The 300 lines of code (Tensorflow 2) completely replicates the Transformer model and is used in neural machine translation tasks and chat bots.
300行代码(Tensorflow 2)完整复现了Transformer模型,并且应用在神经机器翻译任务和聊天机器人上。
python 3.6 tensorflow 2 tensorflow-datasets
cd machine_translation_application
python train_translation_model.py
python inference_translation_model.py
cd machine_translation_application
python train_chatbot.py
python inference_by_chatbot.py
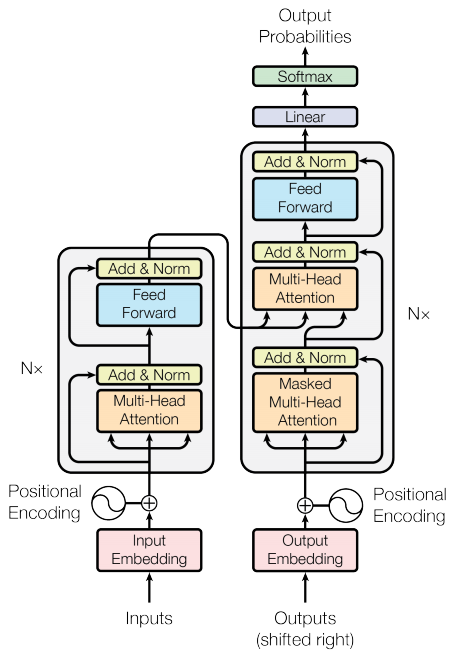
The transformer model follows the same general pattern as a standard sequence to sequence with attention model.
- The input sentence is passed through
Nencoder layers that generates an output for each word/token in the sequence. - The decoder attends on the encoder's output and its own input (self-attention) to predict the next word.
See Attention is All You Need for more details!
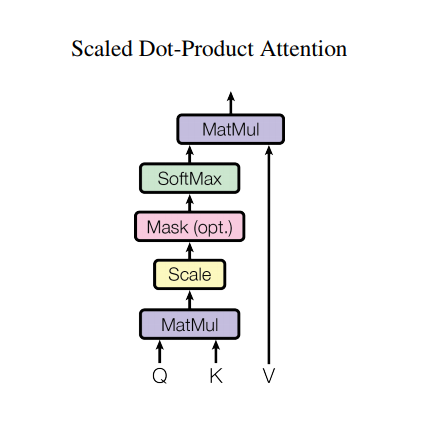
The attention function used by the transformer takes three inputs: Q (query), K (key), V (value). The equation used to calculate the attention weights is:
The dot-product attention is scaled by a factor of square root of the depth. This is done because for large values of depth, the dot product grows large in magnitude pushing the softmax function where it has small gradients resulting in a very hard softmax.
For example, consider that Q and K have a mean of 0 and variance of 1. Their matrix multiplication will have a mean of 0 and variance of dk. Hence, square root of dk is used for scaling (and not any other number) because the matmul of Q and K should have a mean of 0 and variance of 1, so that we get a gentler softmax.
The mask is multiplied with -1e9 (close to negative infinity). This is done because the mask is summed with the scaled matrix multiplication of Q and K and is applied immediately before a softmax. The goal is to zero out these cells, and large negative inputs to softmax are near zero in the output.
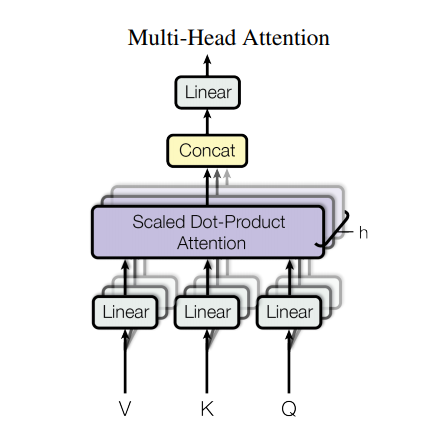
Multi-head attention consists of four parts:
- Linear layers and split into heads.
- Scaled dot-product attention.
- Concatenation of heads.
- Final linear layer.
Each multi-head attention block gets three inputs; Q (query), K (key), V (value). These are put through linear (Dense) layers and split up into multiple heads.
The scaled_dot_product_attention defined above is applied to each head (broadcasted for efficiency). An appropriate mask must be used in the attention step. The attention output for each head is then concatenated (using tf.transpose, and tf.reshape) and put through a final Dense layer.
Instead of one single attention head, Q, K, and V are split into multiple heads because it allows the model to jointly attend to information at different positions from different representational spaces. After the split each head has a reduced dimensionality, so the total computation cost is the same as a single head attention with full dimensionality.
- 理解Transformer原理 Attention is All You Need
- Transformer 代码实现及应用