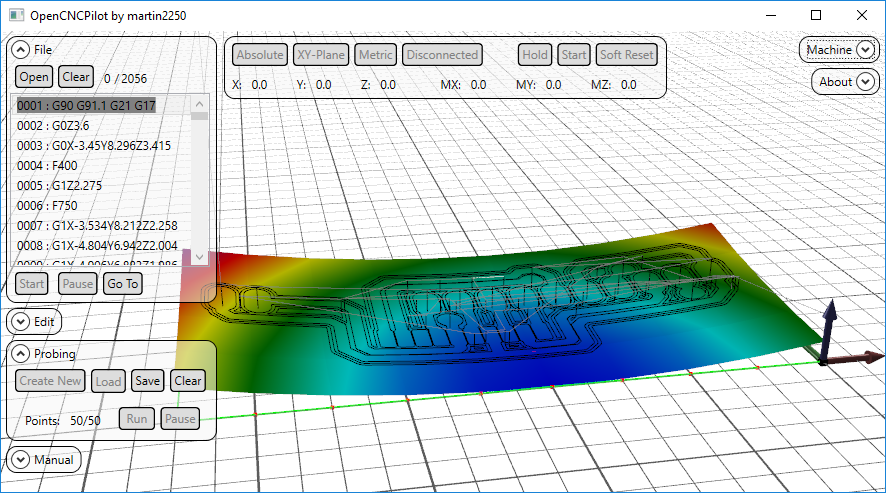
OpenCNCPilot is a GRBL compatible G-Code Sender.
It's main feature is it's ability to probe user-defined areas for warpage and wrap the toolpath around the curved surface. This is especially useful for engraving metal surfaces with V-shaped cutters where any deviation in the Z-direction will result in wider or narrower traces, eg for isolation milling PCBs where warpage would result in broken or shorted traces.
It is written in C# and uses WPF for it's UI. Sadly this means that it will not run under linux as Mono does not support WPF. The 3D viewport is managed with HelixToolkit.
Here is a quick overview on YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XDCu3cgOjCY
Install .NET 4.6, this has been the cause of at least 6 support requests so far.
Go to the Releases section and download the latest binaries (or compile it from source).
Unzip all files to your hard drive and run "OpenCNCPilot.exe"
Make sure to use GRBL version 1.1f (later versions may work but are yet untested). Earlier versions (0.8, 0.9, 1.0) will NOT work! There are no workarounds, so you need to update your controller to use OpenCNCPilot.
Before the first run, you have to select a Serial Port, the selector is hidden in the Settings menu that you can access in the "Machine" tab. Other than that you don't need to modify any settings.
Now you can connect to your machine.
Open gcode or height map files by dragging them into the window, or using the according buttons.
To create a new height map, open the "Probing" tab and click "Create New". You will be asked to enter the dimensions.
Be sure to enter the actual coordinates eg when your toolpath is in the negative X-direction, enter "-50" to "0" instead of "0" to "50". You can also use the "Size from GCode" button to fill in everything automatically.
You will see a preview of the area and the individual points in the main window
To probe the area, set up your work coordinate system by going to your selected origin and using the "Zero (G10)" in the "Manual" tab, remember that this doesn't actually send the line, you can review it must send it manually. You can also use G92, but remember that G92 isn't permanent and will be lost after a reset.
Make sure to connect A5 of your Arduino to the tool and GND to your surface, and hit "Run".
OpenCNCPilot will now probe your board at the locations marked with a red dot and build the map from that data.
Once it's done probing the surface, hit the "Apply HeightMap" button in the "Edit" tab. Now you can run the code with the "Start" button in the "File" tab.
The 1.5 update adds an interpreter for mathematical expressions to use with manual send and macros. To use it, enter your expression in parentheses, like so: "G0 X(2*MX - 1)".
Available variables are:
- MX, MY, MZ: machine position; WX, WY, WZ: work position
- PMX, PMY, PMZ, PWX, PWY, PWZ: last probed position in machine/work coordinates
- TLO: current tool length offset
the parentheses will be replaced with whatever the expression evaluates to. My Calculator library is used to evaluate the expressions.
The probing data is stored in an array of (double precision) floats, the intermediate values are obtained via bilinear interpolation between the four nearest points. All GCode commands whose length exceeds the GridSize are split up into sections smaller than the GridSize. This includes arcs.
In the input files, arcs can be defined via center (IJ) coordinates or by a radius (R). The output file will always use IJ notation, absolute coordinates and metric units. Both relative coordinates and imperial units are supported, but are converted to the aforementioned format.
- G0, G1 linear motion
- G2, G3 arc motion
- G4 dwell
- G20, G21 units
- G90, G91 distance mode
- S spindle speed
- M M-codes
Since this project did get some attention, I'll include a donation button. Getting this application to a point where it's 'production-ready' took many days of non-stop work before and during the fist three semesters of my physics studies.
Please note that my programs will always be (ad-)free