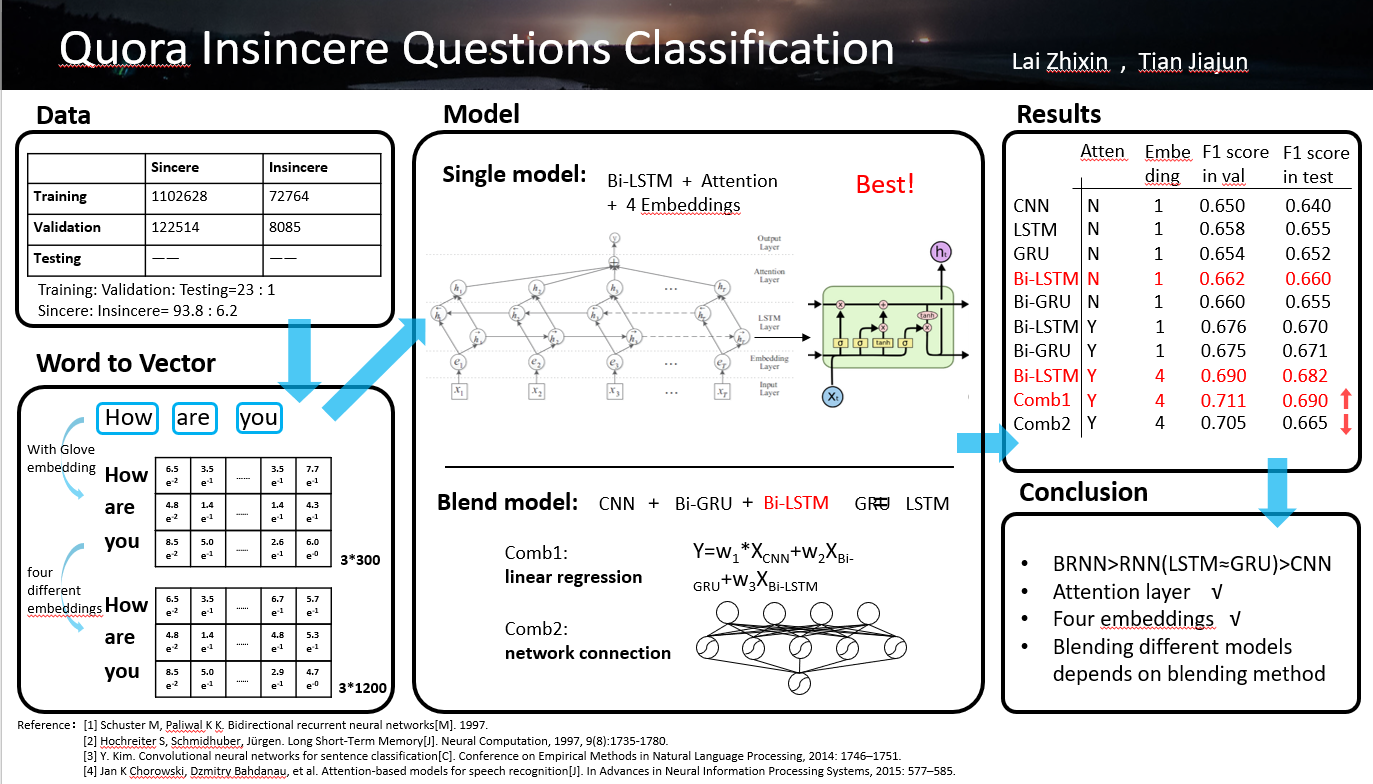
In kaggle, Quora Insincere Questions Classification aims at labeling insincere questions, which are founded upon false premises or intend to make a statement rather than look for helpful answers. It is a sentence-level classification task.
In the competition, 1306122 training data and 56370 test data are provided. In training set, 6.2% of the training data are insincere questions and the rest are sincere questions. We divide training set into two parts, 90% for the and training 10% for the validation. We program from the aspects of sentence preprocess, transmission from word to vector, training model and prediction. We apply different models and compare the results of different models, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM), Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU), and then we add the Bidirectional way in Long Short-Term Memory Networks (LSTM) and Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU). We also blend different models together with the methods of Linear Regression and feedforward neural network. Besides, in order to improve accuracy, we introduce Attention Mechanism and combine four embeddings in the process of transforming world to vector. We selected the best model and got the public F1 score 0:695 with the highest score of 0:711. Finally, we draw some conclusions about comparison of different models and effectiveness of attention mechanism and embeddings combination.
