This repository contains the code and results of simulating live anomaly detection performed on the AURSAD dataset. To view and experiment with different settings of the simulation, an interactive web app is provided.
The project emulates the workings of a system for x number of cycles, where every cycle consists of reading a new sample to the buffer, making a prediction and then appending the results to be summarily saved at the end of the simulation. The simulation measures the accuracy of the predictions, as well as the run times for each cycle. The experiments are performed for the binary version of the dataset, which means that the operation can be normal or anomalous, without distinction between the different types of anomalies. The data is sampled at 50 Hz.
Based on these results, the web app allows experimenting with applying different methods to create the optimal system response accuracy.
The solution has been intended for and tested on Ubuntu & Windows 10. For training new models, a Nvidia GPU with installed and properly configured cuDNN drivers is recommended. More on how to install those drivers can be found here.
- Install Anaconda from here
- Clone the Git repository to chosen directory
- Open the Anaconda prompt and navigate to the project's directory
- Enter the following to create and activate the new virtual environment:
> conda env create -f environment.yml
> conda activate anomaly_simulation- Download the AURSAD dataset and move it to the directory anomaly_simulation/Data
- All the following commands must be run from the activated virtual environment
The project can be used in several ways.
The easiest and quickest way is to run the web app and explore the included simulation results. To do this, in your Python enabled terminal (terminal or IDE terminal on Ubuntu, Anaconda Prompt or IDE terminal on Windows) run the following command from the project's directory:
/anomaly_simulation/Source> python visualisation/app.pyThe results of this command should look similar to this:
Dash is running on http://127.0.0.1:8050/
* Serving Flask app "app" (lazy loading)
* Environment: production
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: off
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:8050/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)Copy the IP address to your web browser. The visualisation may take a minute to load and process the data. It should look like this:
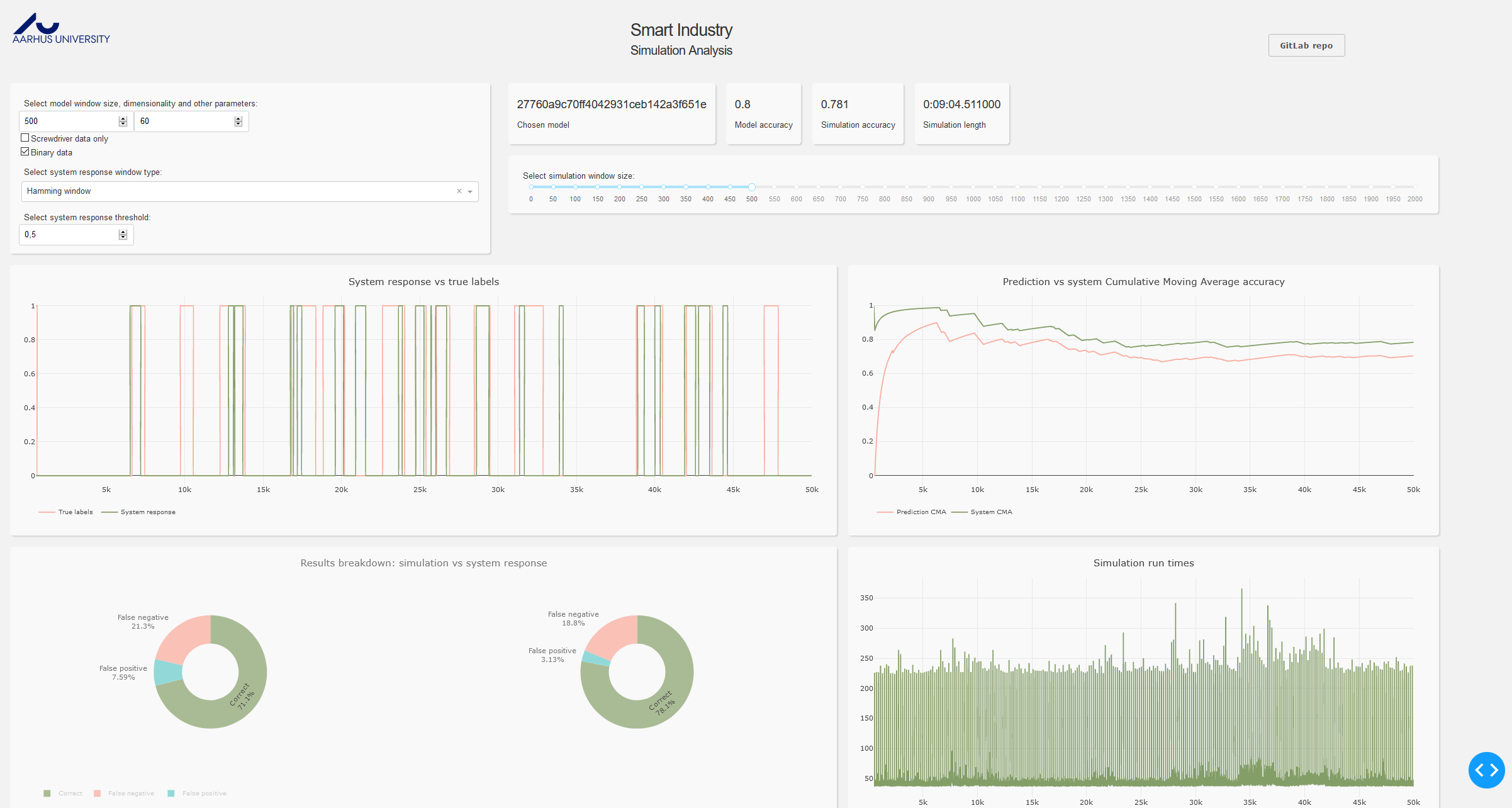
In the top left section model parameters can be chosen:
- Model window size - describes how many previous samples the model takes into account to predict the class of the next sample
- Model dimensionality - describes how many dimensions the input data has. Original data in the AURSAD dataset contains 125 dimensions, any number below that is achieved by applying PCA dimensionality reduction method.
