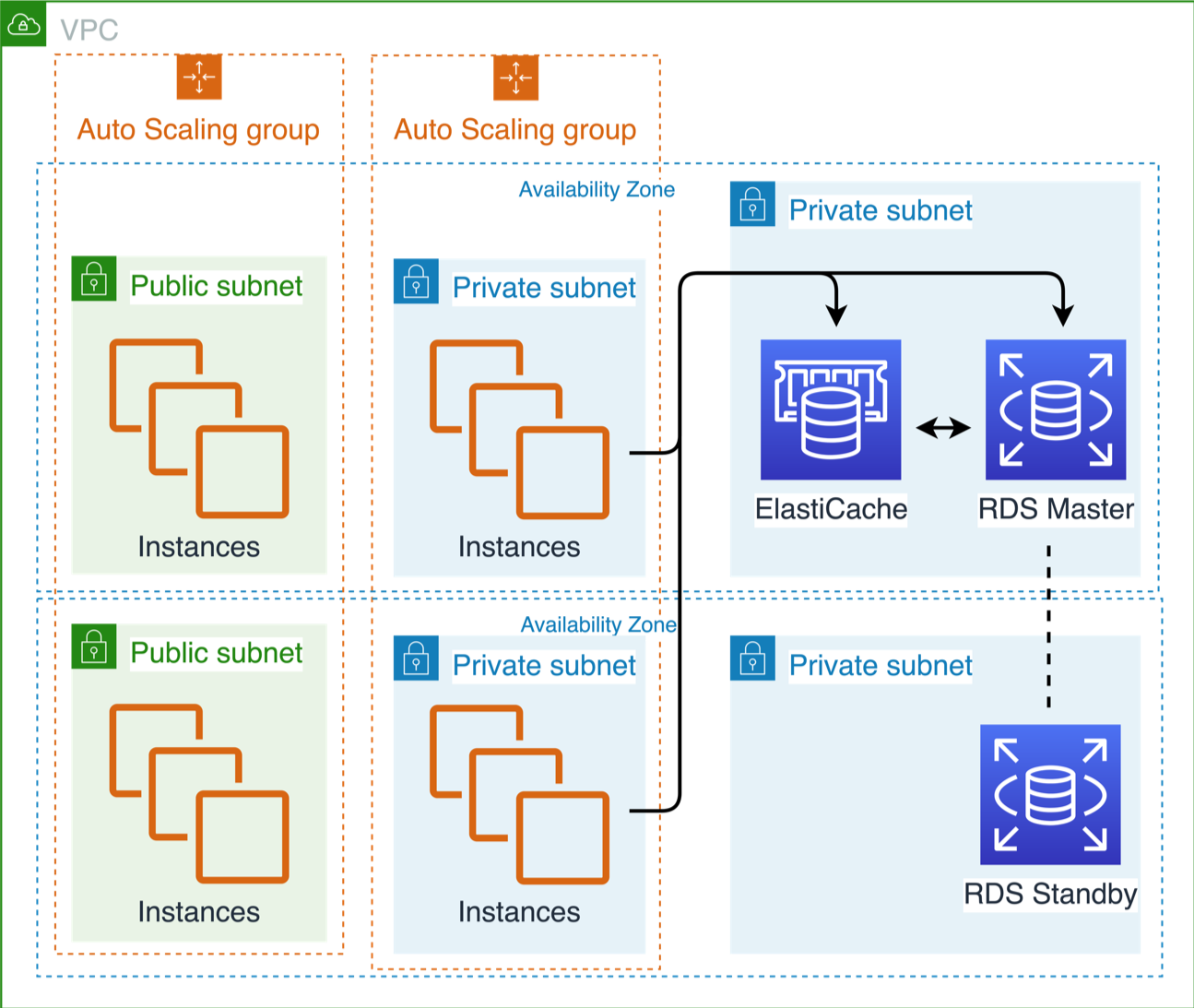
Scale horizontally to increase aggregate system availability:
Replace one large resource with multiple small resources to reduce the impact of a single failure on the overall system. Distribute requests across multiple, smaller resources to ensure that they don't share a common point of failure.
-
Stop guessing capacity
A common cause of failure in on-premises systems is resource saturation, when the demands placed on a system exceed the capacity of that system (this is often the objective of denial of service attacks). In the cloud, you can monitor demand and system utilization, and automate the addition or removal of resources to maintain the optimal level to satisfy demand without overor under- provisioning.
-
Manage change in automation
Changes to your infrastructure should be done using automation. The changes that need to be managed are changes to the automation.
-
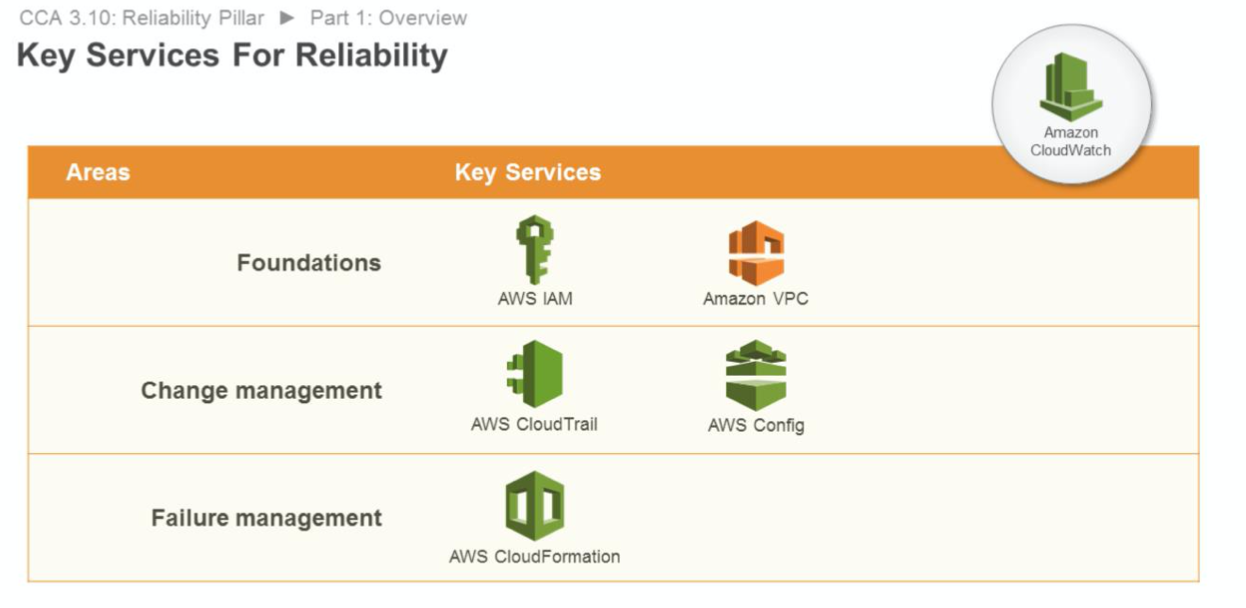
Foundations
AWS IAM enables you to securely control access to AWS services and resources. Amazon VPC lets you provision a private, isolated section of the AWS Cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network. AWS Trusted Advisor provides visibility into service limits. AWS Shield is a managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service that safeguards web applications running on AWS.
- IAM
- VPC
-
Change Management
AWS CloudTrail records AWS API calls for your account and delivers log files to you for auditing. AWS Config provides a detailed inventory of your AWS resources and configuration, and continuously records configuration changes. Amazon Auto Scaling is a service that will provide an automated demand management for a deployed workload. Amazon CloudWatch provides the ability to alert on metrics, including custom metrics. Amazon CloudWatch also has a logging feature that can be used to aggregate log files from your resources.
- Amazon Auto Scaling
- CloudTrail
- CloudWatch
-
Failure Management
AWS CloudFormation provides templates for the creation of AWS resources and provisions them in an orderly and predictable fashion. Amazon S3 provides a highly durable service to keep backups. Amazon Glacier provides highly durable archives. AWS KMS provides a reliable key management system that integrates with many AWS services.