[CNN] CNN utilizes layers with convolving filters that are applied to capture local features. Originally invented
for computer vision, CNN models have subsequently been shown to be effective for NLP and have achieved excel-
lent results in many traditional NLP tasks. Yoon Kims paper successfully applied CNN to Sentence Classification
[1]. We follow the CNN architecture of Kim. We connect two Convolutional layers with and 32 feature maps, one
Max-over-time pooling layer and two fully connected layrs with dropout. We test our model on testing set and
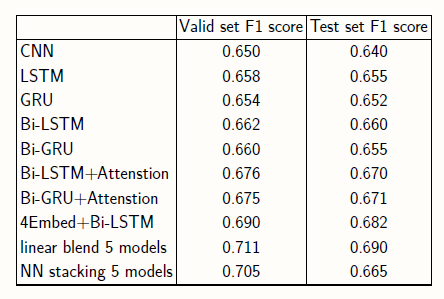
get public score of 0.640.
[LSTM] LSTM is an efficient gradient-based method with the application of multiplicative gate units [2]. We
train a LSTM based model, including two 64-units LSTM layers with dropout and two fully connected layers with
dropout. The public score based on this model is 0.655.
[GRU] Proposed by K.Cho, GRU only has two gates and has fewer parameters than LSTM [3], and thus it is eas-
ier to train. The GRU based model includes two 64-units GRU layers with dropout and two fully connected layers
with dropout. The public score based on this model is 0.652.
[Bi-LSTM] Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Networks(Bi-LSTM) can be trained without the limita-
tion of using input information just up to a preset future frame by training it simultaneously in positive and nega-
tive time direction [4].We train a Bi-LSTM based model, including two 64-units LSTM layers with dropout and two
fully connected layers with dropout, and get the public score of 0.660.
[Bi-GRU] The principle of Bidirectional GRU(Bi-GRU) is the same as Bi-LSTM. We subsitute the LSTM layers
in Bi-LSTM based model with GRU layers and get the public score of 0.655.
Without Attention Mechanism, machine reads the whole sentence equally and compresses all information into a fixlength vector. The idea of Attention Mechanism enalbles machine to capture keywords and reweight hidden layer[5]. Here, we combine the Bi-LSTM and Bi-GRU with attension layer seperately and get the public score of 0.670 and 0.671 respectively.
Embedding is used to transform word to vector. Google-News, Glove, Paragram and Wiki are provided in the kernel of Kaggle. Among those four embeddings, we focus on Glove. Besides, We try to combine four embeddings to generate 1200 dimensional vector by connecting 4 vectors of 300 dimensions. The public scores of Bi-LSTM with attention layer and four embeddings is 0.682.
We blend different models together, including CNN, Bi- LSTM with attension layer, Bi-LSTM with average pooling and maxpooling, Bi-GRU with attension layer, Bi-GRU with average pooling and maxpooling. We use two methods of blending,the linear blend and neural network stacking. We use the outputs of five models to retrain a linear regression. The public scores of linear blend is 0.690. We also use outputs of five models to train a feedforward neural network with one 64-units hidden layer. However, the public scores of neural network stacking is 0.665 and overfitting problem may lead to the bad performance.
CNN has achieved excellent result in the project, but RNN performs better because RNN could capture long-distance dependency information. In the project, the performance of LSTM is close to the performance of GRU. Bi-GRU and Bi-LSTM have better performance than GRU and LSTM respectively, because BRNN accomplishes training simultaneously in both positive and negative time directions.
From the results of Bi-LSTM and Bi-GRU with attention mechanism, attention layer helps improve the model’s performance, because it would reweight the hidden layer and emphasize the important information
From the results of Bi-LSTM with glove embedding and Bi-LSTM with four embeddings, the input vector of 1200 dimensions contains more information than input vector of 300 dimensions and thus Bi-LSTM with four embeddings gets higher score.
Different models on the same data set have different deviations and blending different models might neutralize different deviations. In the project, blending different models by linear blend has better performance than single model, while blending different models with feedforward neural network does not because of overfitting.
[1] Y. Kim. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification[C]. Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2014: 17461751.
[2] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber, Jürgen. Long Short-Term Memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8):1735-1780.
[3] Cho K, Van Merrienboer B, et al. Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation[J]. Computer Science, 2014.
[4] Schuster M, Paliwal K K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks[M]. 1997.
[5] Jan K Chorowski, Dzmitry Bahdanau, et al. Attention-based models for speech recognition[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015: 577585.