- Screwdriver data only - only the screwdriver's sensors data will be used
- Binary data - binary labels will be used (normal and anomaly)
The app then proceeds to find the best model with such parameters from those available under the anomaly_simulation/Zoo/Results/runs directory.
The dropdown box and slider below the model controls provide the means to manipulate the parameters of the sliding window averages with the aim of creating the most accurate system response. The threshold box changes the decision threshold value. The system calculates the mean label value in each window, and then applies that threshold to it. If the value exceed the threshold, the sample on which the window is centered is assigned an anomaly label, otherwise it gets a normal label.
The figures are described as follows:
- The four figures below show the results of applying these methods on the raw model predictions output.
- The top left figure presents the labels predicted by the system compared to the true labels. 0 means a normal operation, 1 indicates an anomaly.
- The top right figure shows the Cumulative Mean Average of system response accuracy. It allows the user to see how certain trends in data affect the model's accuracy. The last value in this graph corresponds to the 'simulation accuracy' value displayed in the box above it, and represents the average accuracy for the whole simulation.
- The bottom left figure compares the results of the raw model output, and the processed system response. The figure on the left is a benchmark upon which we want to improve using the post-processing.
- The bottom right figure presents run times for each cycle.
To run a new simulation using one of the available models, run the following in your terminal
/anomaly_simulation/Source> python simulation.py --model_dir model_nameThe simulation requires the user to give the starting symbols of the mo/ \el to use in the simulation, and allows to set several other parameters.
/anomaly_simulation/Source>python simulation.py --help
Usage: simulation.py [OPTIONS]
Starts the processes and runs the simulations
Options:
--version Show the version and exit.
--cycle_count INTEGER Number of simulation cycles. Default: 50000
--binary_labels BOOLEAN True for binary labels, False for multi-class.
Default: True
--window INTEGER Rolling window size. Default: 500
--n_dim INTEGER Data dimensionality. Default: 60
--screwdriver_only BOOLEAN If True use only the data from screwdriver
sensors. Default: False
--n_cpu INTEGER Number of cpu cores to use if running multiple
simulations: Default: max - 2
--run_mode TEXT Determines how many simulations will be run:
single will run 1 simulation with a specified
model, all will run all models, fill will run
all models that do not havesimulation results
yet. Default: single
--model_dir TEXT The first symbols of folder name in
Results/runs. Default: 27760
--verbose INTEGER Logging level, from {0 (debug), 1 (info), 2
(warning), 3 (error)}. Default: 1
--help Show this message and exit.This will run the simulation and save its results to anomaly_simulation/Results. This simulation will be then available for the web app to automatically detect and load.
To create a new variant of an already created model, open the anomaly_simulation/Zoo/guild.yml file. This is the file where model parameters are defined. Example ResNet configuration looks like this:
- model: ResNet
description: ResNet classifier
operations:
train:
description: Train ResNet on sliding windows
main: ResNet/train
flags:
window:
description: The sliding window size
default: 100
horizon:
description: Prediction horizon
default: 1
dimensionality:
description: Data dimensionality
default: 60
binarize:
description: Use binary labels
default: False
optimizer:
description: Loss optimizer
default: 'adam'
learning_rate:
description: Initial learning rate
default: 0.001
n_feature_maps:
description: Number of feature maps
default: 64
dev:
description: Fast development run
default: False
remote:
description: If running on remote
default: False
output-scalars:
train_f1_avg: 'Train f1_avg: (\value)'
test_f1_avg: 'Test f1_avg: (\value)'There are two ways now to run the model with new parameters. One is to change the default values of the parameters and save the file. Next, in your terminal run the following to see available models:
anomaly_simulation/Zoo> guild operations
Refreshing flags...
Pure_LSTM:train Train Pure_LSTM on sliding windows
ResNet:train Train ResNet on sliding windows
TABL:train Train TABL on sliding windowsTo run the ResNet model type, with being the absolute path of the anomaly_simulation/Zoo/Results folder, into the terminal:
anomaly_simulation/Zoo> guild -H <path> run ResNet:train
Refreshing flags...
You are about to run ResNet:train
binarize: no
dev: no
dimensionality: 60
horizon: 1
learning_rate: 0.001
n_feature_maps: 64
optimizer: adam
remote: no
window: 100
Continue? (Y/n) # Tyoe Y and press enter to commence model trainingThis will run the model with the default flags as configured in the guild.yml file.
To run a model with grid search of certain attributes, or change the flags without changing the default values, run the previous command with additional options:
anomaly_simulation/Zoo> guild -H <path> run ResNet:train window=[100,200,500]
You are about to run ResNet:train as a batch (3 trials)
binarize: no
dev: no
dimensionality: 60
horizon: 1
learning_rate: 0.001
n_feature_maps: 64
optimizer: adam
remote: no
window: [100, 200, 500]
Continue? (Y/n) # Tyoe Y and press enter to commence model trainingThis will automatically queue and train 3 separate ResNet models with different window sizes.
Adding new model construction To add a new model that is compatible with the project, please inspect and recreate the pattern of the files associated with the already implemented models.
For support, create a new Issue on this repository's GitHub page or email bl@ece.au.dk.