-
CloudFormation
- rollback
-
S3
- backup
-
-
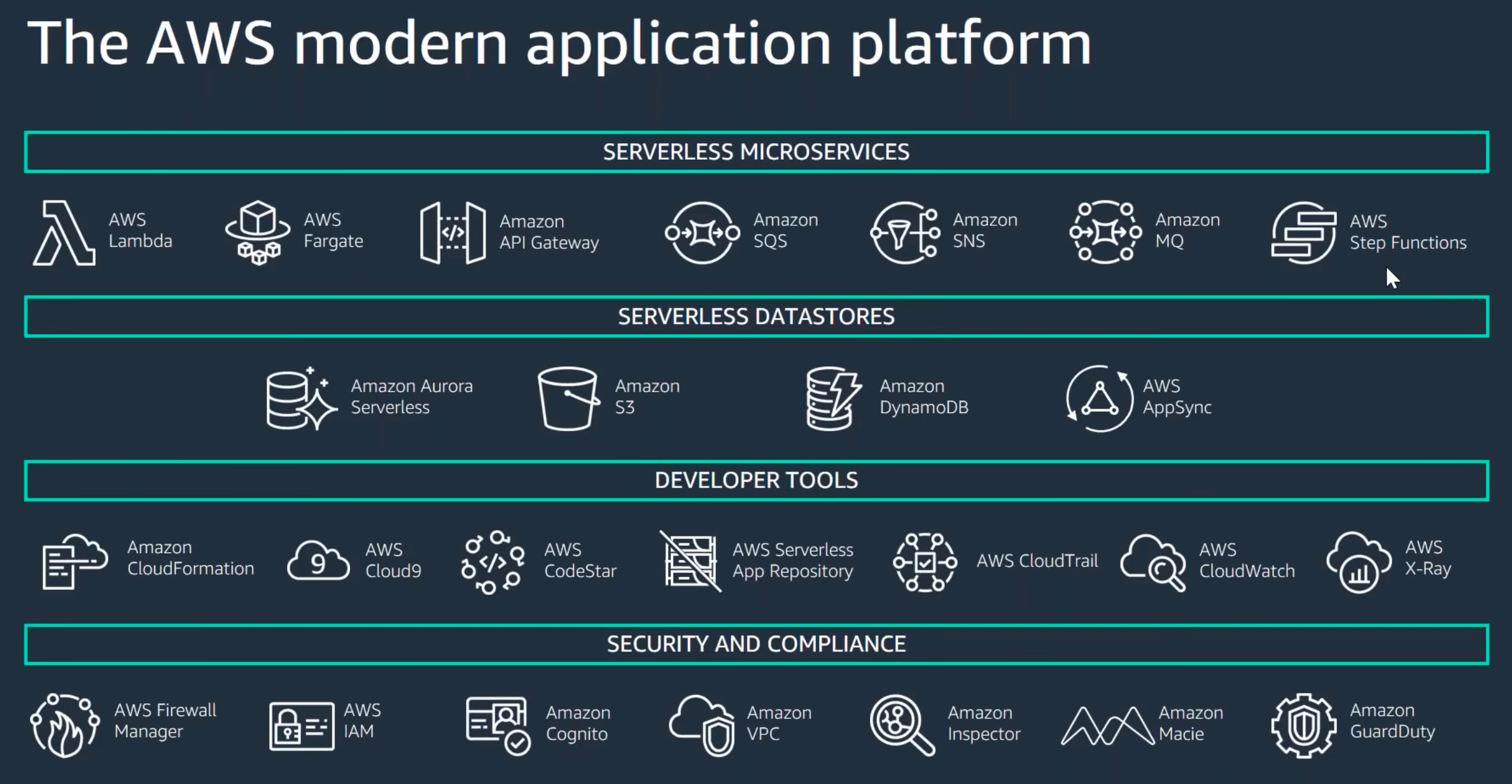
Democratize advanced technologies
Technologies that are difficult to implement can become easier to consume by pushing that knowledge and complexity into the cloud vendor's domain. Rather than having your IT team learn how to host and run a new technology, they can simply consume it as a service. For example, NoSQL databases, media transcoding, and machine learning are all technologies that require expertise that is not evenly dispersed across the technical community. In the cloud, these technologies become services that your team can consume while focusing on product development rather than resource provisioning and management.
-
Go global in minutes
Easily deploy your system in multiple Regions around the world with just a few clicks. This allows you to provide lower latency and a better experience for your customers at minimal cost.
-
Use serverless architectures
In the cloud, serverless architectures remove the need for you to run and maintain servers to carry out traditional compute activities. For example, storage services can act as static websites, removing the need for web servers, and event services can host your code for you. This not only removes the operational burden of managing these servers, but also can lower transactional costs because these managed services operate at cloud scale.
-
Experiment more often
With virtual and automatable resources, you can quickly carry out comparative testing using different types of instances, storage, or configurations.
-
Mechanical sympathy
Use the technology approach that aligns best to what you are trying to achieve. For example, consider data access patterns when selecting database or storage approaches.
-
Selection
-
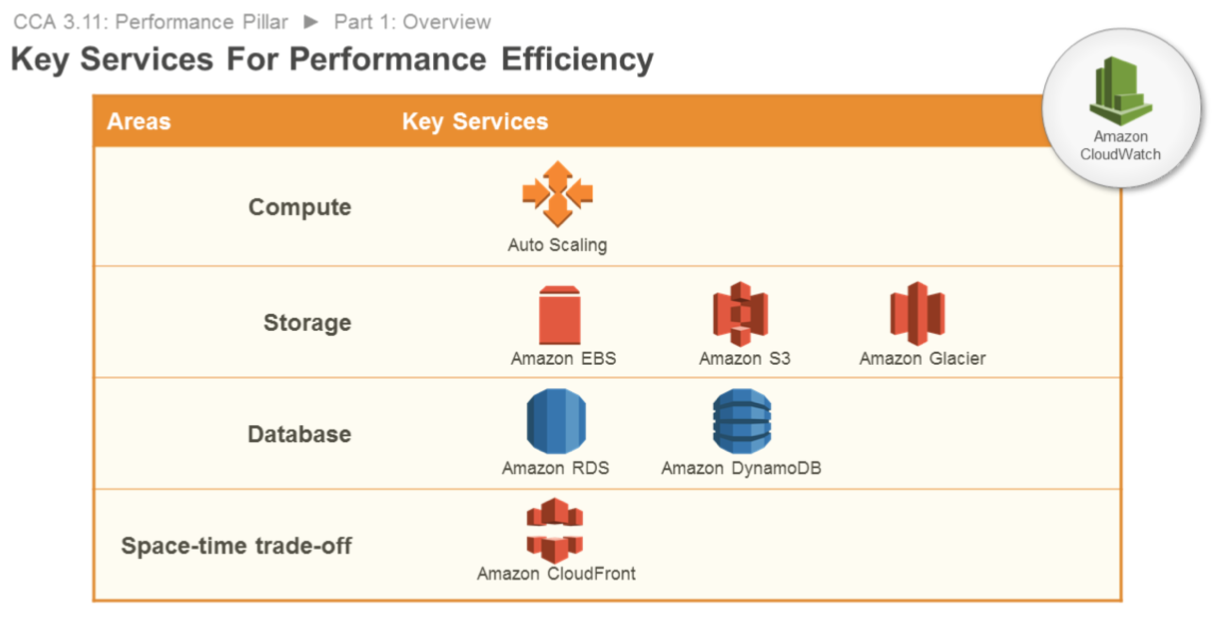
Compute
Auto Scaling is key to ensuring that you have enough instances to meet demand and maintain responsiveness.
- Amazon Auto Scaling
-
Storage
Amazon EBS provides a wide range of storage options (such as SSD and provisioned input/output operations per second (PIOPS)) that allow you to optimize for your use case. Amazon S3 provides serverless content delivery, and Amazon S3 transfer acceleration enables fast, easy, and secure transfers of files over long distances.
- S3
- EBS
-
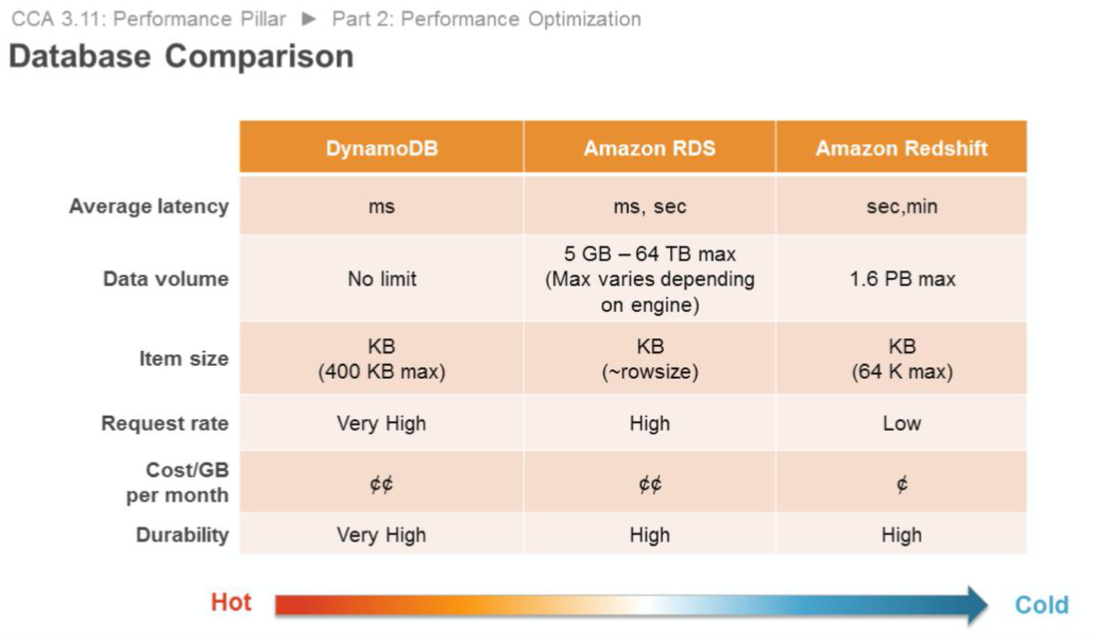
Database
Amazon RDS provides a wide range of database features (such as PIOPS and read replicas) that allow you to optimize for your use case. Amazon DynamoDB provides single-digit millisecond latency at any scale.
- RDS
- DynamoDB
-
Network
Amazon Route 53 provides latency-based routing. Amazon VPC endpoints and AWS Direct Connect can reduce network distance or jitter.
- VPC
- Route 53
- Direct Connect
-
-
Review
The AWS Blog and the What's New section on the AWS website are resources for learning about newly launched features and services.
-
Monitoring
Amazon CloudWatch provides metrics, alarms, and notifications that you can integrate with your existing monitoring solution, and that you can use with AWS Lambda to trigger actions.
- CloudWatch
- Lambda
-
Tradeoffs
Amazon ElastiCache, Amazon CloudFront, and AWS Snowball are services that allow you to improve performance. Read replicas in Amazon RDS can allow you to scale read-heavy workloads.
-
Adopt a consumption model
Pay only for the computing resources that you require and increase or decrease usage depending on business requirements, not by using elaborate forecasting. For example, development and test environments are typically only used for eight hours a day during the work week. You can stop these resources when they are not in use for a potential cost savings of 75% (40 hours versus 168 hours).
-
Measure overall efficiency
Measure the business output of the workload and the costs associated with delivering it. Use this measure to know the gains you make from increasing output and reducing costs.
-
Stop spending money on data center operations
AWS does the heavy lifting of racking, stacking, and powering servers, so you can focus on your customers and organization projects rather than on IT infrastructure.
-
Analyze and attribute expenditure
The cloud makes it easier to accurately identify the usage and cost of systems, which then allows transparent attribution of IT costs to individual workload owners. This helps measure return on investment (ROI) and gives workload owners an opportunity to optimize their resources and reduce costs.
