Official code repository for ICLR'24 paper Large Language Models to Enhanbe Bayesian Optimization.
[Paper link]
Authors: Tennison Liu*, Nicolás Astorga*, Nabeel Seedat, Mihaela van der Schaar (* equal contribution)
Bayesian optimization (BO) is a powerful approach for optimizing complex and expensive-to-evaluate black-box functions. Its importance is underscored in many applications, notably including hyperparameter tuning, but its efficacy depends on efficiently balancing exploration and exploitation. While there has been substantial progress in BO methods, striking this balance still remains a delicate process. In this light, we present LLAMBO, a novel approach that integrates the capabilities of large language models (LLM) within BO. At a high level, we frame the BO problem in natural language terms, enabling LLMs to iteratively propose promising solutions conditioned on historical evaluations. More specifically, we explore how combining contextual understanding, few-shot learning proficiency, and domain knowledge of LLMs can enhance various components of model-based BO. Our findings illustrate that LLAMBO is effective at zero-shot warmstarting, and improves surrogate modeling and candidate sampling, especially in the early stages of search when observations are sparse. Our approach is performed in context and does not require LLM finetuning. Additionally, it is modular by design, allowing individual components to be integrated into existing BO frameworks, or function cohesively as an end-to-end method. We empirically validate LLAMBO's efficacy on the problem of hyperparameter tuning, highlighting strong empirical performance across a range of diverse benchmarks, proprietary, and synthetic tasks.
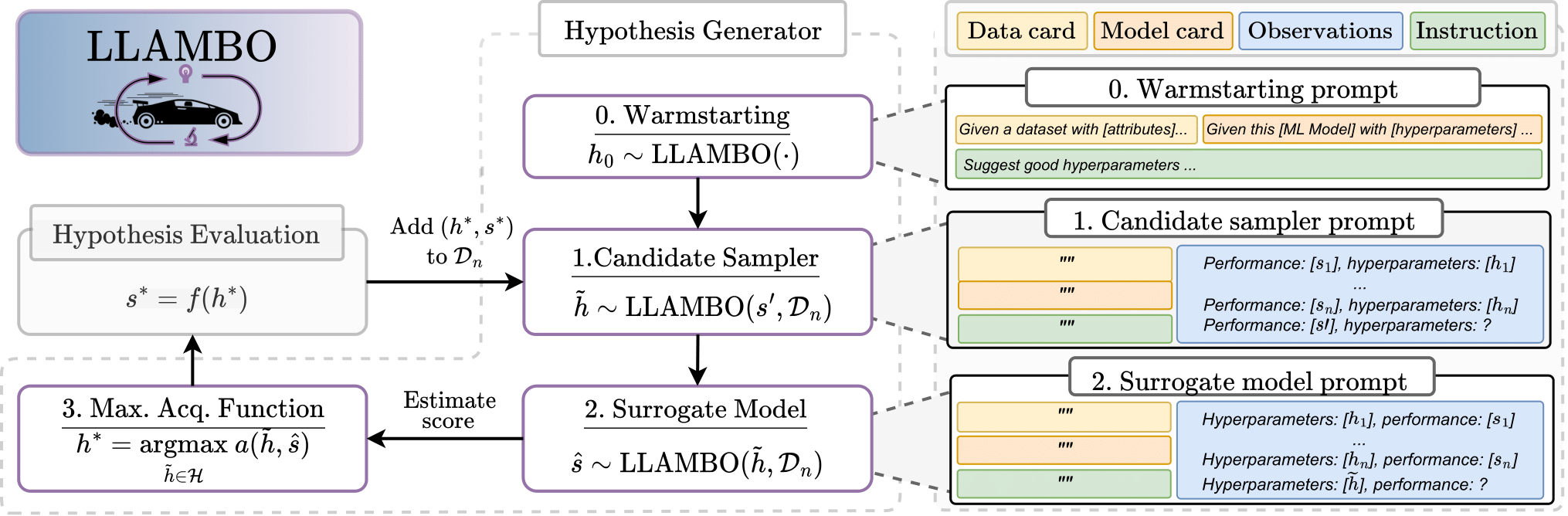 Overview of LLAMBO. In order: LLAMBO can initialize BO through (1) zero-shot warmstarting, (2) efficiently sample candidate points from high-potential regions given past observations and problem description, and (3) evaluate these candidate points via a surrogate model.
Overview of LLAMBO. In order: LLAMBO can initialize BO through (1) zero-shot warmstarting, (2) efficiently sample candidate points from high-potential regions given past observations and problem description, and (3) evaluate these candidate points via a surrogate model.
- If using OpenAI, set up environment variables:
echo "export OPENAI_API_KEY={api_key}" >> ~/.zshrc
echo "export OPENAI_API_VERSION={api_version}" >> ~/.zshrc
## Note: these might be optional
echo "export OPENAI_API_BASE={api_base}" >> ~/.zshrc
echo "export OPENAI_API_TYPE={api_type}" >> ~/.zshrc
In our experiments, we used gpt-turbo-3.5 for all modules and gpt-turbo-3.5-instruct for the generative surrogate model (Note: these models might require separate set of credentials).
- Update the shell with the new variables:
source ~/.zshrc
- Confirm that environmental variables are set:
echo $OPENAI_API_KEY
echo $OPENAI_API_VERSION
echo $OPENAI_API_BASE
echo $OPENAI_API_TYPE
- Set up Conda environment:
git clone https://github.com/tennisonliu/llambo.git
conda create -n llambo python=3.8.8
conda install jupyter
conda activate llambo
## Note: {project_dir} is the path to where to your local directory
export PROJECT_DIR={project_dir}
conda env config vars set PYTHONPATH=${PYTHONPATH}:${PROJECT_DIR}
conda env config vars set PROJECT_DIR=${PROJECT_DIR}
conda deactivate
conda activate llambo
- Install requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt
To reproduce results, execute any of the shell experimental shell scripts:
- To run Bayesmark benchmark:
run_bayesmark_public.sh - To run HPOBench benchmark:
run_hpo_bench.sh - To evaluate the surrogate model:
run_evaluate_dis_sm.sh(discriminative SM) orrun_evaluate_gen_sm.sh(generative SM) - To evaluate candidate point sampler:
run_evaluate_sampling.sh - To execute prompt ablations:
run_prompt_ablation.sh
Note: please follow HPOBench instructions to download data files for HPOBench experiments.
Refer to tutorial.ipynb for brief tutorial on how to run LLAMBO on your own BO tasks.
If our paper or code helped you in your own research, please cite our work as:
@inproceedings{
liu2024large,
title={Large Language Models to Enhance Bayesian Optimization},
author={Tennison Liu and Nicol{\'a}s Astorga and Nabeel Seedat and Mihaela van der Schaar},
booktitle={The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=OOxotBmGol}
}