The SSH directory ✨
With Wishlist you can have a single entrypoint for multiple SSH endpoints, whether they are Wish apps or not.
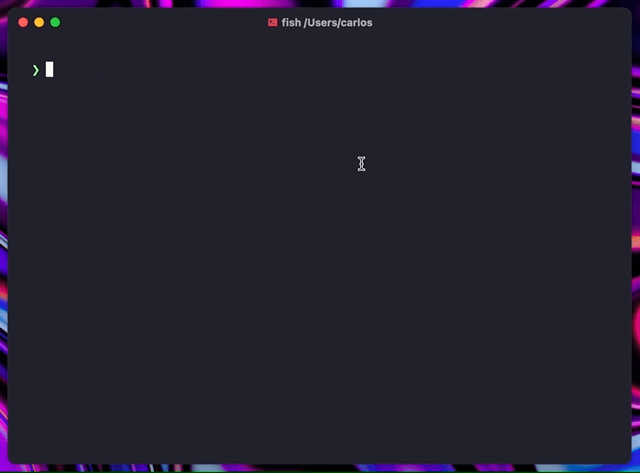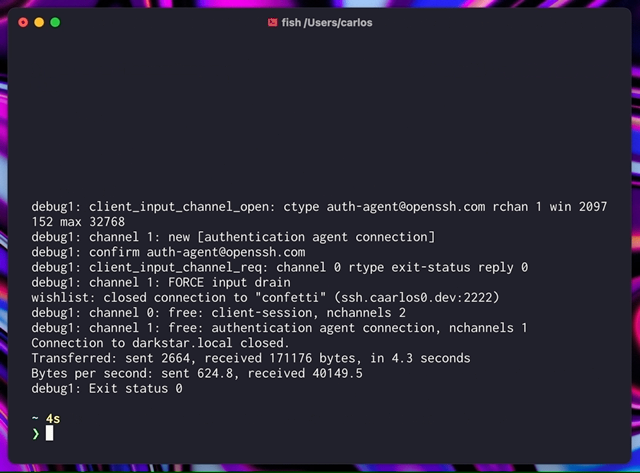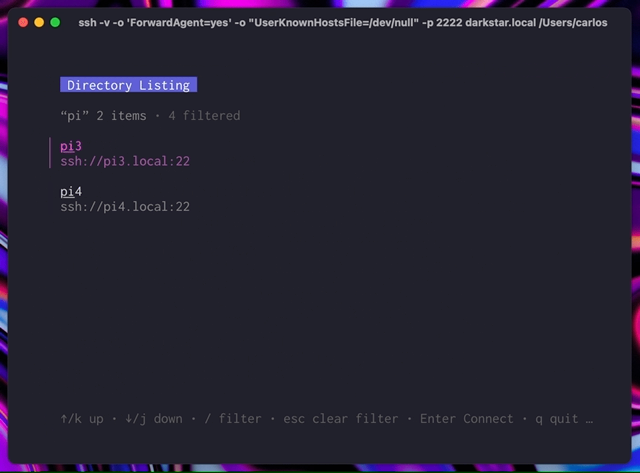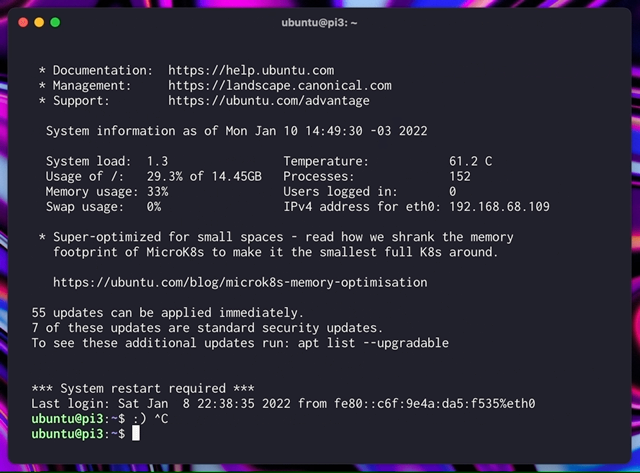
As a server, it can be used to start multiple SSH apps within a single package and list them over SSH. You can list apps provided elsewhere, too.
You can also use the wishlist CLI to list and connect to servers in your ~/.ssh/config or a YAML config file.
If you just want a directory of existing servers, you can use the wishlist CLI and a YAML config file. You can also just run it without any arguments to list the servers in your ~/.ssh/config.
Check the example config file file as well as wishlist --help for details.
Wishlist is also available as a library which allows you to start several apps within the same process.
Check out the _example folder for a working example.
- if ssh agent forwarding is available, it will be used
- otherwise, each session will create a new ed25519 key and use it, in which case your app will be to allow access to any public key
- password-based auth is not supported
eval (ssh-agent)
ssh-add -k # adds all your pubkeys
ssh-add -l # should list the added keys
ssh \
-o 'ForwardAgent=yes' \ # forwards the agent
-o 'UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null' \ # do not add to ~/.ssh/known_hosts, optional
-p 2222 \ # port
foo.bar \ # host
-t list # optional, app nameYou can also add this to your ~/.ssh/config, for instance:
Host wishlist
HostName foo.bar
Port 2222
ForwardAgent yes
UserKnownHostsFile /dev/null
Wishlist will read and store all its information in a .wishlist folder in the current working directory:
- the server keys
- the client keys
- known hosts
- config files
Config files may be provided in either YAML or SSH Config formats:
The config files are tried in the following order:
- the
-configflag in either YAML or SSH config formats .wishlist/config.yaml.wishlist/config.yml$HOME/.ssh/config/etc/ssh/ssh_config
The first one that is loaded and parsed without errors will be used.
This means that if you have your common used hosts in your ~/.ssh/config, you can simply run wishlist and get it running right away.
It also means that if you don't want that, you can pass a path to -config, and it can be either a YAML or a SSH config file.
wishlistmkdir .wishlist
$EDITOR .wishlist/config.yaml # either an YAML or a SSH config
docker run \
-p 2222:22 \
-v $PWD/.wishlist:/.wishlist \
docker.io/charmcli/wishlist:latestThe gif above shows a lot of Maas Lalani’s confeTTY.
We'd love to hear your thoughts on this project. Feel free to drop us a note!
Part of Charm.
Charm热爱开源 • Charm loves open source