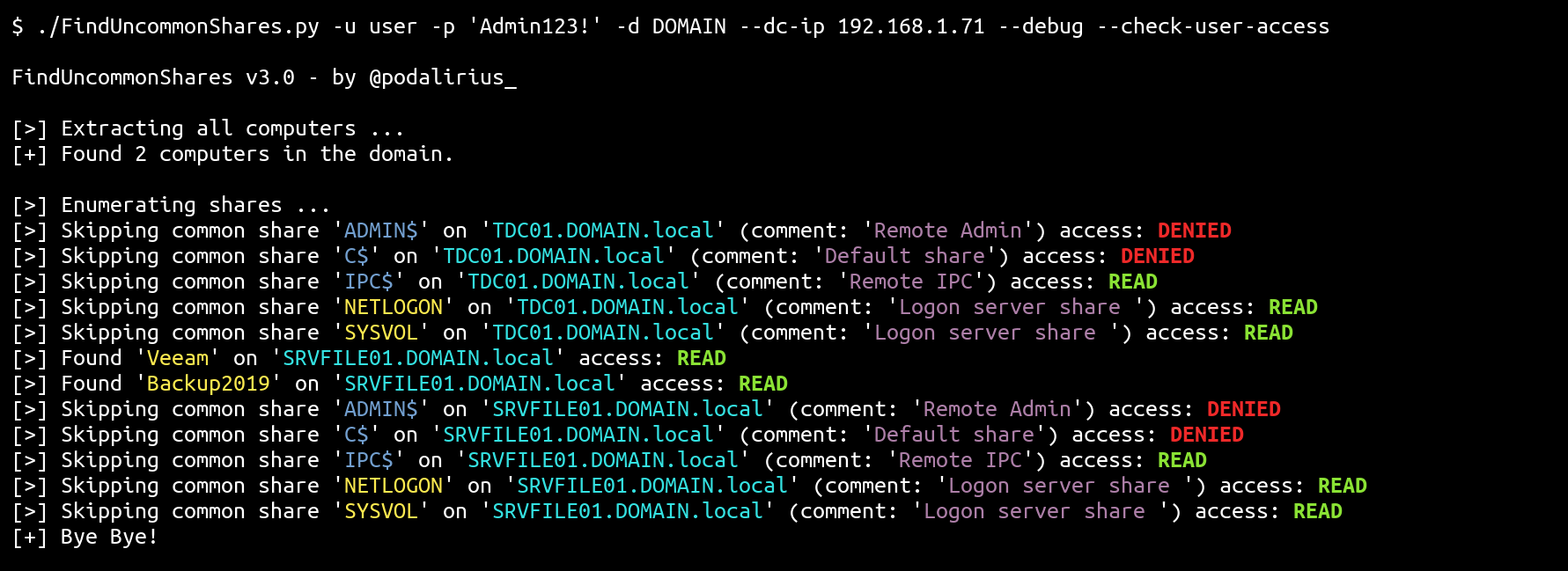
The script FindUncommonShares.py is a Python equivalent of PowerView's Invoke-ShareFinder.ps1 allowing to quickly find uncommon shares in vast Windows Active Directory Domains.



- Only requires a low privileges domain user account.
- Automatically gets the list of all computers from the domain controller's LDAP.
- Ignore the hidden shares (ending with
$) with--ignore-hidden-shares. - Multithreaded connections to discover SMB shares.
- Export results in JSON with IP, name, comment, flags and UNC path with
--export-json <file.json>. - Export results in XLSX with IP, name, comment, flags and UNC path with
--export-xlsx <file.xlsx>. - Export results in SQLITE3 with IP, name, comment, flags and UNC path with
--export-sqlite <file.db>. - Iterate on LDAP result pages to get every computer of the domain, no matter the size.
