Read this in other languages: **.
- 基于区块链的众筹防御架构,采用边缘计算的理念,将DDoS大规模流量攻击从源头处断绝。
- 思路:
- 通过各个边缘节点,进行本地的流量异常检测;
- 各个节点将本地异常信息共享至整个overlay区块链网络
- 区块链选取特定节点基于规则,进行汇总分析,并提交DDoS异常连接
- 目标节点确认完毕,奖励所有提交有效异常的节点
- 准备阶段1234,展示阶段567
- .submit1_User.sh:注册12个边缘节点和4个目标用户
- .submit2_1AbnormalInfo.sh:
- 11个边缘节点随机提交150条异常,包括对10个非目标用户IP的50条假异常,和对2个目标用户IP的100条真异常
- 同时给elk服务器发送150条同样的数据
- .submit3_1DDoS.sh:边缘节点1提交针对2提交的150条异常的汇总DDoS预警
- .submit4_1Reward.sh:目标用户1给针对目标自己的有效异常进行奖励
- .submit2_2AbnormalInfo.sh:
- 11个边缘节点随机提交50条异常,包括对10个非目标用户IP的10条假异常,和对2个目标用户IP的40条真异常
- 同时给elk服务器发送50条同样的数据
- .submit3_2DDoS.sh:边缘节点2提交针对3提交的50条异常的汇总DDoS预警
- .submit4_2Reward.sh:目标用户2给针对目标自己的有效异常进行奖励
- 区块链环境:
- 虚拟机多节点搭建区块链Hyperledger fabric1.0环境
- 具体环境部署参考hyperledger composer即可
- 边缘节点:
- 每个虚拟机就是一个边缘节点
- 每个边缘节点含有众多IoT设备,由docker模拟多个设备
- 攻击数据:
- 实际通过SD卡注入等方式攻击某yi摄像头
- 在内网搭建Mirai攻击服务器,对内网中的边缘节点下属IoT设备进行攻击
- 并通过重放流量,在每个节点重放攻击
- 在边缘节点处,用tcpdump+wireshark捕获攻击流量
- 异常检测:
- 对wireshark捕获的流量数据进行数据清洗
- 每个边缘节点采用基于规则和基于统计(Kmeans聚类)的方法进行本地的流量异常检测
- 区块链智能合约:
- 采用hyperledger composer框架进行智能合约的实现
- 节点注册
- 异常提交
- DDoS提交
- 奖励提交
- 前端展示:
- 采用angular2进行web的开发
- 读取区块链的数据,采用canvas渲染进行动态的展示
- 节点注册:动态添加一个节点
- 异常提交:动态显示交易结果,提交节点闪烁
- DDoS提交:动态显示交易结果,被攻击节点闪烁
- 奖励提交:奖励发放者与异常提交者的连线闪烁
-
Mirai攻击部署与实现
- DDoS模拟实现:
- sudo trafgen --cpp --dev eno1 --conf synflood.trafgen --verbose
- eno1是网卡
- synflood.trafgen是攻击配置文件
- Mirai:
- 包含多种DDoS类型,SYN/ACK/UDP/TCP/HTTP/VSE/DNS等
- DDoS模拟实现:
-
区块链多节点部署
- 单机测试:
- 运行example.