-
Use managed and application level services to reduce cost of ownership
In the cloud, managed and application level services remove the operational burden of maintaining servers for tasks such as sending email or managing databases. As managed services operate at cloud scale, they can offer a lower cost per transaction or service.
-
Expenditure Awareness
AWS Cost Explorer allows you to view and track your usage in detail. AWS Budgets notify you if your usage or spend exceeds actual or forecast budgeted amounts
- AWS Cost Explorer
-
Cost-Effective Resources
You can use Cost Explorer for Reserved Instance recommendations, and see patterns in how much you spend on AWS resources over time. Use Amazon CloudWatch and Trusted Advisor to help right size your resources. You can use Amazon Aurora on RDS to remove database licensing costs. AWS Direct Connect and Amazon CloudFront can be used to optimize data transfer.
-
Matching supply and demand
Auto Scaling allows you to add or remove resources to match demand without overspending.
- Amazon Auto Scaling
-
Optimizing Over Time
The AWS News Blog and the What's New section on the AWS website are resources for learning about newly launched features and services. AWS Trusted Advisor inspects your AWS environment and finds opportunities to save you money by eliminating unused or idle resources or committing to Reserved Instance capacity.
- AWS Trusted Advisor
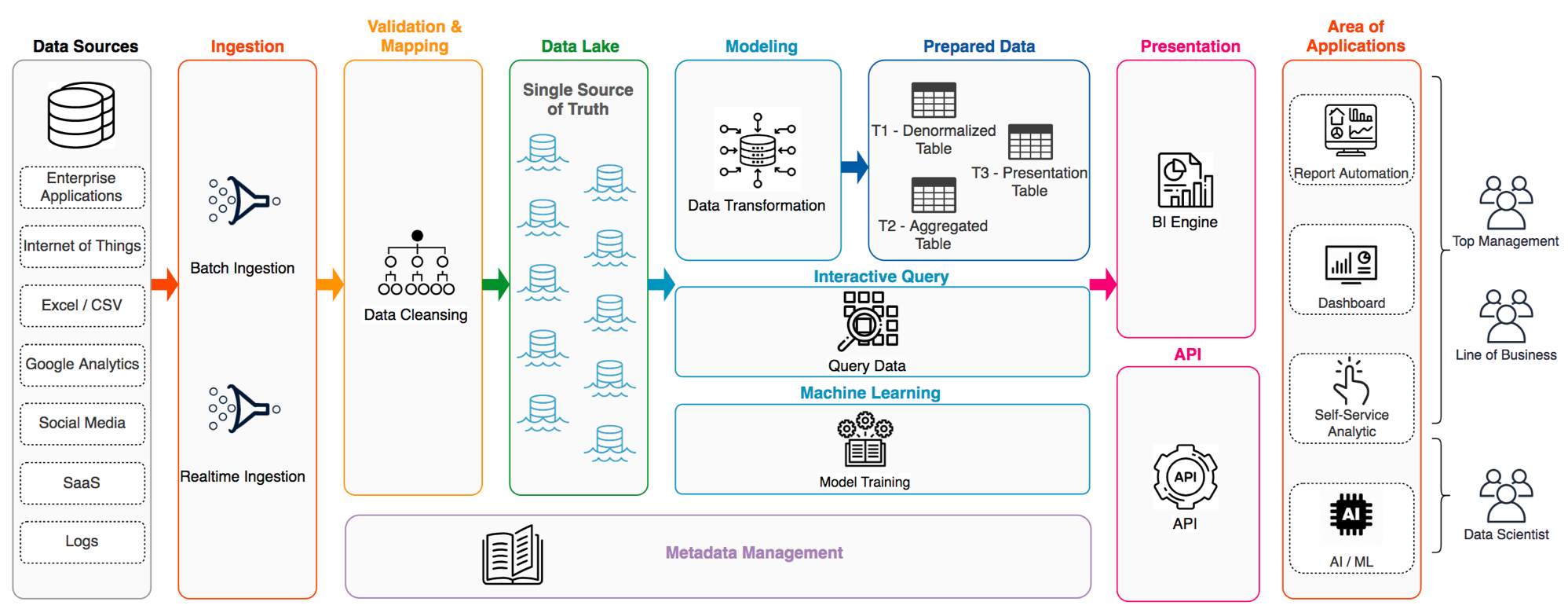
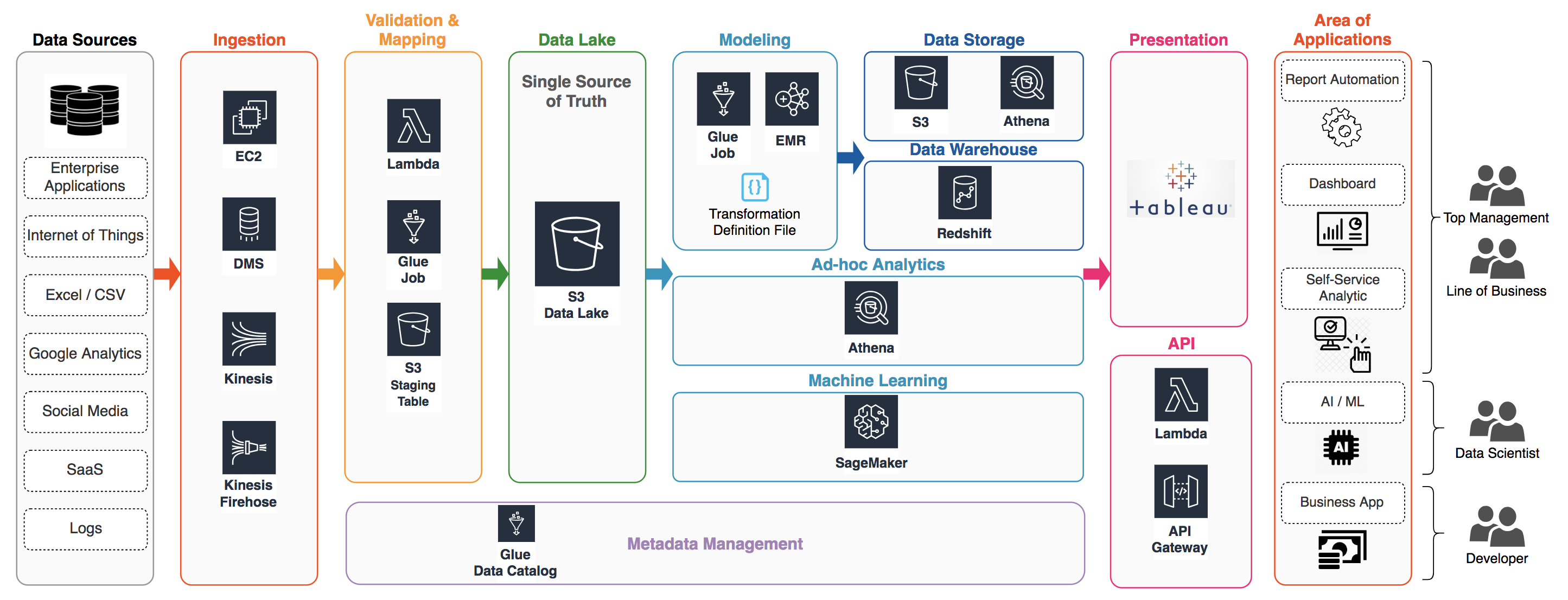
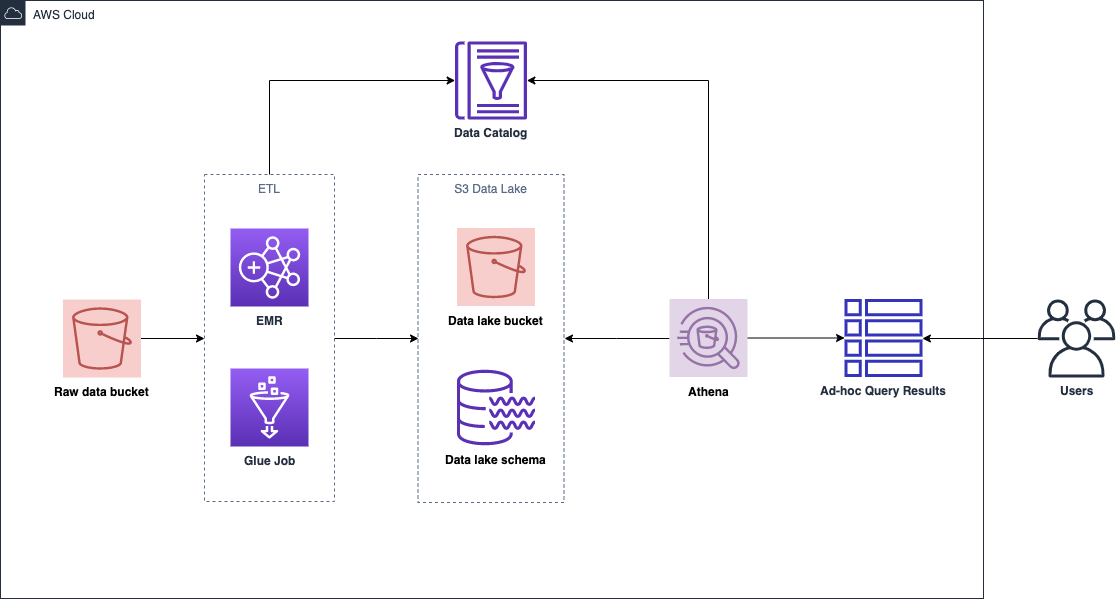
Nowadays an advanced data platform required a myriad of functionalities
To build a scalable data platform, AWS is a panacea for most companies. However, it is imperative to take the well-architected concept into the data application
This section will introduce the AWS big data services and elucidate the best practice of each service. The services including Kinesis, Lambda, EMR, Glue, DynamoDB, Redshift, Elastisearch and Athena
-
Ideal Usage Patterns
- Real-time data analytics
- Log and data feed intake and processing
- Real-time metrics and reporting
-
Cost Model
- Amazon Kinesis Data Streams has simple pay-as-you-go pricing, with no upfront costs or minimum fees, and you only pay for the resources you consume. An Amazon Kinesis stream is made up of one or more shards, each shard gives you a capacity 5 read transactions per second, up to a maximum total of 2 MB of data read per second.