-
List all shares where your current user has WRITE access:
./FindUncommonShares.py -u user -p 'Podalirius123!' -d DOMAIN --dc-ip 192.168.1.71 --writable -
Export list of shares in the domain to an Excel file for the client:
./FindUncommonShares.py -u user -p 'Podalirius123!' -d DOMAIN --dc-ip 192.168.1.71 --export-xlsx ./examples/results.xlsx -
List all shares with access rights for your current user:
./FindUncommonShares.py -u user -p 'Podalirius123!' -d DOMAIN --dc-ip 192.168.1.71 --check-user-access
$ ./FindUncommonShares.py -h
FindUncommonShares v3.0 - by @podalirius_
usage: FindUncommonShares.py [-h] [-v] [--use-ldaps] [-q] [--debug] [-no-colors] [-t THREADS] [-l LDAP_QUERY] [-ns NAMESERVER]
[--check-user-access] [--readable] [--writable] [-I] [-i IGNORED_SHARES] [-s ACCEPTED_SHARES]
[--export-xlsx EXPORT_XLSX] [--export-json EXPORT_JSON] [--export-sqlite EXPORT_SQLITE] --dc-ip ip
address [-d DOMAIN] [-u USER] [--no-pass | -p PASSWORD | -H [LMHASH:]NTHASH | --aes-key hex key] [-k]
Find uncommon SMB shares on remote machines.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --verbose Verbose mode. (default: False).
--use-ldaps Use LDAPS instead of LDAP.
-q, --quiet Show no information at all.
--debug Debug mode. (default: False).
-no-colors Disables colored output mode.
-t THREADS, --threads THREADS
Number of threads (default: 20).
-l LDAP_QUERY, --ldap-query LDAP_QUERY
LDAP query to use to extract computers from the domain.
-ns NAMESERVER, --nameserver NAMESERVER
IP of the DNS server to use, instead of the --dc-ip.
--check-user-access Check if current user can access the share.
--readable Only list shares that current user has READ access to.
--writable Only list shares that current user has WRITE access to.
-I, --ignore-hidden-shares
Ignores hidden shares (shares ending with $)
-i IGNORED_SHARES, --ignore-share IGNORED_SHARES
Specify shares to ignore explicitly. (e.g., --ignore-share 'C$' --ignore-share 'Backup')
-s ACCEPTED_SHARES, --show-share ACCEPTED_SHARES
Specify shares to show explicitly. (e.g., --show-share 'C$' --show-share 'Backup')
Output files:
--export-xlsx EXPORT_XLSX
Output XLSX file to store the results in.
--export-json EXPORT_JSON
Output JSON file to store the results in.
--export-sqlite EXPORT_SQLITE
Output SQLITE3 file to store the results in.
Authentication & connection:
--dc-ip ip address IP Address of the domain controller or KDC (Key Distribution Center) for Kerberos. If omitted it will use the
domain part (FQDN) specified in the identity parameter
-d DOMAIN, --domain DOMAIN
(FQDN) domain to authenticate to
-u USER, --user USER user to authenticate with
Credentials:
--no-pass Don't ask for password (useful for -k)
-p PASSWORD, --password PASSWORD
Password to authenticate with
-H [LMHASH:]NTHASH, --hashes [LMHASH:]NTHASH
NT/LM hashes, format is LMhash:NThash
--aes-key hex key AES key to use for Kerberos Authentication (128 or 256 bits)
-k, --kerberos Use Kerberos authentication. Grabs credentials from .ccache file (KRB5CCNAME) based on target parameters. If
valid credentials cannot be found, it will use the ones specified in the command line
Each JSON entry looks like this:
{
"computer": {
"fqdn": "TDC01.DOMAIN.local",
"ip": "192.168.1.71"
},
"share": {
"name": "IPC$",
"comment": "Remote IPC",
"hidden": true,
"uncpath": "\\\\192.168.1.71\\IPC$\\",
"type": {
"stype_value": 2147483651,
"stype_flags": [
"STYPE_IPC",
"STYPE_TEMPORARY"
]
},
"access_rights": {
"readable": true,
"writable": false
}
}
}- Feature suggested in impacket issue #1176 by @CaledoniaProject