- 节点部署:
- 5个节点:1个orderer+4个peer
- 1个vmware作为一个节点
- 1个vmware里面跑hyperledger环境,分别作为
- Orderer+ca节点
- Peer+Cli节点
- 1个vmware里面运行多个docker模拟设备,发动ddos攻击
- 克隆虚拟机后,需要修改:
- hostname
- mac地址
- IP地址
- 单机测试:
-
流量捕获部署
- 流量类型:
- 模拟攻击:使用实际流量回放和trafgen多线程数据包生成器
- 实际攻击:通过交换机镜像,捕获Miria攻击下的摄像头数据;
- 部署:
- 路由器下局域网:mirai主机+交换机
- 交换机下接:摄像头+捕获PC
- 借助交换机的端口镜像,将摄像头流量镜像到捕获端PC
- 捕获:
- Tcpdump+wireshark
- Tcpdump捕获的时候需要过滤:只保留摄像头和路由器的流量:
- tcpdump -i enp2s0 host 192.168.1.6 -w save_cam.cap
- tcpdump host 192.168.1.1
- wireshark数据预处理:
- 捕获过滤:BFP语法,可以由tcpdump实现
- 显示过滤:正则表达式:ip.src==172.23.52.2 && udp
- 导出展示层为csv文件:需要选择packet details为All expanded
- 到处数据流:文件-导出特定分组-txt
- 数据处理: +
- 流量类型:
-
异常检测
-
智能合约
- 资产获取的api的返回结果是以资产id的顺序,没有按照
-
前端展示:
- 动态节点效果图
- canvas绘制矩形 和 圆形
- canvas动画渲染
- 自动化执行:
- 目的:方便前段模拟调试
- 所有的ID号:采用4位表示,0001
- shell脚本语法:
- 条件判断:[EXPRESSION]
- 与:-a
- 或:-o
- 非:!
- 大于:-gt(greater than)
- 大于等于:-ge(greater equal)
- 小于:-lt(less than)
- 小于等于:-le(less equal)
- 不等于:-ne(not equal)
- if:
- if [条件]; then
- fi
- for:
- while ["$index" -lt "N"]; do
- ((index++))
- done
- 数组:
- 赋值:array=(a, b, $c)
- 长度:${#array[*]} 或 ${#array[@]}
- 引用单个值:${array[i]}
- 引用所有值:${array[*]}
- 字符串拼接:
- 变量+字符串:res=${val}"a"
- 字符串+变量:res="a${val}"
- 单引号:内部全看作是字符串
- 单引号内插入变量:'"'内容'"' 替换原来的 "内容"
- 随机数:RANDOM是Bash内建函数,产生0-32767内的整数
- 求余数:res=$((index%M+1))
- 条件判断:[EXPRESSION]
- submit0_init.sh:删除已有的交易信息,否则调试需要重启区块链。
- 仅限调试提交交易、注册用户
- coins、cash不删除
- 异常连接energy删除、DDoS删除
- submit1_User.sh:注册用户
- 包括:N个Gateway节点+M个TargetCompany节点
- 每个Gateway的:coins注册(初始5coins),cash注册(初始5cash)
- 每个TargetCompany的:coins注册(初始500coins)
- submit2_Abnormalinfo.sh:提交异常
- 包括:Abnormal个异常连接数
- 定义异常类型descriptions=("TCP中SYN握手未完成", "udp数据包异常", "HTTP数据包异常", "DNS反射攻击")
- 攻击顺序:先无效提交k个、再有效提交
- 攻击类型description:随机化选取
- 提交者ID:前k个无效提交,后面节点随机化选取
- 攻击目标targetIP:前k个无效随机化,后面有效异常的targetIP后缀取对M的余数
- submit3_DDoS.sh:提交DDoS
- 问题:DDoS提交是应该通过网络随机选择节点进行提交交易;
- 解决:后续将改为随机选定节点自动执行
- submit4_Reward.sh:提交奖励
- 问题:奖励分发什么时候执行?