-
Performance
- Amazon Kinesis Data Streams allows you to choose throughput capacity you require in terms of shards. With each shard in an Amazon Kinesis stream, you can capture up to 1 megabyte per second of data at 1,000 write transactions per second.
-
Durability and Availability
- Amazon Kinesis Data Streams synchronously replicates data across three Availability Zones in an AWS Region, providing high availability and data durability.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
- You can increase or decrease the capacity of the stream at any time according to your business or operational needs, without any interruption to ongoing stream processing.
-
Anti-Patterns
- Small scale consistent throughput
- Long-term data storage and analytics
-
Ideal Usage Patterns
- Real-time File Processing
- Real-time Stream Processing
- Extract, Transform, Load
- Replace Cron (Use schedule expressions to run a Lambda function)
- Process AWS Events (Event handler)
-
Cost Model
- With AWS Lambda you only pay for what you use. You are charged $0.20 per 1 million requests thereafter ($0.0000002 per request).
-
Performance
- Lambda is designed to process events within milliseconds. Latency will be higher immediately after a Lambda function is created, updated, or if it has not been used recently.
-
Durability and Availability
- AWS Lambda is designed to use replication and redundancy to provide high availability for both the service itself and for the Lambda functions it operates. On failure, Lambda functions being invoked synchronously respond with an exception. Lambda functions being invoked asynchronously are retried at least 3 times, after which the event may be rejected.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
- There is no limit on the number of Lambda functions that you can run. However, Lambda has a default safety throttle of 1,000 concurrent executions per account per region
-
Anti-Patterns
- Long Running Applications
- Dynamic Websites
- Stateful Applications
-
Ideal Usage Patterns
Amazon EMR’s flexible framework reduces large processing problems and data sets into smaller jobs and distributes them across many compute nodes in a Hadoop cluster. This capability lends itself to many usage patterns with big data analytics. Here are a few examples:
- Large extract, transform, and load (ETL) data movement
- Log processing and analytics
- Risk modeling and threat analytics
- Ad targeting and click stream analytics
- Predictive analytics
-
Cost Model
- Amazon EMR supports a variety of Amazon EC2 instance types (standard, high CPU, high memory, high I/O, and so on) and all Amazon EC2 pricing options (On-Demand, Reserved, and Spot).
-
Performance
- Amazon EMR performance is driven by the type of EC2 instances you choose to run your cluster on and how many you chose to run your analytics. You should choose an instance type suitable for your processing requirements, with sufficient memory, storage, and processing power.
-
Durability and Availability
- By default, Amazon EMR is fault tolerant for core node failures and continues job execution if a slave node goes down. Amazon EMR will also provision a new node when a core node fails. However, Amazon EMR will not replace nodes if all nodes in the cluster are lost. Customers can monitor the health of nodes and replace failed nodes with CloudWatch.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
- With Amazon EMR, it is easy to resize a running cluster. You can add core nodes which hold the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) at any time to increase your processing power and increase the HDFS storage capacity (and throughput). Additionally, you can use Amazon S3 natively or using EMRFS along with or instead of local HDFS which allows you to decouple your memory and compute from your storage providing greater flexibility and cost efficiency.
-
Anti-Patterns
- Small data sets
- ACID transaction requirements
-
Ideal Usage Patterns
AWS Glue is designed to easily prepare data for extract, transform, and load (ETL) jobs. Using AWS Glue gives you the following benefits:
- AWS Glue can automatically crawl your data and generate code to execute or data transformations and loading processes.
- Integration with services like Amazon Athena, Amazon EMR, and Amazon Redshift
- Serverless, no infrastructure to provision or manage
- AWS Glue generates ETL code that is customizable, reusable, and portable, using familiar technology – Python and Spark.
-
Cost Model
- With AWS Glue, you pay an hourly rate, billed by the minute, for crawler jobs (discovering data) and ETL jobs (processing and loading data).
-
Performance
- AWS Glue uses a scale-out Apache Spark environment to load your data into its destination. You can simply specify the number of Data Processing Units (DPUs) that you want to allocate to your ETL job.
-
Durability and Availability
- AWS Glue connects to the data source of your preference, whether it is in an Amazon S3 file, an Amazon RDS table, or another set of data.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
- AWS Glue provides a managed ETL service that runs on a Serverless Apache Spark environment. This allows you to focus on your ETL job and not worry about configuring and managing the underlying compute resources.
-
Anti-Patterns
- Streaming data
- Multiple ETL engines
- NoSQL Databases
-
Ideal Usage Patterns
DynamoDB is ideal for existing or new applications that need a flexible NoSQL database with low read and write latencies, and the ability to scale storage and throughput up or down as needed without code changes or downtime. Common use cases include:
- Mobile apps
- Gaming
- Digital ad serving
- Metadata storage for Amazon S3 objects
- E-commerce shopping carts
- Web session management
-
Cost Model
- DynamoDB has three pricing components: provisioned throughput capacity (per hour), indexed data storage (per GB per month), data transfer in or out (per GB per month).
-
Performance
- SSDs and limiting indexing on attributes provides high throughput and low latency and drastically reduces the cost of read and write operations.
-
Durability and Availability
- DynamoDB has built-in fault tolerance that automatically and synchronously replicates data across three data centers in a region for high availability and to help protect data against individual machine, or even facility, failures.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
- DynamoDB is both highly scalable and elastic. There is no limit to the amount of data that you can store in a DynamoDB table, and the service automatically allocates more storage as you store more data using the DynamoDB write API operations.
-
Anti-Patterns
- Prewritten application tied to a traditional relational database
- Joins or complex transactions
- Binary large objects (BLOB) data
- Large data with low I/O rate
-
Ideal Usage Patterns
Amazon Redshift is ideal for online analytical processing (OLAP) using your existing business intelligence tools. Organizations are using Amazon Redshift to:
- Analyze global sales data for multiple products
- Store historical stock trade data
- Aggregate gaming data
-
Cost Model
- Charges are based on the size and number of nodes of your cluster.
-
Performance
- Amazon Redshift uses a variety of innovations to obtain very high performance on data sets ranging in size from hundreds of gigabytes to a petabyte or more.
- Amazon Redshift has a massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture, parallelizing and distributing SQL operations to take advantage of all available resources.
-
Durability and Availability
- Amazon Redshift automatically detects and replaces a failed node in your data warehouse cluster. Additionally, your data warehouse cluster remains available in the event of a drive failure; because Amazon Redshift mirrors your data across the cluster, it uses the data from another node to rebuild failed drives.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
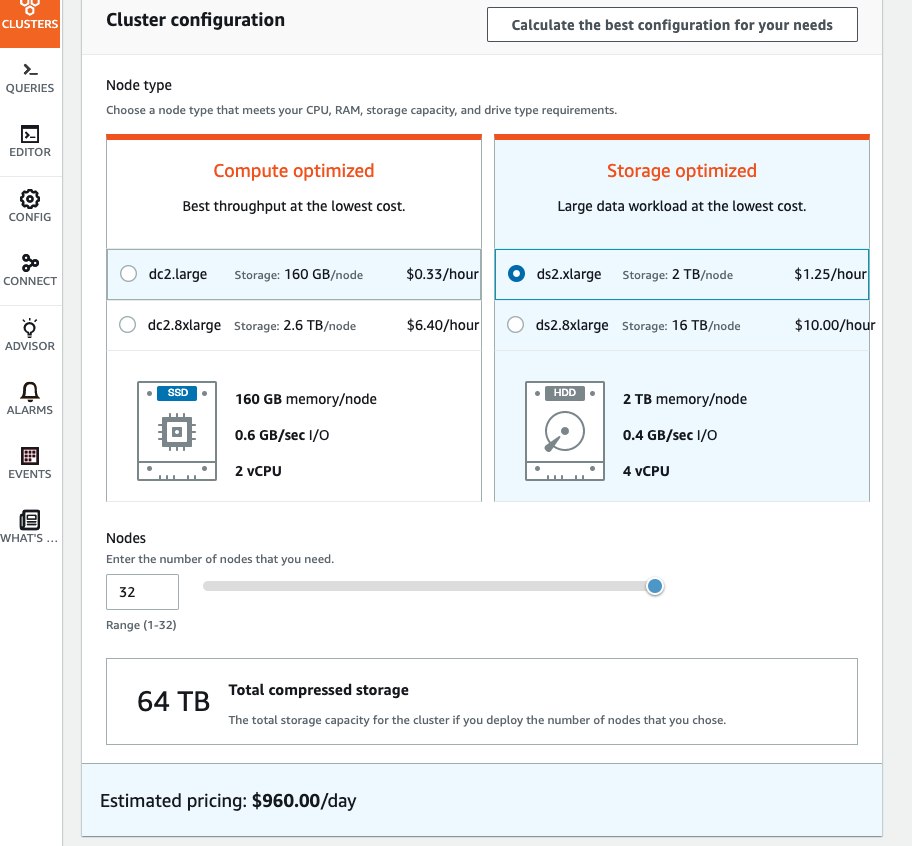
- Amazon Redshift enables you to start with a single 160 GB node and scale up to a petabyte or more of compressed user data using many nodes.
-
Anti-Patterns
- Small data sets
- On-line transaction processing (OLTP)
- Unstructured data
- BLOB data
-
Ideal Usage Patterns
Amazon Elasticsearch Service is ideal for querying and searching large amounts of data. Organizations can use Amazon ES to do the following:
- Analyze activity logs, e.g., logs for customer facing applications or websites
- Analyze CloudWatch logs with Elasticsearch
- Analyze product usage data coming from various services and systems
- Analyze social media sentiments, CRM data and find trends for your brand and products
- Analyze data stream updates from other AWS services, e.g., Amazon Kinesis Data Streams and Amazon DynamoDB
-
Cost Model
- You are charged for Amazon ES instance hours, Amazon EBS storage (if you choose this option), and standard data transfer fees.
