English | 简体中文
- Introduction
- News
- Installation
- Quick Start
- Dataset List
- Leaderboard
- Experiments and Results
- Model Serving Performance Evaluation
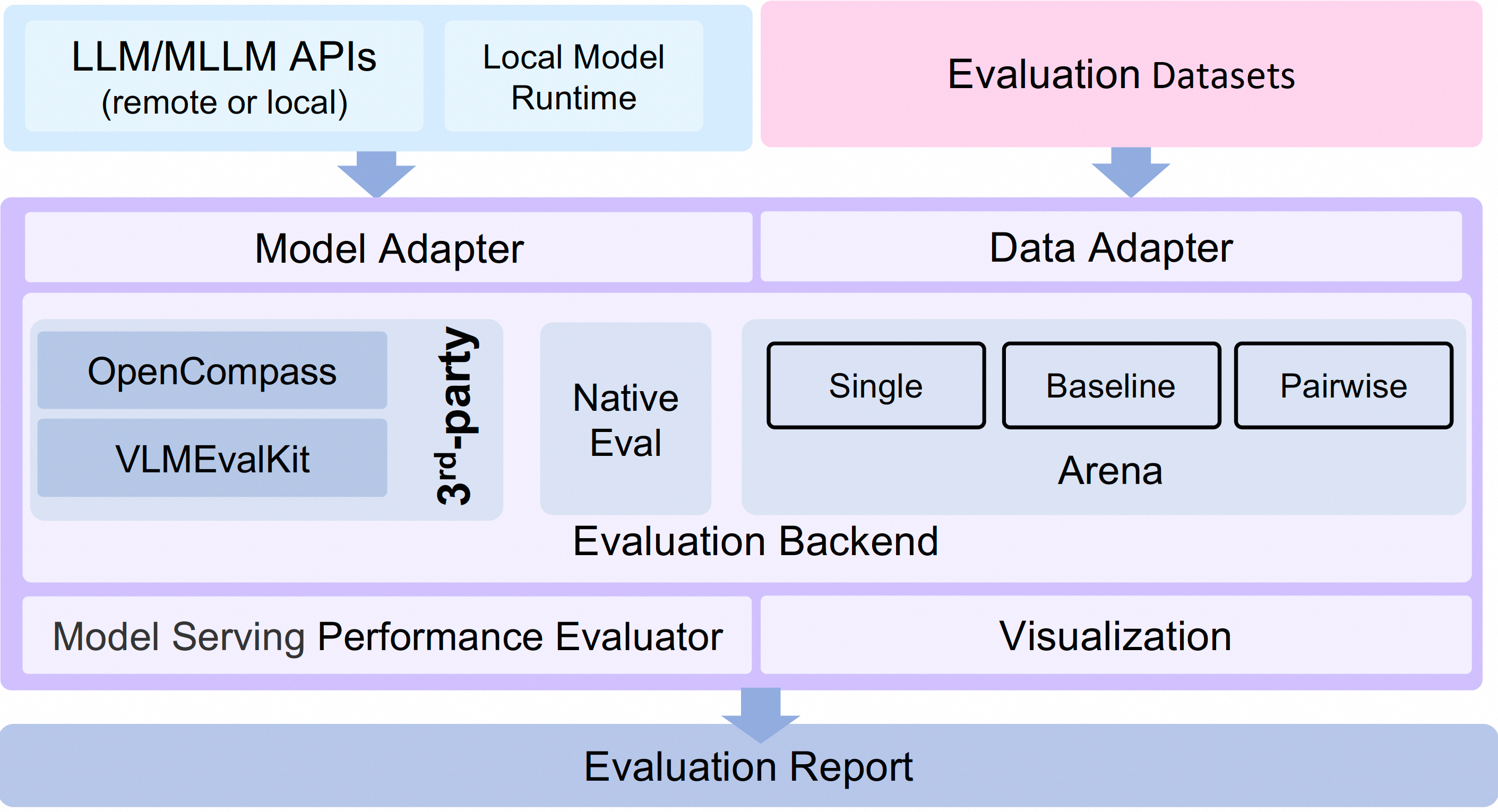
Large Language Model (LLMs) evaluation has become a critical process for assessing and improving LLMs. To better support the evaluation of large models, we propose the EvalScope framework, which includes the following components and features:
- Pre-configured common benchmark datasets, including: MMLU, CMMLU, C-Eval, GSM8K, ARC, HellaSwag, TruthfulQA, MATH, HumanEval, etc.
