Authors: Ankur Sikarwar and Mengmi Zhang
This work has been accepted to the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023).
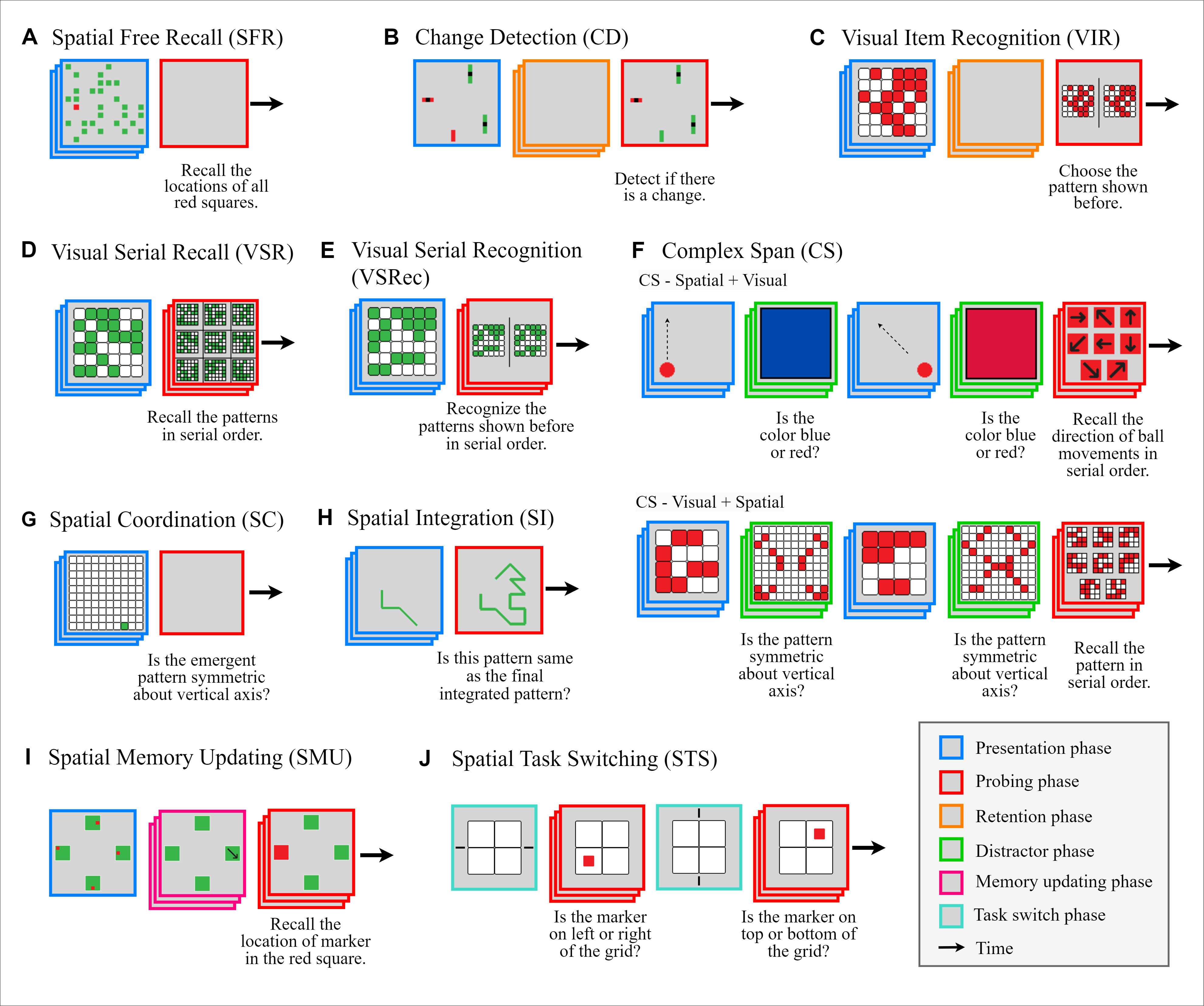
Working memory (WM), a fundamental cognitive process facilitating the temporary storage, integration, manipulation, and retrieval of information, plays a vital role in reasoning and decision-making tasks. Robust benchmark datasets that capture the multifaceted nature of WM are crucial for the effective development and evaluation of AI WM models. Here, we introduce a comprehensive Working Memory (WorM) benchmark dataset for this purpose. WorM comprises 10 tasks and a total of 1 million trials, assessing 4 functionalities, 3 domains, and 11 behavioral and neural characteristics of WM.
Download the WorM dataset from HERE
Extract the dataset to WorM/wm_bench_data/
wm_bench_data contains raw stimulus and metadata for all trials for all working memory (WM) tasks.
- tested with python 3.8 and cuda 11.3
- dependencies can be installed using
WorM/requirements.txt
Download pre-trained models from HERE
We provide pre-trained models for rnn-96, rnn-256, rnn-1024, gru-96, gru-256, gru-1024, lstm-96, lstm-256, lstm-1024, trf-96, trf-256, and trf-1024.