-
Performance
- Performance of Amazon ES depends on multiple factors including instance type, workload, index, number of shards used, read replicas, storage configurations –instance storage or EBS storage (general purpose SSD). Indexes are made up of shards of data which can be distributed on different instances in multiple Availability Zones.
-
Durability and Availability
- You can configure your Amazon ES domains for high availability by enabling the Zone Awareness option either at domain creation time or by modifying a live domain. You can use snapshots to recover your domain with preloaded data or to create a new domain with preloaded data. Snapshots are stored in Amazon S3, which is a secure, durable, highly-scalable object storage.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
- You can add or remove instances, and easily modify Amazon EBS volumes to accommodate data growth. With the default maximum of 20 data nodes allowed per Amazon ES domain, you can allocate about 30 TB of EBS storage to a single domain.
-
Anti-Patterns
- Online transaction processing (OLTP)
- Ad hoc data querying
-
Ideal Usage Patterns
- Interactive ad hoc querying for the data
- To query staging data before loading into Redshift
- Building Interactive Analytical Solutions
-
Cost Model
- It is priced per query, $5 per TB of data scanned, and charges based on the amount of data scanned by the query. You can save from 30% to 90% on your per-query costs and get better performance by compressing, partitioning, and converting your data into columnar formats.
-
Performance
- You can improve the performance of your query by compressing, partitioning, and converting your data into columnar formats.
-
Durability and Availability
- Amazon Athena is highly available and executes queries using compute resources across multiple facilities, automatically routing queries appropriately if a particular facility is unreachable. Athena uses Amazon S3 as its underlying data store, making your data highly available and durable.
-
Scalability and Elasticity
- Athena is serverless, so there is no infrastructure to setup or manage, and you can start analyzing data immediately. Since it is serverless it can scale automatically, as needed
-
Anti-Patterns
- Enterprise Reporting and Business Intelligence Workloads (Use Redshift)
- ETL Workloads (Use EMR/Glue)
- RDBMS
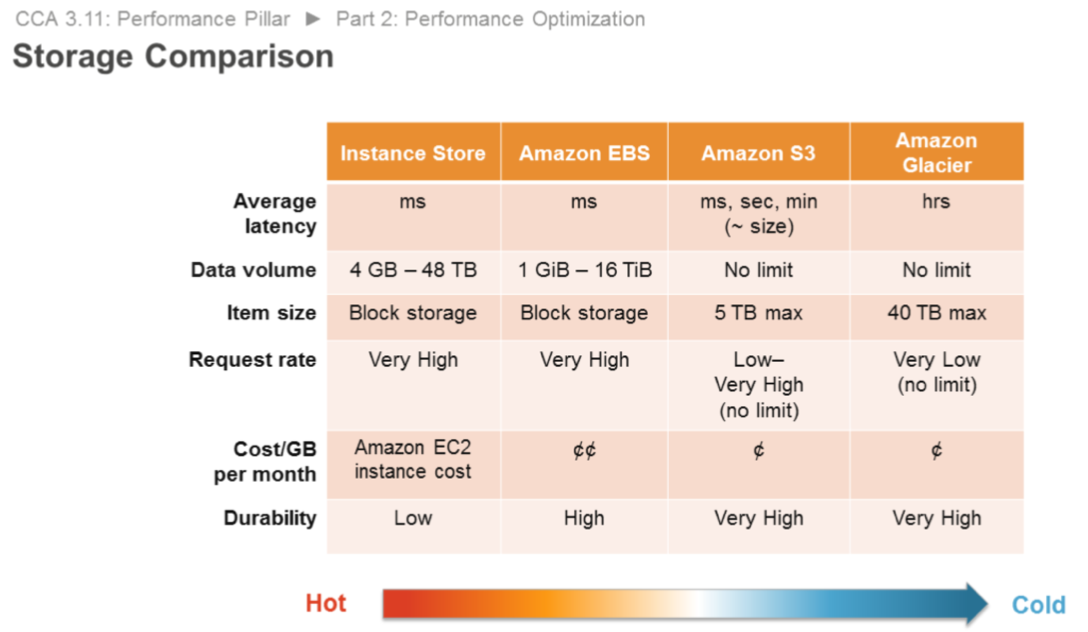
| Service Name | Feature | Performance | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Redshift | Petabyte-scale data warehouse | Fast query performance on a dataset to the GB to EB scale, massively parallel processing (MPP) | PT-scale data warehousing, EB-scale data lake analysis, Infinite Parallelism |
| Athena | An interactive query service (Serverless) | Optimized for high-speed performance with S3, Automatically executes queries in parallel | Query the data (CSV, JSON, ORC, Parquet) from your data lake with high performance |
| EMR | Managed cluster platform that simplifies running big data frameworks (Hadoop, Spark) | Easily scale resources, EMR clusters automatically manage computing resources to meet the performance needs | Massive data processing, ETL job |
| Glue | Fully managed acquisition, transformation, and loading (ETL) service | Glue job performance depends on DPUs | Data catalog, metadata store |
Difference between Redshift and Athena
| Service Name | Setup | Query Engine | Query Speed | Partitioning | Data Formats | UDF | Security | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redshift | Need to initialize and config cluster, and load data | PostgreSQL | Faster than Athena in joins (complex joins and inner query) | Does not support table partitioning (but can define distribution keys) | JSON (simple, nested), CSV, TSV, and Apache logs | Users can create user-defined functions using an SQL SELECT clause or Python | Cluster-level security with support for encryption | High (by cluster & node) |
| Athena | Instant - no need to setup infrastucture (Serverless) | Presto | Faster than Redshift in simple SELECT or WHERE filter | Data partitions on Hive metastore correspond to folders on S3 | CSV, JSON (both simple and nested), Redshift Columnar Storage | Only supports scalar UDFs, built-in Presto functions | Relies on IAM; access to data based on S3 permissions; can read encrypted data from S3 | Low (by query scan) |
Difference between EMR and Glue
| Service Name | Setup | Job Environment | Relation | When to use for ETL job |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMR | Configure cluster | Open-source tools such as Apache Spark, Apache Hive, Apache HBase, Apache Flink, and Presto in Hadoop environment | Use the AWS Glue data catalog as a managed metadata repository for external table metadata for Apache Spark and Apache Hive | Gives you direct access to the Hadoop environment, provides lower-level access, and greater flexibility in using tools other than Spark |
| Glue | No need (Serverless) | Spark | Glue data catalog can stand as metadata to be used by EMR | Operates on top of the Apache Spark environment and simplifies the process of building and maintaining tasks by inferring, evolving, and monitoring your ETL tasks |
What is your data problem?
A multitude of clients often ask for the meaningless question e.g.,
- Redshift vs Athena, which is better?
- Should I use EMR or Glue to implement ETL pipeline?
- Should I replace the relational database with the NoSQL database?
- Should I use serverless architecture?
However, big data analytics whitepaper indicates that there are additional aspects you should consider when selecting the right tools for your specific use case. In general, each analytical workload has certain characteristics and requirements that dictate which tool to use, such as:
- How quickly do you need analytic results: in real time, in seconds, or is an hour a more appropriate time frame?
- How much value will these analytics provide your organization and what budget constraints exist?
- How large is the data and what is its growth rate?
- How is the data structured?
- What integration capabilities do the producers and consumers have?
- How much latency is acceptable between the producers and consumers?
- What is the cost of downtime or how available and durable does the solution need to be?
- Is the analytic workload consistent or elastic?
Big Data !== Big Costs
Each one of these questions helps guide you to the right tool. In some cases, you can simply map your big data analytics workload into one of the services based on a set of requirements. However, in most real-world, big data analytic workloads, there are many different, and sometimes conflicting, characteristics and requirements on the same data set.
Big data doesn’t need to mean “big costs”. So, when designing your applications, it’s important to make sure that your design is cost efficient. If it’s not, relative to the alternatives, then it’s probably not the right design. Another common misconception is that using multiple tool sets to solve a big data problem is more expensive or harder to manage than using one big tool. If you take the same example of two different requirements on the same data set, the real-time request may be low on CPU but high on I/O, while the slower processing request may be very compute intensive.
Decoupling can end up being much less expensive and easier to manage because you can build each tool to exact specifications and not overprovision. With the AWS pay-as-you-go model, this equates to a much better value because you could run the batch analytics in just one hour and therefore only pay for the compute resources for that hour. Also, you may find this approach easier to manage rather than leveraging a single system that tries to meet all of the requirements.
