This is a PyTorch implementation of our paper:
Ada-LISTA: Learned Solvers Adaptive to Varying Models
Aviad Aberdam, Alona Golts, Michael Elad
Abstract: Neural networks that are based on unfolding of an iterative solver, such as LISTA (learned iterative soft threshold algorithm), are widely used due to their accelerated performance. Nevertheless, as opposed to non-learned solvers, these networks are trained on a certain dictionary, and therefore they are inapplicable for varying model scenarios. This work introduces an adaptive learned solver, termed Ada-LISTA, which receives pairs of signals and their corresponding dictionaries as inputs, and learns a universal architecture to serve them all. We prove that this scheme is guaranteed to solve sparse coding in linear rate for varying models, including dictionary perturbations and permutations. We also provide an extensive numerical study demonstrating its practical adaptation capabilities. Finally, we deploy Ada-LISTA to natural image inpainting, where the patch-masks vary spatially, thus requiring such an adaptation.
Please cite this paper in your publications if this code helps your research:
@article{aberdam2020ada,
title={Ada-LISTA: Learned Solvers Adaptive to Varying Models},
author={Aberdam, Aviad and Golts, Alona and Elad, Michael},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.08456},
year={2020}
}
This repository contains:
- The main script is:
Main.py. You may find several examples below. - The data generating functions are in
generating.py, whiletraining.pycontains the training process of the models appears inmodels.py. eval.pyis the inference of a trained Ada-LISTA on the task of image inpainting.useful_utils.pycontains few technical functions.params.pycontains all the running parameters forMain.py.\figuresdirectory includes output figures.
The prerequisites are detailed in 'requirements.txt'.
We demonstrate the robustness of Ada-LISTA to three types of dictionary perturbations:
- permuted columns
- additive Gaussian noise
- completely random dictionaries
We demonstrate the ability of our model to handle complex and varying signal models while still providing an impressive advantage over both learned and non-learned solvers.
To run training on a small set of signals, use the following command:
python main.py -c0 -ntrain 1000 -epochs 10 -sigsnr 30
c0is the permuted columns scenariontrainis the number of training examplesepochsis the numbber of epochs for trainingsigsnris the SNR of the signal
This performs training with an increasing number of unfoldings as the sample figures in \figures show
To run training on a small dataset with the noisy dictionary scenario, use the following:
python main.py -c1 -ntrain 1000 -epochs 10 -sigsnr 30 -n 20
c1is the noisy dictionary scenarionis the SNR of the dictionary
To run training on a small dataset with the random dictionary scenario, use the following:
python main.py -c2 -ntrain 1000 -epochs 10 -sigsnr 30
c2is the random dictionary scenario
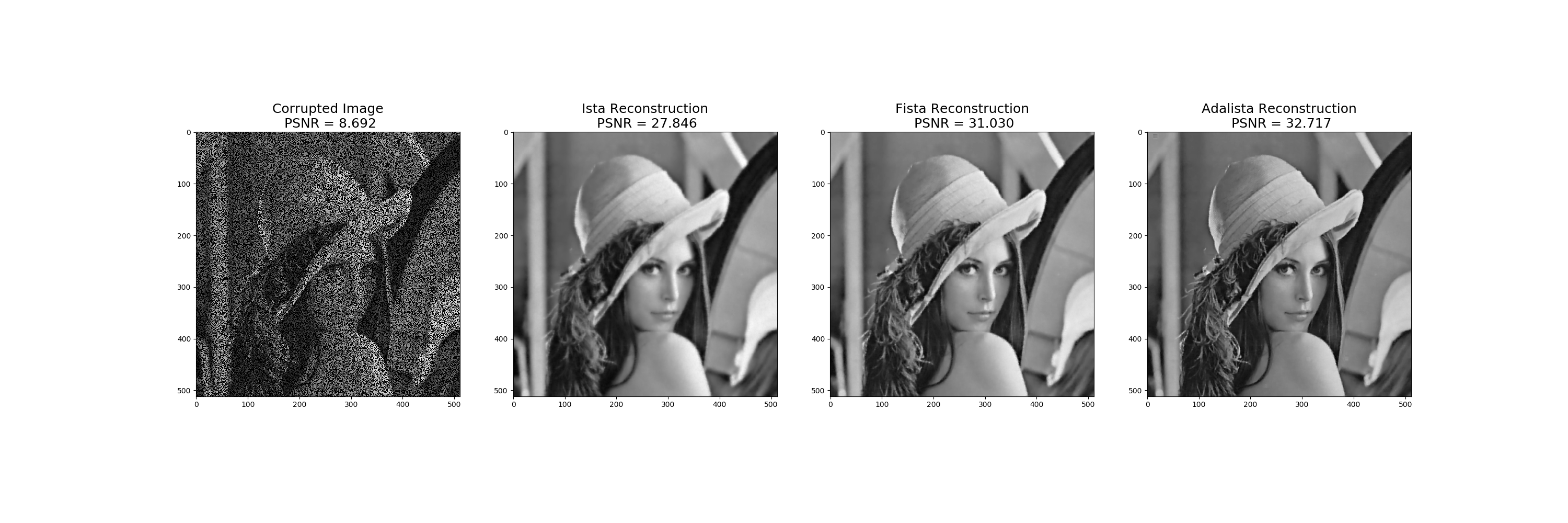
We demonstrate the use of Ada-LISTA on natural image inpainting, which cannot be directly used with hard-coded models as LISTA. We show a clear advantage of Ada-LISTA versus its non-learned counterparts.
In \saved_models_inpainting, there exists a trained Ada-LISTA model.
To train a new model with 10 unfoldings, simply run the following:
python main.py -c3 -tstart 10 -tstep 1 -tend 11
c3is the image inpainting scenariotstartis the initial number of unfoldingststepis the increase in unfoldings during trainingtendis the final number of unfoldings
To evaluate Ada-LISTA on set11 and compare to ISTA and FISTA, run the following:
python eval.py