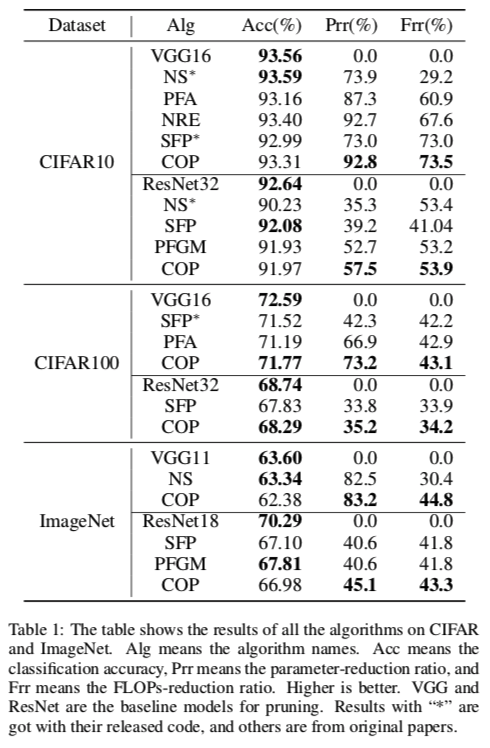
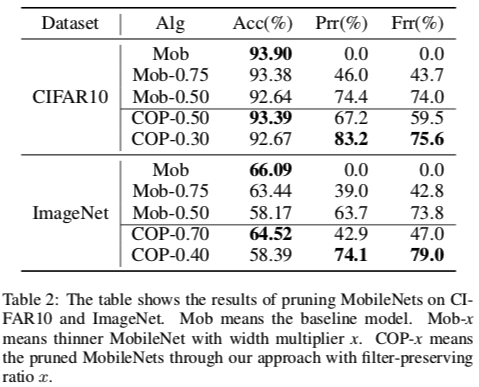
COP is a filter-level pruning algorithm for deep CNNs. It fully considers the correlation among filters and the inequivalence between saving more storage resources and computing resources during the pruning process. This repository is a Tensorflow implementation of our algorithm in IJCAI2019 paper: COP: Customized Deep Model Compression via Regularized Correlation-Based Filter-Level Pruning
Ubuntu 16.04
Python == 3.x
Tensorflow >= 1.10.0
Numpy >= 1.14.1
Older versions of dependencies are to be tested.
You are highly recommended to use our docker image (branch 9.0-cudnn7-devel-ubuntu16.04), which satisfies all the requirements above.
# arguments:
# --train_dir: the directory to save the log file and checkpoint
# --dataset: it could be "cifar10", "cifar100" and "imagenet"
# --data_dir: the directory to read data.
# - For cifar10: The data files are $data_dir/cifar-10-batches-bin/*.bin
# - For cifar100: The data files are $data_dir/cifar-100-binary/*.bin
# - For imagenet: The data files are $data_dir/train/* and $data_dir/validation/*(TFRecord-type)
# --network: it could be "vgg16", "vgg11", "resnet18", "resnet32", "mobilenet_for_cifar" and "mobilenet_for_imagenet"
# --alpha, beta, gamma: they are the coefficients when computing the importance of filts, see the paper for details
# --prune_rate: the ratio of filters to be pruned
## to train a model
mkdir data && cd data && wget https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-binary.tar.gz && tar -zxvf cifar-10-binary.tar.gz
python train.py --train_dir=vgg-cifar10-model --dataset="cifar10" --data_dir="./data" --network="vgg16"
## to prune and finetune a pretrained model
train_dir=vgg-cifar10-model
python auto_prune.py --train_dir=$train_dir --dataset="cifar10" --data_dir="./data" --network="vgg16" --alpha=1.0 --beta=0.0 --gamma=3.0 --prune_rate=0.1Please see train.sh and prune.sh for more usage. The imagenet dataset need to transforming to TFRecord-type first, see extra/README.md for details.
NS (code): Learning Efficient Convolutional Networks through Network Slimming
PFA: Network Compression using Correlation Analysis of Layer Responses
SFP (code): Soft Filter Pruning for Accelerating Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
NRE: Efficient DNN Neuron Pruning by Minimizing Layer-wise Nonlinear Reconstruction Error
PFGM: Filter Pruning via Geometric Median for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Acceleration
COP (Ours): COP: Customized Deep Model Compression via Regularized Correlation-Based Filter-Level Pruning
The following table shows the datasets and models which could be used directly now. You could also use other datasets and models with minor changes. Please see next section for how to experiments with your own datasets and models
| CIFAR10 | CIFAR100 | ImageNet | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VGG11 | N | N | Y |
| VGG16 | Y | Y | N |
| ResNet18 | N | N | Y |
| ResNet32 | Y | Y | N |
| MobileNet | Y | Y | Y |
| ... |
-
You should put your new dataset in
./datasets/, please see./datasets/cifar10.pyfor reference. -
A dataset is obliged to parse the dataset file, do data augmentation, and batch the dataset
-
You need to implement at least 2 interfaces, they are
train_input_fnandtest_input_fn, one for training and the other for testtrain_input_fnshould take 3 parameters, which are "data_directory", "batch_size" and "epochs" respectively, and it should return a tf.data.Dataset-type class. You should also do shuffling, data augmentation and batch internally.test_input_fnshould take 2 parameters, which are "data_directory" and "batch_size", and it should return a tf.data.Dataset-type class too.
-
Import the new dataset to
config.pyand add the new term toparse_net_and_datasetinconfig.py(just mimic what CIFAR10 does).
Totally speaking, you should create a new file datasets/new_dataset.py which contains at least the following 2 functions and tell config.py to parse the dataset correctly.
def train_input_fn(data_dir, batch_size, epochs, **kargs):
"""
Args:
data_dir: the path of the dataset file
batch_size: the batch size of the dataset
epochs: the dataset could provide how many epochs, -1 for infinity
**kargs: any other parameters you want
Return:
dataset: an object of type tf.data.Dataset(or its sub-classes)
"""
pass
def test_input_fn(data_dir, batch_size, **kargs):
"""
Args:
data_dir: the path of the dataset file
batch_size: the batch size of the dataset
**kargs: any other parameters you want
Return:
dataset: an object of type tf.data.Dataset(or its sub-classes)
"""
pass
- You need to create 2 new files to use a new model, one for the definition of the model and the other for the pruning details of the model. Put the first file in
./networks/and the second file in./prune_algorithm/.
- For the definition of the model, you should inherit from the class
ClassificationBase, it has implement some essential functions for you. You only need to implement all abstract methods defined inClassificationBase. See the comments inClassificationBasefor details. (You could see./networks/vgg16for reference). - For the pruning algorithm of the model, you should inherit from the class
PruneBase, you need to implement all abstract methods defined inPruneBaseand overload other methods if needed. See the comments inPruneBasefor details. (You could see./prune_algorithm/prune_vgg16for reference).
- Import the new model to
config.pyand parse the model correctly.
Reference to cite when you use COP in a research paper
@inproceedings{wang2019cop,
title={COP: Customized Deep Model Compression via Regularized Correlation-Based Filter-Level Pruning},
author={Wang, Wenxiao and Fu, Cong and Guo, Jishun and Cai, Deng and He, Xiaofei},
booktitle={International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
volume={2019},
year={2019},
}