The goal of the client
- To enhance the performance for data processing
- Aggregate the data among all the stores and gain insights into the sales
- Automate the data pipeline
Project content
End-to-end Extract, Load and Transform (ELT) design and implementation of sales transaction data which generate transformed table for Tableau dashboard to use in daily basis
Difficulties and Tricky stuff
- Massive data cleansing job
- A large scale of data aggregation
- Unfathomable business logic
- Indispensable data validation and error handling
- Performance Tuning
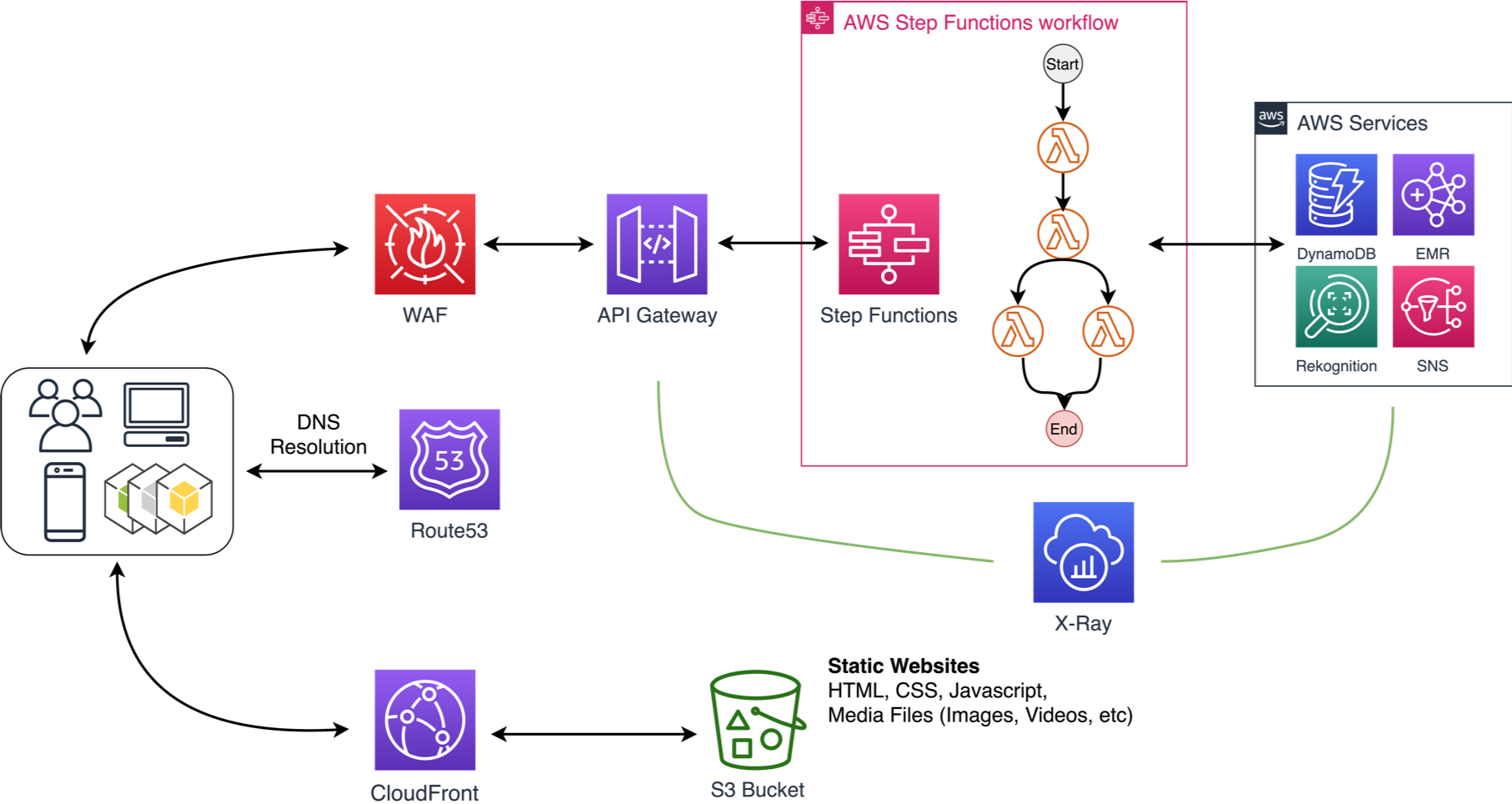
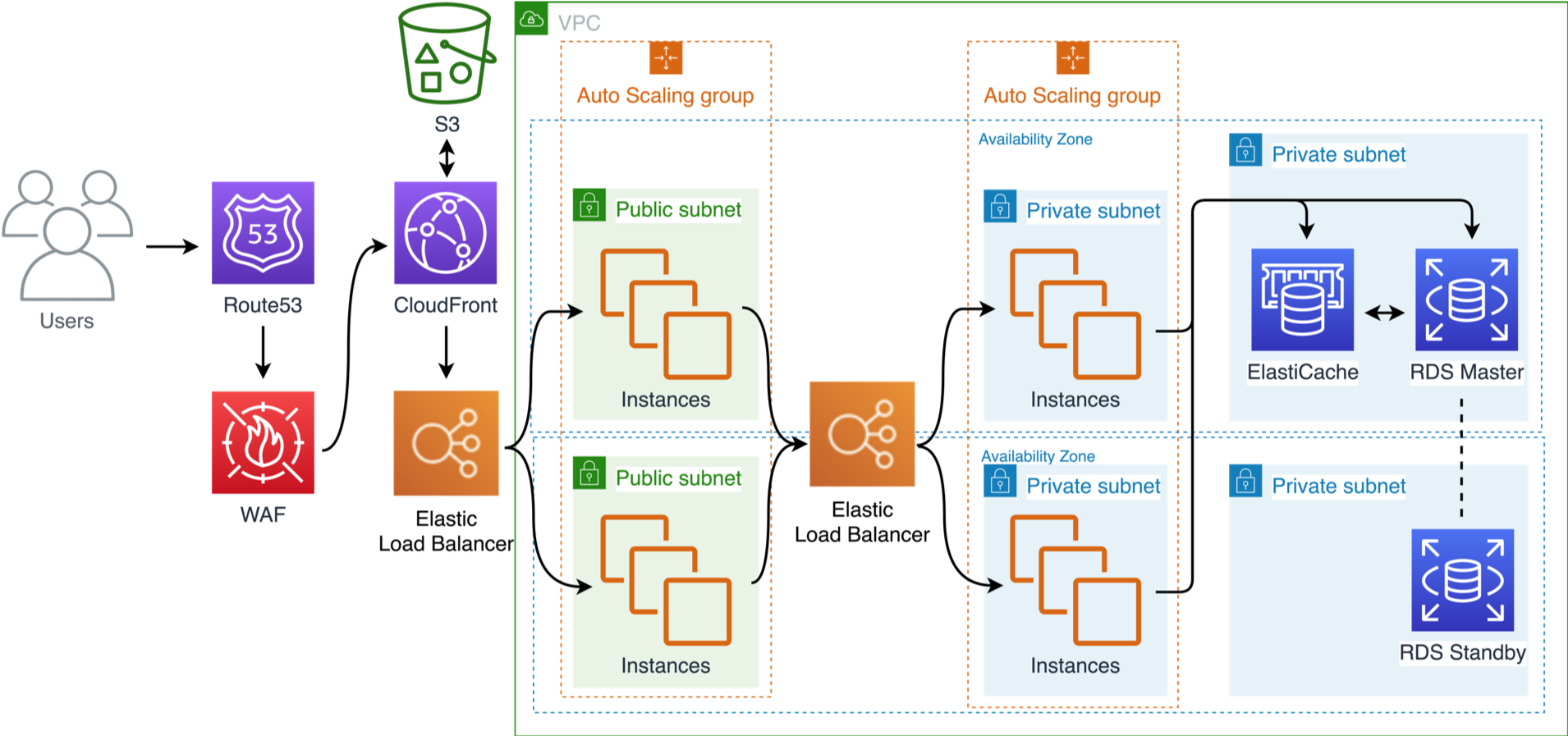
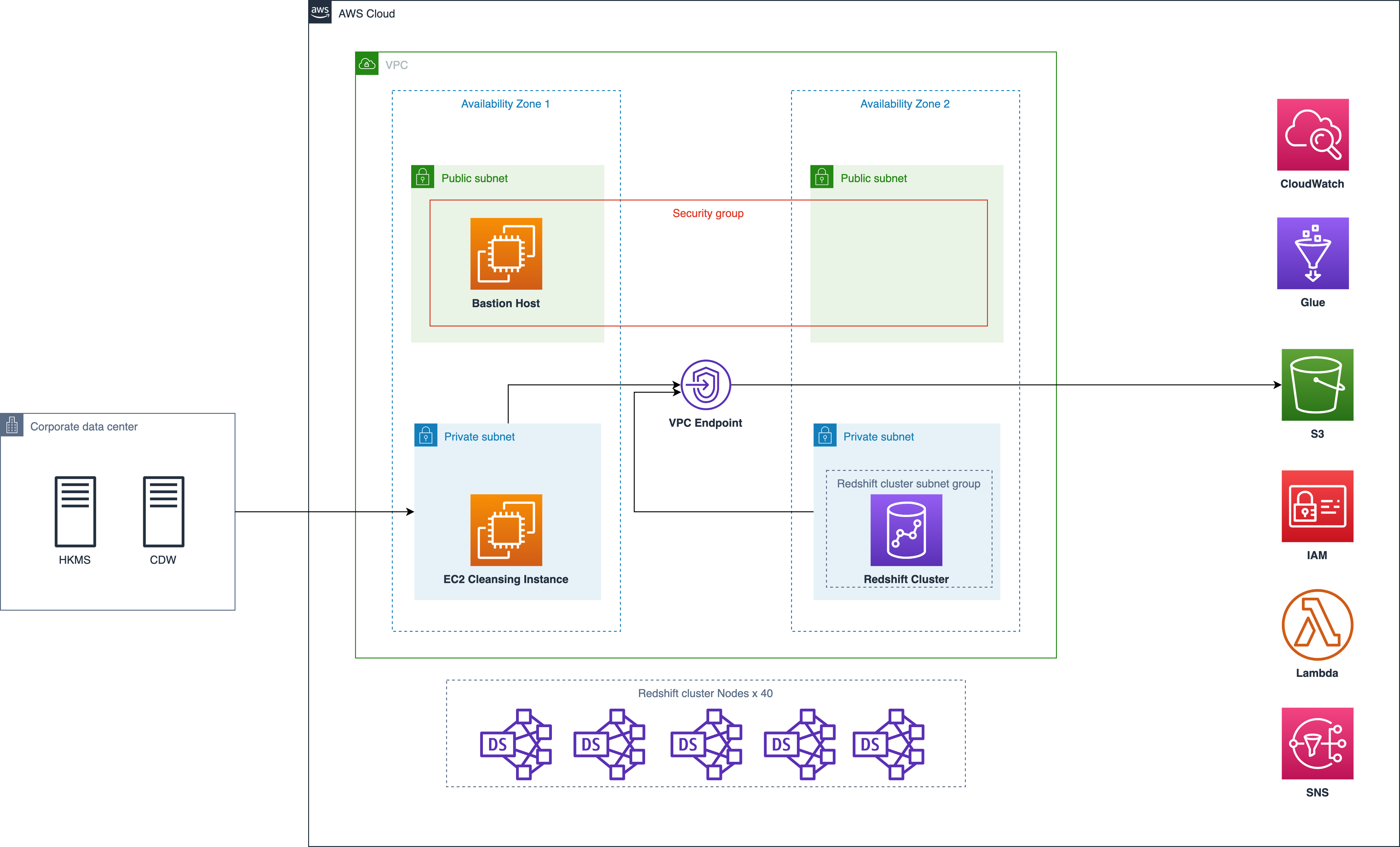
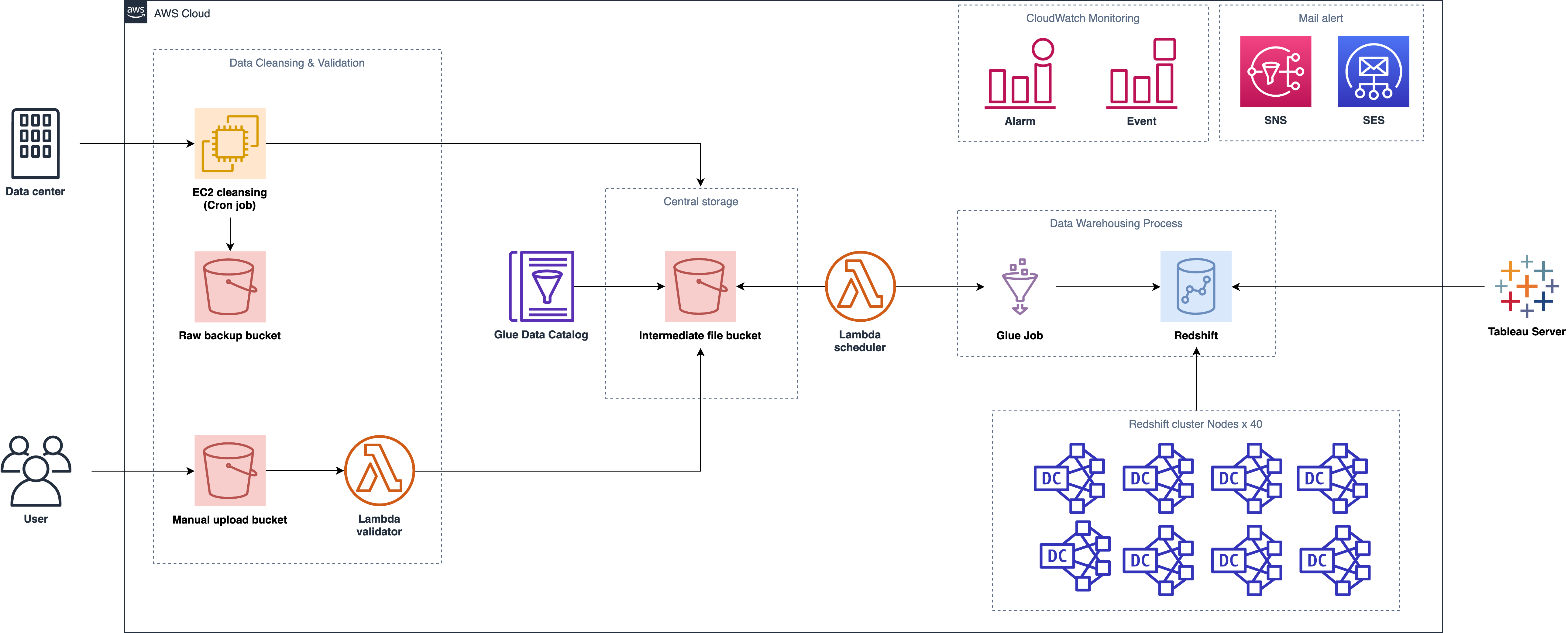
Network Diagram
Whether follow the well-architected concept
- Data can only transfer on AWS? No traffic out of VPC?
- No security issues?
Original Architecture Diagram
Weaken
- Cron schedule and cleansing job may fail due to the downtime of EC2?
- Why do we need Glue job to request Redshift to run queries? (No Spark application in our script)
- 40 node$$$ Red$hift cost a lot and run our ELT task only for 2 hours
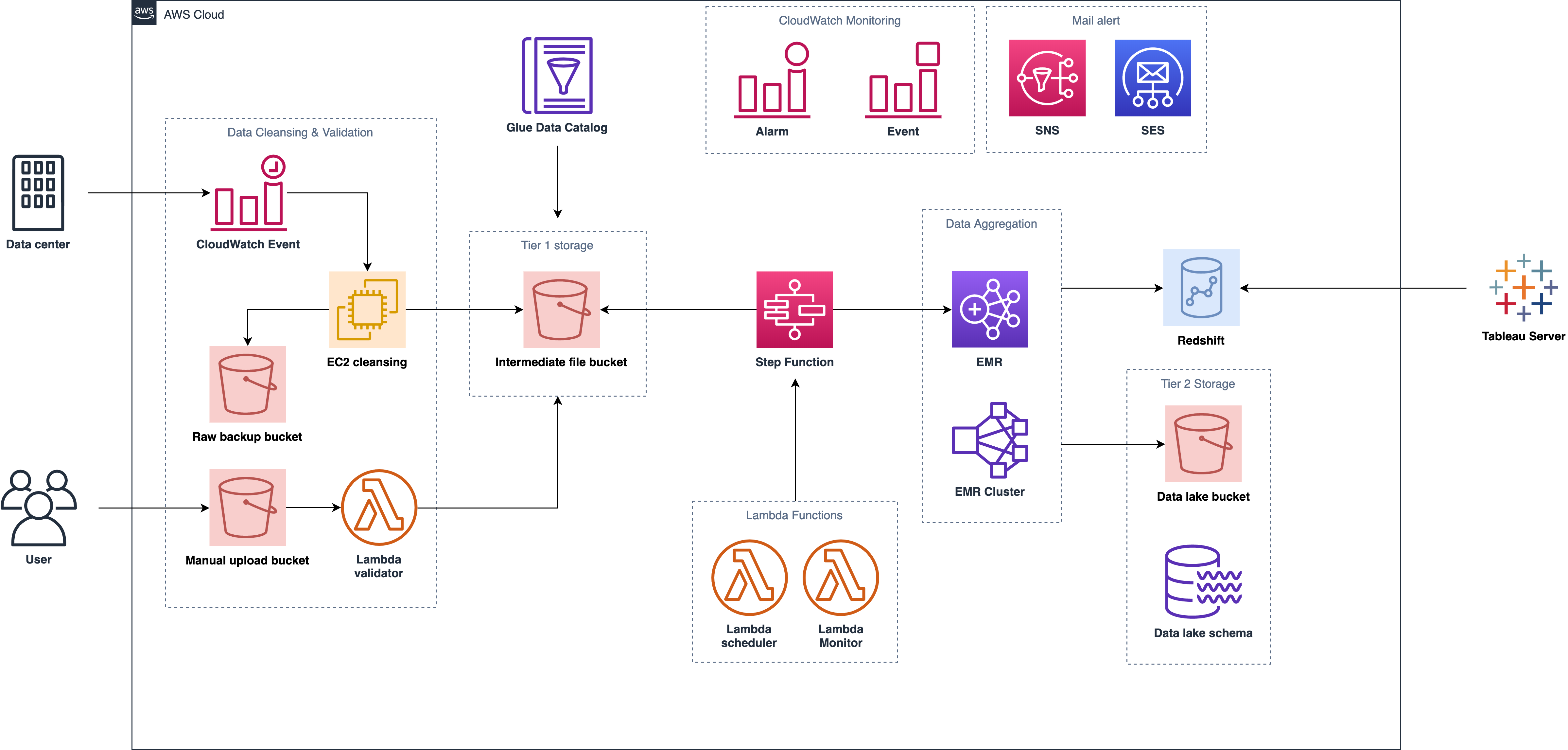
How about this one
