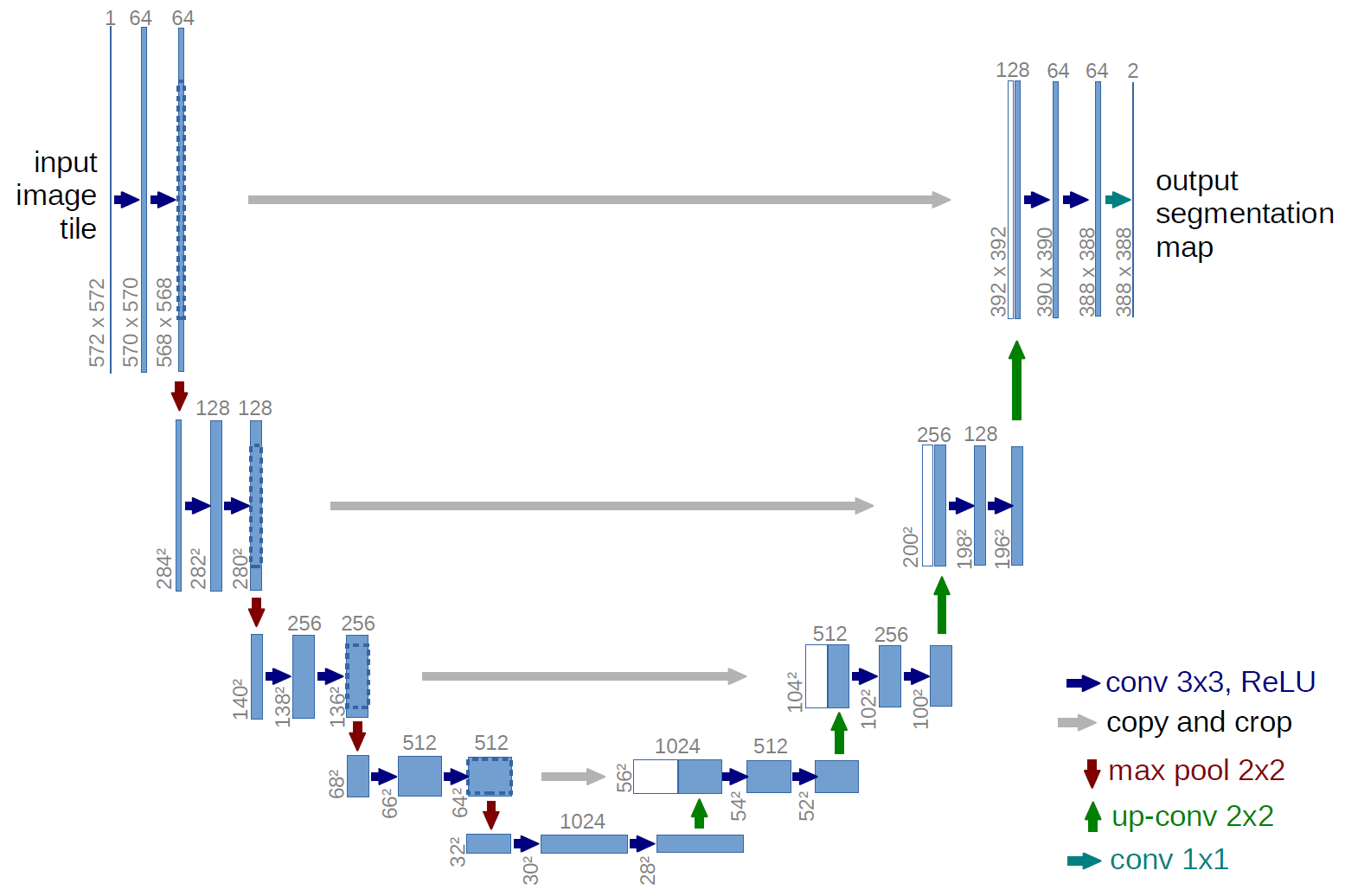
The purpose of this project is to decompose a music audio signal into its vocal and backing track components. Once decomposed, clean vocal or backing signals are useful for other MIR tasks such as singer identification, lyric transcription, and karaoke application [1]. While there are traditional methods for doing source separation of musical audio, deep learning models have emerged as powerful alternatives. In [1], the authors propose a method for decomposing music audio signals into a backing track using modified convolutional neural networks called U-Net [2]. While U-Net was developed for biomedical imaging [2,3], this architecture can be used in the context of singing voice separation. The results of experimentation in [1] shows that U-Net achieves better performance than the other state-of-the-art deep learning technique. We find this paper [1] would be interesting to prove, especially from a video in [4], where the presenter uses U-Net to show how clean this technique does voice separation.
- is a U-shape Convolutional Neural Networks designed for Biomedical Image Segmentation
- (in the context of MIR) allows recreating low-level detail for high quality audio reproduction
- is a type of fully convolutional network (FCN), which has only convolutional layers (i.e. layers are not fully connected).
- has two parts:
- Encoder that learns highly abstract representation of the input image.
- Decoder takes encoder's input and maps it into segmented groundtruth data (e.g. by transposing convolutions and unpooling).
- is a set of convolutional layers that reduce the inputs dimensionality while preserving prevalent information
- applies Localization:
- combines high resolution features from the contracting path with the upsampled output
- each successive convolution layers learn to assemble a more precise output
- has 6 blocks of:
- 5x5 convolutions (filters) with stride = 2
- stride controls how the filter convolves around the input volume
- the first layer has 16 filters, which doubled at each downsampling layer (and half number of channels)
- batch normalization
- leaky ReLU activations with leakiness (alpha = 0.2)
- each downsampling (maxpooling) step doubles the number of features map
-
recreates the input from the contracted representation by encoder
-
is symmetric to the Encoder (i.e. has the same number of filters, sizes, strides, and output dimensions)
-
has 6 blocks of:
- 50% dropout (p = 0.5) for the first three layers
- 5x5 deconvolutions with stride = 2 (i.e. halved layer, double number of channels)
- plain ReLU
- sigmoid activation in the final layer
-
128 size for Mini-batch training, with ADAM optimizer
- U-Net tutorial:
- Basic project structure:
- Implementations:
- Speedy compiler for jupyter:
1 Singing Voice Separation With Deep U-NET Convolutiinal Networks
2 U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
3 MICCAI BraTS 2017: Scope | Section for Biomedical Image Analysis (SBIA)