- 解决:应该设置奖励分发之后才进行流量清洗;则奖励智能合约也需要重新修改;
-
流量清洗
-
模型更新
- 借助区块链不断增长的大数据的特点:进行边缘节点的模型更新;
-
前端动态效果方案选型: ①遍历所有的交易:可以解析具体的交易函数,但是无法传入参数,因为奖励函数使用的是遍历的方式,没有给定返回值;如果用这种方法就得返回所有的异常提交者,但是只能奖励合约好像没有返回值。 ②给TargetCompany增加属性:当前奖励的对象,也就是异常提交用户,也可以是一个字符串变量,但是好像就不好显示顺序实时结果,只按照遍历TargetCompany的顺序。 ③创建、从而遍历奖励对象:可以是字符串变量,每创建一笔奖励交易,就创建一个奖励对象/奖励说明。
-
疑惑:
- 问题:正常的奖励应该是由系统自动触发的; ①DDoS异常的submitter是Gateway, ②奖励交易的submitter是TargetCompany,而且是谁提交,就遍历谁的targetIP的异常连接energy
- 解决: ①现在改为了由TargetCompany主动触发, ②触发之后,异常提交者Gateway才去在本地过滤掉通向该targetIP的流量
-
任务一:
- 动态显示空间连线图
- 解决: ①采用html5的canvas画图直接实现,较为复杂。 ②采用2D的连线图:d3.js可以直接实现 d3.js是数据可视化的工具包 d3.js的力导向图 还需要进一步研究一下其example实例 ③采用3D的连线图:需要three.js才能实现 是一些列游戏引擎之一 ④采用HT for Web 或者 html5的Qunee
- 技术对比:
- canvas:使用的是即时渲染,更底层,消耗内存资源更少,适合复杂图形构建
- svg:使用的是保留渲染
-
任务二:
- 问题:修改已有的区块链配置,将UtilityCompany改为TargetCompany
- 解决: ①修改angular-app下的所有项目文件 model.cto,以及transactions.js, ②重启网络的时候出现问题,BNA文件无法创建: 解决:在根目录下的..acl,qry等文件是业务逻辑以及各种权限的配置,需要修改相应的位置
-
任务三:
- 问题:修改无法创建多个奖励的bug
- 解决:
- 找到了智能合约遍历participant的函数getParticipantRegistry()
- 修改后,Log资产无法正确创建,因为Log的新增属性lastEnergyCount设置为了string,所以使用的时候要转化为int:parseInt(string_),String(int_)
-
任务四:
- 问题:修改添加的矩形点的渲染和数据绑定,实现动态添加和闪烁
- 解决:
- 创建上次点状态,记录;
-
任务五:
- 问题:修复得到的transactions是乱序的?
- 解决:通过测试,发现transactions是按照资产ID顺序进行创建,所以需要用多位数ID表示,如:0001,0002等
-
任务六:
- 问题:增加创建众多用户、异常连接、ddos、奖励
- 解决:
- bash的多行注释:
:<<BLOCK‘ 注释内容 ’BLOCK- for循环实现添加用户
- for循环实现添加异常连接
-
任务七:
- 问题:修复bug:
- 当ddos交易按顺序执行,提交了2条ddos
- 奖励交易发起之后,顺序问题,若先奖励了最后一条ddos,就不会去奖励上一条ddos;因为奖励每次遍历所有不现实
- 解决:
- 奖励每次遍历所有~
- 暂且这样。
- 问题:修复bug:
-
任务八:
- 问题:bug:
- 一次提交多笔DDoS交易是同一个用户提交,而且时间戳相同,因为是同一时间提交
- 一次提交多笔奖励交易是不同用户提交,但是无法完全实现coins的转移
- 解决:
- DDoS交易默认应该是自动由节点来完成的,脚本提交只是暂时展示效果;后期应该实现存在一笔DDoS就选取某节点自动化DDoS提交
- transactions.js智能合约内没有写多用户奖励,还未实现!
- transactions.js智能合约目前采用的是遍历所有异常连接资产Energy,实现多用户,需要再上层加入DDoS资产的循环,找到多个TargetCompany目标用户;
- 问题:bug:
- 节点和用户
- 两者是什么关系?