- Use CloudWatch event schedule trigger EC2 and setup some failover logic to launch another instance to run the job when EC2 is failed (HA)
- We can use Step Function or Lambda to handle the query task more easily
- We can use EMR (equipped with parallel computing power as well) to transform the data instead of using Redshift
- To handle large scale of data aggregation, Spark can take lots of advantages
The goal of the client
- Aims to track the whole customers’ journey from how they entered the sourcing website, the items they consider and request quotations to finally they exit the website
- High performance on historical data analytics leads decision-makers to take less time to do more accurate strategies
Project content
End to end stream processing and Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) design and implementation of clickstream data transaction which generate transformed table for Tableau dashboard to use in daily basis
Difficulties and Tricky stuff
- Nested JSON with a complex format
- Need to process large historical data and combine with the latest data
- Performance Tuning
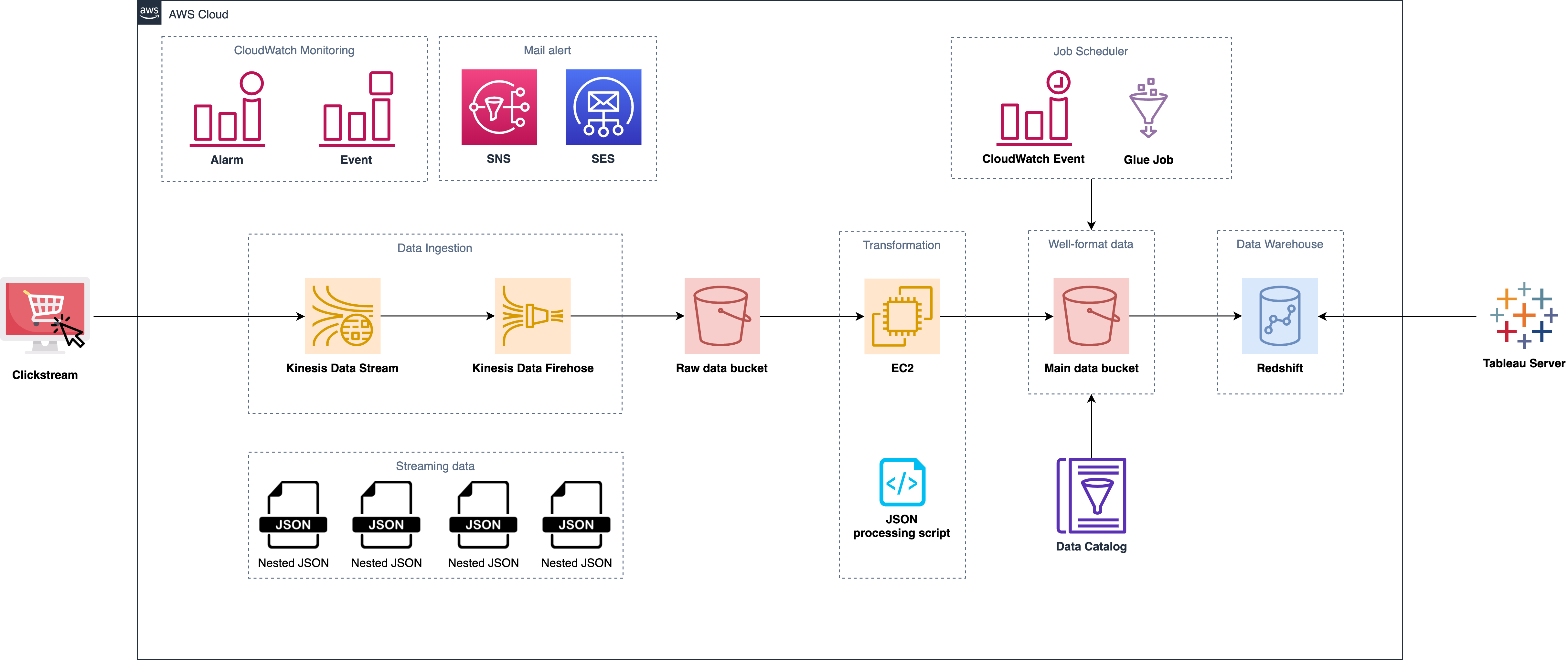
Original Architecture Diagram
Weaken
- If EC2 will run out of the memory because of Nested JSON processing (Poor performance)?