After extracting the WorM dataset, run the following command from WorM/ directory to jointly train and test on all working memory (WM) tasks.
python -m src.main
Refer below for possible arguments and modify them in src/args.py as per your needs:
--data_folder(default:./wm_bench_data/): Path to the WorM dataset folder.--log_folder(default:./log/): Path to the folder for saving logs.--model_folder(default:./model/): Path to the folder for saving models.--output_folder(default:./output/): Path to the folder for saving outputs.
--stage(default:Train): Execution stage.--num_tasks(default:14): Number of tasks.--gen_test(default:0): Flag to generate test data.
--resume(default:0): Flag to resume training from a checkpoint.--resume_epoch(default:0): Epoch to resume training from.--resume_run_name(default:''): Name of the run to resume.--resume_wandb_id(default:''): Weights and Biases ID for resuming.
--img_size(default:96): Input image size for generating dataset.--rs_img_size(default:32): Resized image size to be used in training.--num_input_channels(default:3): Number of input image channels.--max_seq_len(default:20): Maximum trial length.--task_embedding(default:Learned): Task embedding type.--task_embedding_given(default:All_TS): Task embedding type.--use_cnn(default:1): Flag to use CNN encoder.--mem_architecture(default:GRU): Memory architecture.--mem_input_size(default:512): Memory input size.--mem_hidden_size(default:96): Memory hidden size.--mem_num_layers(default:1): Number of memory layers.--trf_dim_ff(default:2048): Transformer feed-forward dimension.--projection(default:linear): Projection layer type.--classifier(default:linear): Classifier layer type.
--lr(default:0.0001): Learning rate for training.--batch_size(default:10): Batch size for training (Number of trials sampled from each task in one batch).--num_epochs(default:200): Number of training epochs.--samples_per_task(default:96000): Samples per task.
--gpu(default:0): GPU index to use (if available).--seed(default:86): Random seed for reproducibility.--num_workers(default:4): Number of data loading workers.--use_extracted_feats(default:0): Flag to use extracted features.--test_interval(default:5): Interval between testing stages.
To generate your own version of data for a specific task with different conditions, navigate to WorM/ and use the Dataset class for the specific task. The dataset class for each task contains a docstring for a detailed explanation of the arguments.
Following shows a docstring example for Spatial Memory Updating (SMU) task:
class Spatial_Memory_Updating_Dataset(Dataset):
"""Dataset for the Spatial Memory Updating task.
Args:
data_path (str): Path to the data folder.
max_seq_len (int, optional): Maximum trial length.
grid_size (int, optional): Size of the grid within the green square.
set_size_options (list, optional): Set sizes (Number of green squares).
presentation_time_options (list, optional): Number of presentation time steps.
num_updates_options (list, optional): Number of memory updates in each trial.
held_out_set_sizes (list, optional): Held-out set sizes.
held_out_num_updates (list, optional): Held-out number of memory updates.
gen_random_trials (bool, optional): Generate random trials.
num_samples (int, optional): Total samples to generate (includes all splits).
img_size (int, optional): Input image size (for generation).
rs_img_size (int, optional): Resized image size (for training).
write (bool, optional): Write data to disk.
split (str, optional): Split type ('train', 'test', 'gen_test').
"""For example, in WorM/ directory, one can use a few python lines to generate and load your own dataset for any task. The below line of code shows an example of generating and loading dataset for the Visual Item Recognition (VIR) task.
from src.data.dataset import Visual_Item_Recognition_Dataset
# Generates the dataset for the VIR task with given parameters and loads the training split
VIR_Task_TrainVal_Dataset = Visual_Item_Recognition_Dataset(data_path='./your-folder-choice',
max_seq_len=20,
grid_size=6,
list_length_options=[4, 6, 8, 10],
distractor_difference_options=[4],
ri_options=[0, 2, 4, 5, 6],
gen_random_trials=True,
num_samples=96000,
img_size=96,
rs_img_size=32,
write=True,
split='train')
# Loads the testing split of the generated dataset
VIR_Task_Test_Dataset = Visual_Item_Recognition_Dataset(data_path='./your-folder-choice',
max_seq_len=20,
rs_img_size=32,
split='test')In this repo, we also provide multiple notebooks for data visualization, evaluation, and neural analysis. Here is a non-comprehensive list of them, with their purposes,
viz_data.ipynb: visualize trials of different WM tasks.bench_cd_task.ipynb: evaluation and analysis of CD task.bench_cs_task.ipynb: evaluation and analysis of CS task.bench_smu_task.ipynb: evaluation and analysis of SMU task.bench_vir_task.ipynb: evaluation and analysis of VIR task.bench_vsr_task.ipynb: evaluation and analysis of VSR task.bench_vsrec_task.ipynb: evaluation and analysis of VSRec task.bench_sts_task.ipynb: evaluation and neural analysis on STS task.bench_neural_analysis.ipynb: neural analysis of computational models.