参考项目:Decentralized Energy with Hyperledger Composer PS:以下为参考项目分布式能源介绍,包括环境搭建。
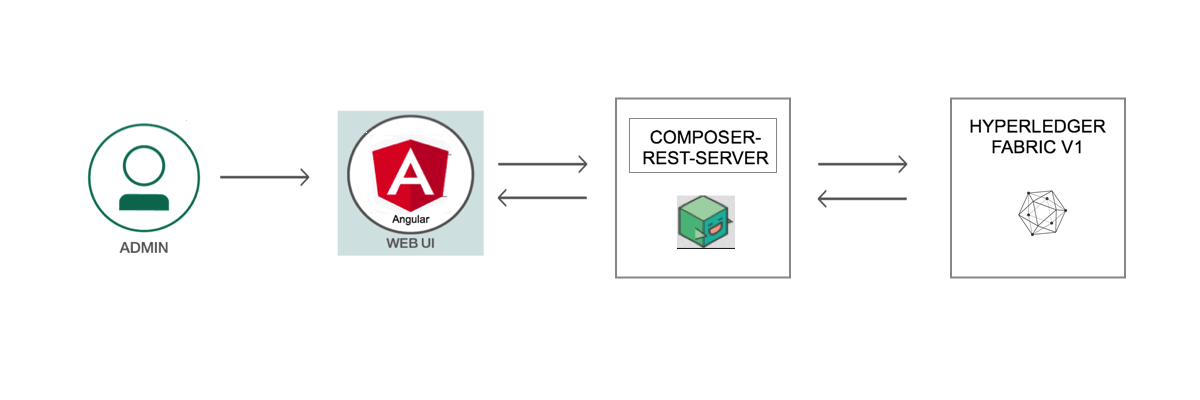
- The administrator interacts with Decentralized Energy UI comprising of Angular framework
- The application processes user requests to the network through a REST API.
- Implements requests to the Blockchain state database on Hyperledger Fabric v1
- The REST API is used to retrieve the state of the database
- The Angular framework gets the data through GET calls to the REST API
- Hyperledger Composer
- Angular Framework
- Loopback
Follow these steps to setup and run this developer journey. The steps are described in detail below.
- Docker (Version 17.03 or higher)
- npm (v3.x or v5.x)
- Node (version 6.x - note version 7 is not supported)
- to install Node v6.x you can use nvm
- Hyperledger Composer
- to install composer cli
npm install -g composer-cli - to install composer-rest-server
npm install -g composer-rest-server - to install generator-hyperledger-composer
npm install -g generator-hyperledger-composer
- to install composer cli
- Clone the repo
- Setup Fabric
- Generate the Business Network Archive
- Deploy to Fabric
- Run Application
- Create Participants
- Execute Transactions
Clone the Decentralized-Energy-Composer code locally. In a terminal, run:
git clone https://github.com/IBM/Decentralized-Energy-Composer
These commands will kill and remove all running containers, and should remove all previously created Hyperledger Fabric chaincode images:
docker kill $(docker ps -q)
docker rm $(docker ps -aq)
docker rmi $(docker images dev-* -q)
Set Hyperledger Fabric version to v1.0:
export FABRIC_VERSION=hlfv1
All the scripts will be in the directory /fabric-tools. Start fabric and create peer admin card:
cd fabric-tools/
./downloadFabric.sh
./startFabric.sh
./createPeerAdminCard.sh
Next generate the Business Network Archive (BNA) file from the root directory:
cd ../
npm install
The composer archive create command in package.json has created a file called decentralized-energy-network.bna in the dist folder.
Now, we are ready to deploy the business network to Hyperledger Fabric. This requires the Hyperledger Composer chaincode to be installed on the peer,then the business network archive (.bna) must be sent to the peer, and a new participant, identity, and associated card must be created to be the network administrator. Finally, the network administrator business network card must be imported for use, and the network can then be pinged to check it is responding.