- How do we handle EC2 failover?
- Will EC2 fail easily when processing the large scale of data? (No auto scaling mechanism)
- Why do we need Glue job to request Redshift to run queries? (No Spark application in our script)
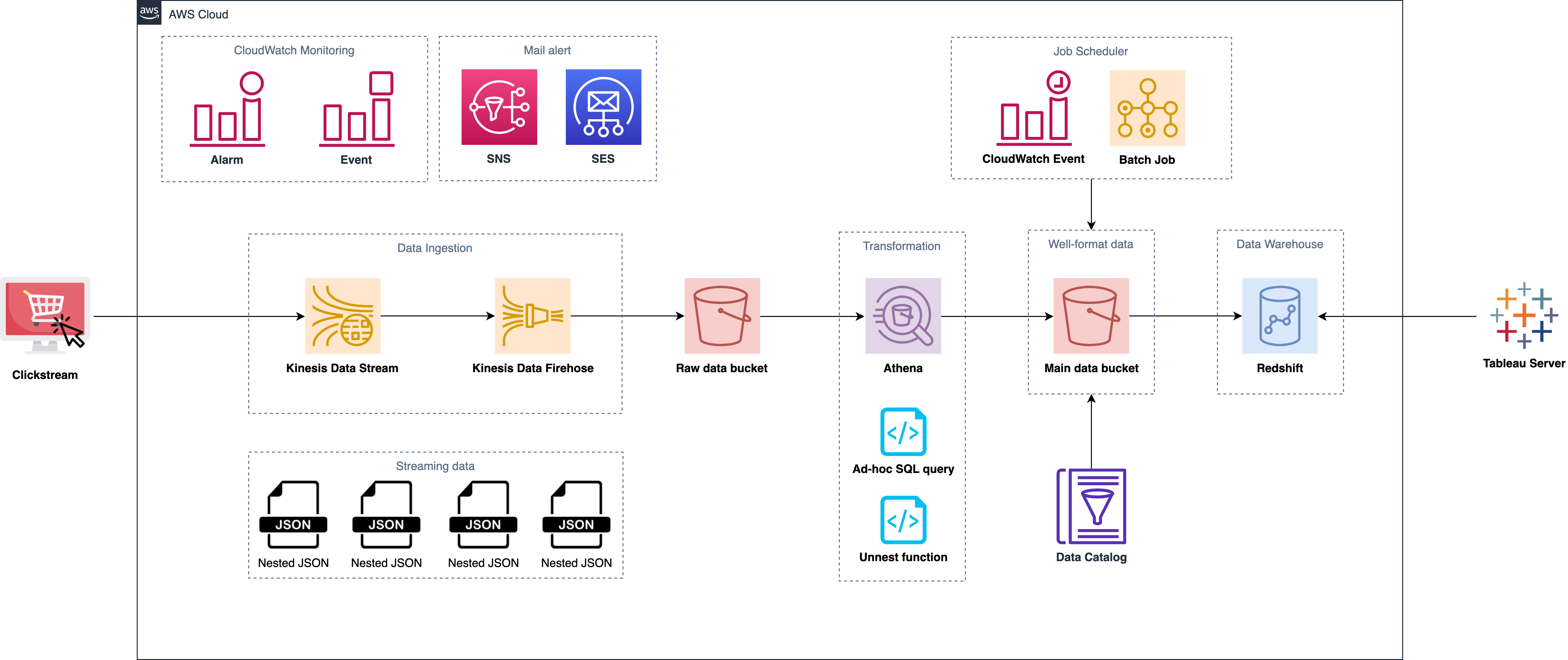
After performance tunning
- Replace EC2 with Athena (Serverless, flexible and scalable)
- Use Athena (Presto query) to transform the nested JSON into columnar data instead of using EC2 to run program
- Replace Glue job with AWS Batch in charge of task scheduling
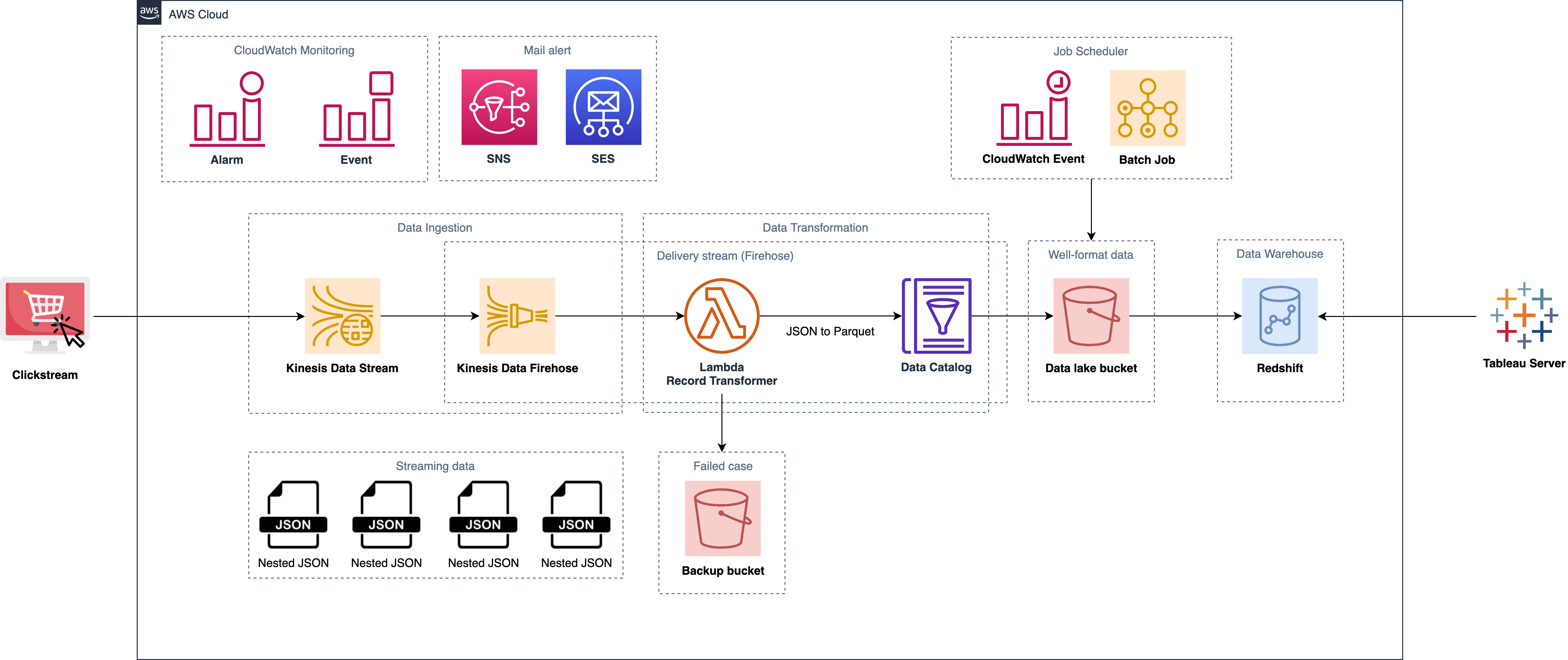
How about this one
- Configure Lambda function into the delivery stream (Stream data transformer)
- Configure Glue data catalog into the delivery stream (Define the schema mapping for the data type) (JSON to Parquet)
- Redefine the bucket type as a backup tier and data lake tier
AWS well-architected framework is always about the trade-offs; however, the fundamental concept of five pillars is paramount imperative. It is comparable to the principal organ of the human
{"CloudFormation": "Infrastructure as code"}
- Level 101 - VPC basic Configuration
- about 10 mins
- Level 201 - Automate container creation on AWS
- about 10 mins - 20 mins
- Level 301 - Data Lake Quick Start Template
- about 40 mins - 50 mins
- Level 401 - Automate Amazon Redshift cluster creation
- about 40 mins - 60 mins
More Labs
Other Resources
- AWS CloudFormation samples
- AWS Quick Start samples
- Advanced CloudFormation design for different solutions
This lab is brought to you by eCloudvalley Data team