- Implementation of common evaluation metrics
- Unified model integration, compatible with the generate and chat interfaces of multiple model series
- Automatic evaluation (evaluator):
- Automatic evaluation for objective questions
- Implementation of complex task evaluation using expert models
- Reports of evaluation generating
- Arena mode
- Visualization tools
- Model Inference Performance Evaluation Tutorial
- Support for OpenCompass as an Evaluation Backend, featuring advanced encapsulation and task simplification to easily submit tasks to OpenCompass for evaluation.
- Supports VLMEvalKit as the evaluation backend. It initiates VLMEvalKit's multimodal evaluation tasks through EvalScope, supporting various multimodal models and datasets.
- Full pipeline support: Seamlessly integrate with SWIFT to easily train and deploy model services, initiate evaluation tasks, view evaluation reports, and achieve an end-to-end large model development process.
Features
- Lightweight, minimizing unnecessary abstractions and configurations
- Easy to customize
- New datasets can be integrated by simply implementing a single class
- Models can be hosted on ModelScope, and evaluations can be initiated with just a model id
- Supports deployment of locally hosted models
- Visualization of evaluation reports
- Rich evaluation metrics
- Model-based automatic evaluation process, supporting multiple evaluation modes
- Single mode: Expert models score individual models
- Pairwise-baseline mode: Comparison with baseline models
- Pairwise (all) mode: Pairwise comparison of all models
- [2024.07.31] Breaking change: The sdk name has been changed from
llmusestoevalscope, please update the sdk name in your code. - [2024.07.26] Supports VLMEvalKit as a third-party evaluation framework, initiating multimodal model evaluation tasks. User Guide 🔥🔥🔥
- [2024.06.29] Supports OpenCompass as a third-party evaluation framework. We have provided a high-level wrapper, supporting installation via pip and simplifying the evaluation task configuration. User Guide 🔥🔥🔥
- [2024.06.13] EvalScope has been updated to version 0.3.x, which supports the ModelScope SWIFT framework for LLMs evaluation. 🚀🚀🚀
- [2024.06.13] We have supported the ToolBench as a third-party evaluation backend for Agents evaluation. 🚀🚀🚀
- create conda environment [Optional]
conda create -n evalscope python=3.10
conda activate evalscope- Install EvalScope
pip install evalscope # Installation with Native backend (by default)
pip install evalscope[opencompass] # Installation with OpenCompass backend
pip install evalscope[vlmeval] # Installation with VLMEvalKit backend
pip install evalscope[all] # Installation with all backends (Native, OpenCompass, VLMEvalKit)DEPRECATION WARNING: For 0.4.3 or older versions, please use the following command to install:
pip install llmuses<=0.4.3
# Usage:
from llmuses.run import run_task
...
- Download source code
git clone https://github.com/modelscope/evalscope.git- Install dependencies
cd evalscope/
pip install -e .command line with pip installation:
python -m evalscope.run --model ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b --template-type chatglm3 --datasets arc --limit 100command line with source code:
python evalscope/run.py --model ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b --template-type chatglm3 --datasets mmlu ceval --limit 10Parameters:
- --model: ModelScope model id, model link: ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b
python evalscope/run.py --model ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b --template-type chatglm3 --model-args revision=v1.0.2,precision=torch.float16,device_map=auto --datasets mmlu ceval --use-cache true --limit 10python evalscope/run.py --model qwen/Qwen-1_8B --generation-config do_sample=false,temperature=0.0 --datasets ceval --dataset-args '{"ceval": {"few_shot_num": 0, "few_shot_random": false}}' --limit 10Parameters:
- --model-args: Parameters of model: revision, precision, device_map, in format of key=value,key=value
- --datasets: datasets list, separated by space
- --use-cache:
trueorfalse, whether to use cache, default isfalse - --dataset-args: evaluation settings,json format,key is the dataset name,value should be args for the dataset
- --few_shot_num: few-shot data number
- --few_shot_random: whether to use random few-shot data, default is
true - --local_path: local dataset path
- --limit: maximum number of samples to evaluate for each sub-dataset
- --template-type: model template type, see Template Type List
Note: you can use following command to check the template type list of the model:
from evalscope.models.template import TemplateType
print(TemplateType.get_template_name_list())EvalScope supports using third-party evaluation frameworks to initiate evaluation tasks, which we call Evaluation Backend. Currently supported Evaluation Backend includes:
- Native: EvalScope's own default evaluation framework, supporting various evaluation modes including single model evaluation, arena mode, and baseline model comparison mode.
- OpenCompass: Initiate OpenCompass evaluation tasks through EvalScope. Lightweight, easy to customize, supports seamless integration with the LLM fine-tuning framework ModelScope Swift.