First, install the composer runtime:
cd dist/
composer runtime install --card PeerAdmin@hlfv1 --businessNetworkName decentralized-energy-network
Deploy the business network:
composer network start --card PeerAdmin@hlfv1 --networkAdmin admin --networkAdminEnrollSecret adminpw --archiveFile decentralized-energy-network.bna --file networkadmin.card
Import the network administrator identity as a usable business network card:
composer card import --file networkadmin.card
Check that the business network has been deployed successfully, run the following command to ping the network:
composer network ping --card admin@decentralized-energy-network
First, go into the angular-app folder and install the dependency:
cd ../angular-app/
npm install
To start the application:
npm start
The application should now be running at:
http://localhost:4200
The REST server to communicate with network is available here:
http://localhost:3000/explorer/
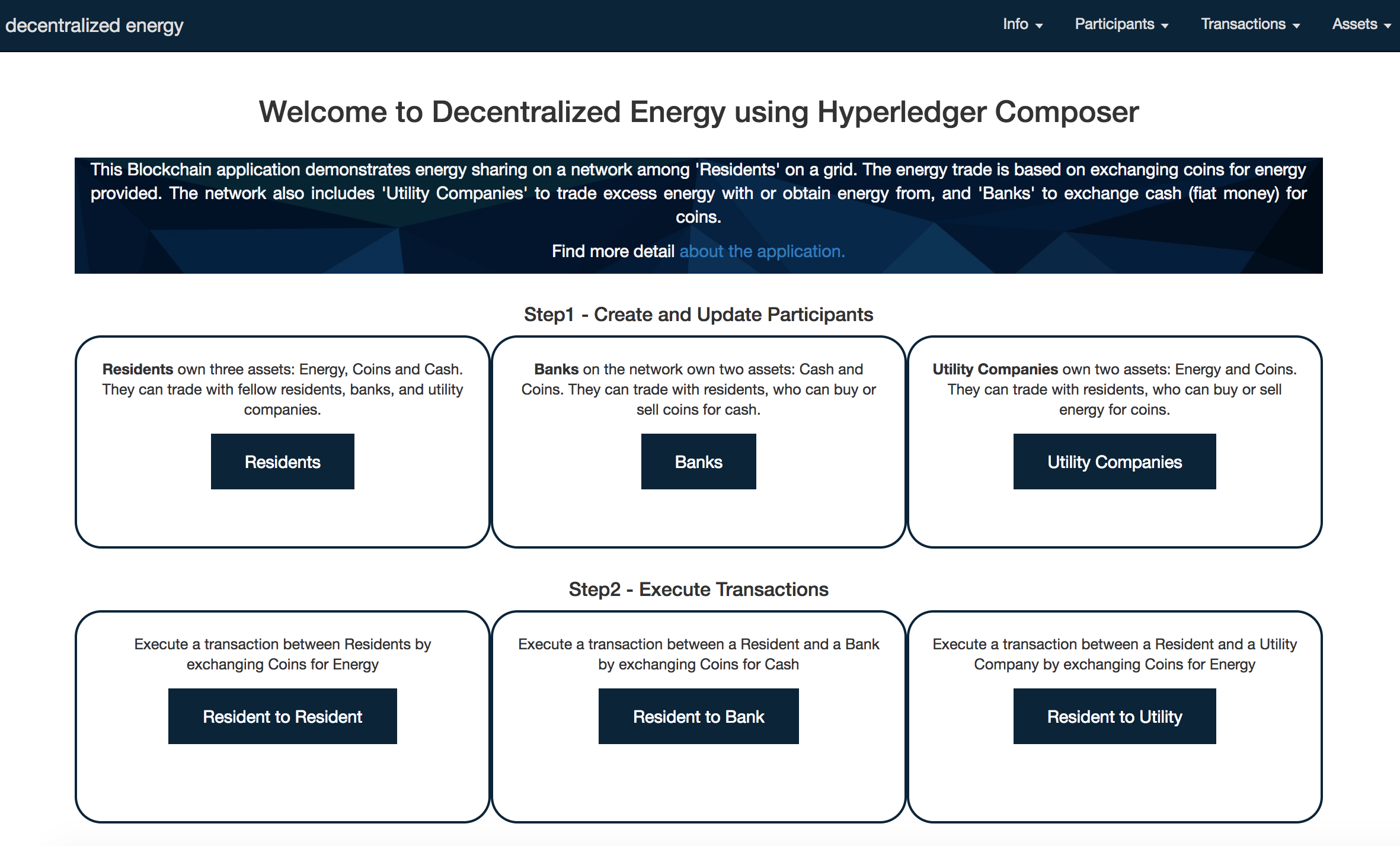
Once the application opens, create participants and fill in dummy data. Create Residents, Banks and Utility Companies.
Execute transactions manually between Residents, Resident and Bank, and Resident and Utility Company. After executing transactions, ensure the participants account values are updated.
At the end of your session, stop fabric:
cd ~/fabric-tools
./stopFabric.sh
./teardownFabric.sh
This application demonstrates a basic idea of a decentralized energy network using Blockchain and can be expanded in several ways:
- Adding specific permissions and participant access
- Setting up real time transactions among participants
- Integrating with IoT to read from power meter and distribute energy