This guide explains how to install Ansible and create a playbook to automate the deployment and configuration of VMs running on VMware vSphere 6.5 The following steps were tested on a MacBook Pro running VMware vSphere 6.5 on VMware Fusion 11.5. Ansible was installed on the Mac but the instructions should also work on Linux.
Python should already be installed on Mac but you might need to install pip by running this command.
sudo easy_install pip
Once pip is installed, we can use it to install Ansible with the following command.
sudo pip install ansible
We also need to install pyVmomi which is the Python SDK for the VMware vSphere API that allows you to manage ESX, ESXi, and vCenter.
sudo pip install pyvmomi
Ansible playbooks are YAML configuratiom files that describe what actions to run on a remote host. For this example, we’ll create a simple playbook called deploy-vms.yml that will use the vmware_guest module to deply a VM from template.
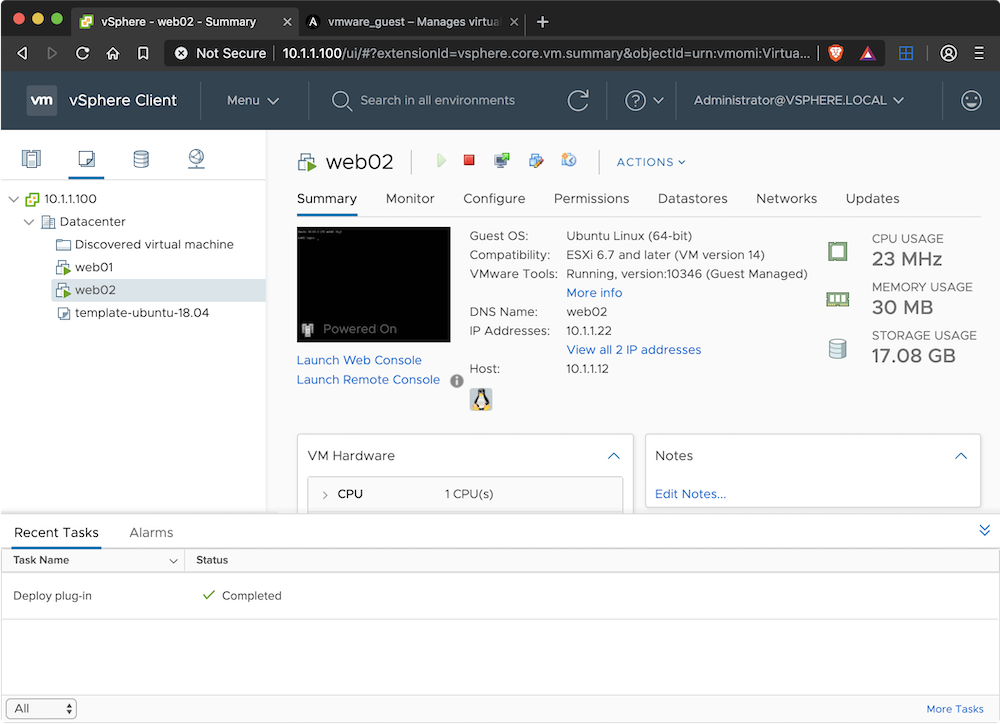
The playbook above will create a new VM called web02 and place it on a datastore called iscsi-datastore01. It will be cloned from a template called template-ubuntu-18.04.
After making the required changes to the deploy-vms.yml file, save it, then run the following command to deploy the VM.
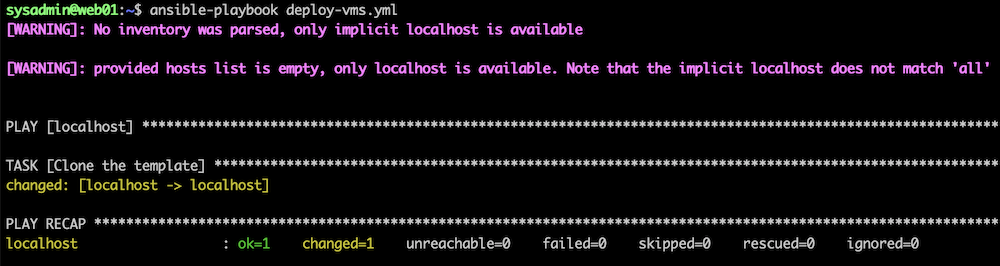
$ansible-playbook deploy-vms.yml
The screenshot below shows the playbook in action.
The playbook might take awhile to complete because we used the wait_for_ip_address: yes option, which means the Ansible command finishes once the VM has been cloned and the network is configured with the static IP address specified.
The screenshot below shows the VM has been created in vCenter.
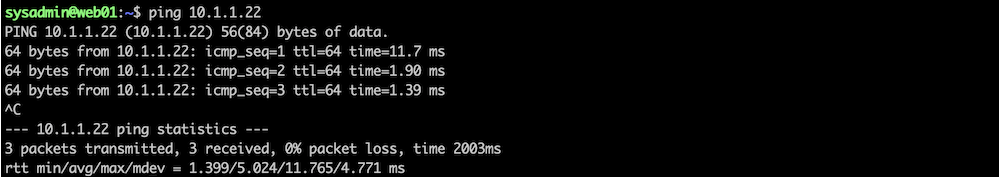
We should also be able to ping the new VM.
This is the list of OS system that support to clone a VM in Vsphere