- VLMEvalKit: Initiate VLMEvalKit multimodal evaluation tasks through EvalScope. Supports various multimodal models and datasets, and offers seamless integration with the LLM fine-tuning framework ModelScope Swift.
- ThirdParty: The third-party task, e.g. ToolBench, you can contribute your own evaluation task to EvalScope as third-party backend.
To facilitate the use of the OpenCompass evaluation backend, we have customized the OpenCompass source code and named it ms-opencompass. This version includes optimizations for evaluation task configuration and execution based on the original version, and it supports installation via PyPI. This allows users to initiate lightweight OpenCompass evaluation tasks through EvalScope. Additionally, we have initially opened up API-based evaluation tasks in the OpenAI API format. You can deploy model services using ModelScope Swift, where swift deploy supports using vLLM to launch model inference services.
# Install with extra option
pip install evalscope[opencompass]Available datasets from OpenCompass backend:
'obqa', 'AX_b', 'siqa', 'nq', 'mbpp', 'winogrande', 'mmlu', 'BoolQ', 'cluewsc', 'ocnli', 'lambada', 'CMRC', 'ceval', 'csl', 'cmnli', 'bbh', 'ReCoRD', 'math', 'humaneval', 'eprstmt', 'WSC', 'storycloze', 'MultiRC', 'RTE', 'chid', 'gsm8k', 'AX_g', 'bustm', 'afqmc', 'piqa', 'lcsts', 'strategyqa', 'Xsum', 'agieval', 'ocnli_fc', 'C3', 'tnews', 'race', 'triviaqa', 'CB', 'WiC', 'hellaswag', 'summedits', 'GaokaoBench', 'ARC_e', 'COPA', 'ARC_c', 'DRCD'
Refer to OpenCompass datasets
You can use the following code to list all available datasets:
from evalscope.backend.opencompass import OpenCompassBackendManager
print(f'** All datasets from OpenCompass backend: {OpenCompassBackendManager.list_datasets()}')Dataset download:
-
Option1: Download from ModelScope
git clone https://www.modelscope.cn/datasets/swift/evalscope_resource.git
-
Option2: Download from OpenCompass GitHub
wget https://github.com/open-compass/opencompass/releases/download/0.2.2.rc1/OpenCompassData-complete-20240207.zip
Unzip the file and set the path to the data directory in current work directory.
We use ModelScope swift to deploy model services, see: ModelScope Swift
# Install ms-swift
pip install ms-swift
# Deploy model
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 swift deploy --model_type llama3-8b-instruct --port 8000Refer to example: example_eval_swift_openai_api to configure and execute the evaluation task:
python examples/example_eval_swift_openai_api.pyTo facilitate the use of the VLMEvalKit evaluation backend, we have customized the VLMEvalKit source code and named it ms-vlmeval. This version encapsulates the configuration and execution of evaluation tasks based on the original version and supports installation via PyPI, allowing users to initiate lightweight VLMEvalKit evaluation tasks through EvalScope. Additionally, we support API-based evaluation tasks in the OpenAI API format. You can deploy multimodal model services using ModelScope swift.
# Install with additional options
pip install evalscope[vlmeval]Currently supported datasets include:
'COCO_VAL', 'MME', 'HallusionBench', 'POPE', 'MMBench_DEV_EN', 'MMBench_TEST_EN', 'MMBench_DEV_CN', 'MMBench_TEST_CN', 'MMBench', 'MMBench_CN', 'MMBench_DEV_EN_V11', 'MMBench_TEST_EN_V11', 'MMBench_DEV_CN_V11', 'MMBench_TEST_CN_V11', 'MMBench_V11', 'MMBench_CN_V11', 'SEEDBench_IMG', 'SEEDBench2', 'SEEDBench2_Plus', 'ScienceQA_VAL', 'ScienceQA_TEST', 'MMT-Bench_ALL_MI', 'MMT-Bench_ALL', 'MMT-Bench_VAL_MI', 'MMT-Bench_VAL', 'AesBench_VAL', 'AesBench_TEST', 'CCBench', 'AI2D_TEST', 'MMStar', 'RealWorldQA', 'MLLMGuard_DS', 'BLINK', 'OCRVQA_TEST', 'OCRVQA_TESTCORE', 'TextVQA_VAL', 'DocVQA_VAL', 'DocVQA_TEST', 'InfoVQA_ VAL', 'InfoVQA_TEST', 'ChartQA_VAL', 'ChartQA_TEST', 'MathVision', 'MathVision_MINI', 'MMMU_DEV_VAL', 'MMMU_TEST', 'OCRBench', 'MathVista_MINI', 'LLaVABench', 'MMVet', 'MTVQA_TEST', 'MMLongBench_DOC', 'VCR_EN_EASY_500', 'VCR_EN_EASY_100', 'VCR_EN_EASY_ALL', 'VCR_EN_HARD_500', 'VCR_EN_HARD_100', 'VCR_EN_HARD_ALL', 'VCR_ZH_EASY_500', 'VCR_ZH_EASY_100', 'VCR_Z H_EASY_ALL', 'VCR_ZH_HARD_500', 'VCR_ZH_HARD_100', 'VCR_ZH_HARD_ALL', 'MMBench-Video', 'Video-MME', 'MMBench_DEV_EN', 'MMBench_TEST_EN', 'MMBench_DEV_CN', 'MMBench_TEST_CN', 'MMBench', 'MMBench_CN', 'MMBench_DEV_EN_V11', 'MMBench_TEST_EN_V11', 'MMBench_DEV_CN_V11', 'MMBench_TEST_CN_V11', 'MM Bench_V11', 'MMBench_CN_V11', 'SEEDBench_IMG', 'SEEDBench2', 'SEEDBench2_Plus', 'ScienceQA_VAL', 'ScienceQA_TEST', 'MMT-Bench_ALL_MI', 'MMT-Bench_ALL', 'MMT-Bench_VAL_MI', 'MMT-Bench_VAL', 'AesBench_VAL', 'AesBench_TEST', 'CCBench', 'AI2D_TEST', 'MMStar', 'RealWorldQA', 'MLLMGuard_DS', 'BLINK'
For detailed information about the datasets, please refer to VLMEvalKit Supported Multimodal Evaluation Sets.
You can use the following to view the list of dataset names:
from evalscope.backend.vlm_eval_kit import VLMEvalKitBackendManager
print(f'** All models from VLMEvalKit backend: {VLMEvalKitBackendManager.list_supported_models().keys()}')If the dataset file does not exist locally when loading the dataset, it will be automatically downloaded to the ~/LMUData/ directory.
There are two ways to evaluate the model:
Model Deployment Deploy the model service using ModelScope Swift. For detailed instructions, refer to: ModelScope Swift MLLM Deployment Guide
# Install ms-swift
pip install ms-swift
# Deploy the qwen-vl-chat multi-modal model service
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 swift deploy --model_type qwen-vl-chat --model_id_or_path models/Qwen-VL-ChatModel Evaluation Refer to the example file: example_eval_vlm_swift to configure the evaluation task. Execute the evaluation task:
python examples/example_eval_vlm_swift.pyModel Inference Evaluation Skip the model service deployment and perform inference directly on the local machine. Refer to the example file: example_eval_vlm_local to configure the evaluation task. Execute the evaluation task:
python examples/example_eval_vlm_local.pyDeploy the local language model as a judge/extractor using ModelScope swift. For details, refer to: ModelScope Swift LLM Deployment Guide. If no judge model is deployed, exact matching will be used.
# Deploy qwen2-7b as a judge
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 swift deploy --model_type qwen2-7b-instruct --model_id_or_path models/Qwen2-7B-Instruct --port 8866You must configure the following environment variables for the judge model to be correctly invoked:
OPENAI_API_KEY=EMPTY
OPENAI_API_BASE=http://127.0.0.1:8866/v1/chat/completions # api_base for the judge model
LOCAL_LLM=qwen2-7b-instruct # model_id for the judge model
Refer to the example file: example_eval_vlm_swift to configure the evaluation task.
Execute the evaluation task:
python examples/example_eval_vlm_swift.pyYou can use local dataset to evaluate the model without internet connection.
# set path to /path/to/workdir
wget https://modelscope.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/open_data/benchmark/data.zip
unzip data.zippython evalscope/run.py --model ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b --template-type chatglm3 --datasets arc --dataset-hub Local --dataset-args '{"arc": {"local_path": "/path/to/workdir/data/arc"}}' --limit 10
# Parameters:
# --dataset-hub: dataset sources: `ModelScope`, `Local`, `HuggingFace` (TO-DO) default to `ModelScope`
# --dataset-args: json format, key is the dataset name, value should be args for the dataset# 1. Prepare the model local folder, the folder structure refers to chatglm3-6b, link: https://modelscope.cn/models/ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b/files
# For example, download the model folder to the local path /path/to/ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b
# 2. Execute the offline evaluation task
python evalscope/run.py --model /path/to/ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b --template-type chatglm3 --datasets arc --dataset-hub Local --dataset-args '{"arc": {"local_path": "/path/to/workdir/data/arc"}}' --limit 10import torch
from evalscope.constants import DEFAULT_ROOT_CACHE_DIR
# Example configuration
your_task_cfg = {
'model_args': {'revision': None, 'precision': torch.float16, 'device_map': 'auto'},
'generation_config': {'do_sample': False, 'repetition_penalty': 1.0, 'max_new_tokens': 512},
'dataset_args': {},
'dry_run': False,
'model': 'ZhipuAI/chatglm3-6b',
'template_type': 'chatglm3',
'datasets': ['arc', 'hellaswag'],
'work_dir': DEFAULT_ROOT_CACHE_DIR,
'outputs': DEFAULT_ROOT_CACHE_DIR,
'mem_cache': False,
'dataset_hub': 'ModelScope',
'dataset_dir': DEFAULT_ROOT_CACHE_DIR,
'stage': 'all',
'limit': 10,
'debug': False
}from evalscope.run import run_task
run_task(task_cfg=your_task_cfg)The Arena mode allows multiple candidate models to be evaluated through pairwise battles, and can choose to use the AI Enhanced Auto-Reviewer (AAR) automatic evaluation process or manual evaluation to obtain the evaluation report. The process is as follows:
a. Data preparation, the question data format refers to: evalscope/registry/data/question.jsonl
b. If you need to use the automatic evaluation process (AAR), you need to configure the relevant environment variables. Taking the GPT-4 based auto-reviewer process as an example, you need to configure the following environment variables:
> export OPENAI_API_KEY=YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY
Refer to : evalscope/registry/config/cfg_arena.yaml
Parameters:
questions_file: question data path
answers_gen: candidate model prediction result generation, supports multiple models, can control whether to enable the model through the enable parameter
reviews_gen: evaluation result generation, currently defaults to using GPT-4 as the Auto-reviewer, can control whether to enable this step through the enable parameter
elo_rating: ELO rating algorithm, can control whether to enable this step through the enable parameter, note that this step depends on the review_file must exist
#Usage:
cd evalscope
# dry-run mode
python evalscope/run_arena.py -c registry/config/cfg_arena.yaml --dry-run
# Execute the script
python evalscope/run_arena.py --c registry/config/cfg_arena.yaml# Usage:
streamlit run viz.py -- --review-file evalscope/registry/data/qa_browser/battle.jsonl --category-file evalscope/registry/data/qa_browser/category_mapping.yamlIn this mode, we only score the output of a single model, without pairwise comparison.
Refer to: evalscope/registry/config/cfg_single.yaml
Parameters:
questions_file: question data path
answers_gen: candidate model prediction result generation, supports multiple models, can control whether to enable the model through the enable parameter
reviews_gen: evaluation result generation, currently defaults to using GPT-4 as the Auto-reviewer, can control whether to enable this step through the enable parameter
rating_gen: rating algorithm, can control whether to enable this step through the enable parameter, note that this step depends on the review_file must exist
#Example:
python evalscope/run_arena.py --c registry/config/cfg_single.yamlIn this mode, we select the baseline model, and compare other models with the baseline model for scoring. This mode can easily add new models to the Leaderboard (just need to run the scoring with the new model and the baseline model).
Refer to: evalscope/registry/config/cfg_pairwise_baseline.yaml
Parameters:
questions_file: question data path
answers_gen: candidate model prediction result generation, supports multiple models, can control whether to enable the model through the enable parameter
reviews_gen: evaluation result generation, currently defaults to using GPT-4 as the Auto-reviewer, can control whether to enable this step through the enable parameter
rating_gen: rating algorithm, can control whether to enable this step through the enable parameter, note that this step depends on the review_file must exist
# Example:
python evalscope/run_arena.py --c registry/config/cfg_pairwise_baseline.yaml| DatasetName | Link | Status | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
mmlu |
mmlu | Active | |
ceval |
ceval | Active | |
gsm8k |
gsm8k | Active | |
arc |
arc | Active | |
hellaswag |
hellaswag | Active | |
truthful_qa |
truthful_qa | Active | |
competition_math |
competition_math | Active | |
humaneval |
humaneval | Active | |
bbh |
bbh | Active | |
race |
race | Active | |
trivia_qa |
trivia_qa | To be intergrated |
The LLM Leaderboard aims to provide an objective and comprehensive evaluation standard and platform to help researchers and developers understand and compare the performance of models on various tasks on ModelScope.
Refer to : Leaderboard
Refer to : Experiments
Refer to : Perf
- Agents evaluation
- vLLM
- Distributed evaluating
- Multi-modal evaluation
- Benchmarks
- GAIA
- GPQA
- MBPP
- Auto-reviewer
- Qwen-max