$ docker-compose pull
$ docker-compose up -d
$ pytest
(Code is commented)
- Classes:
- Race
- Car
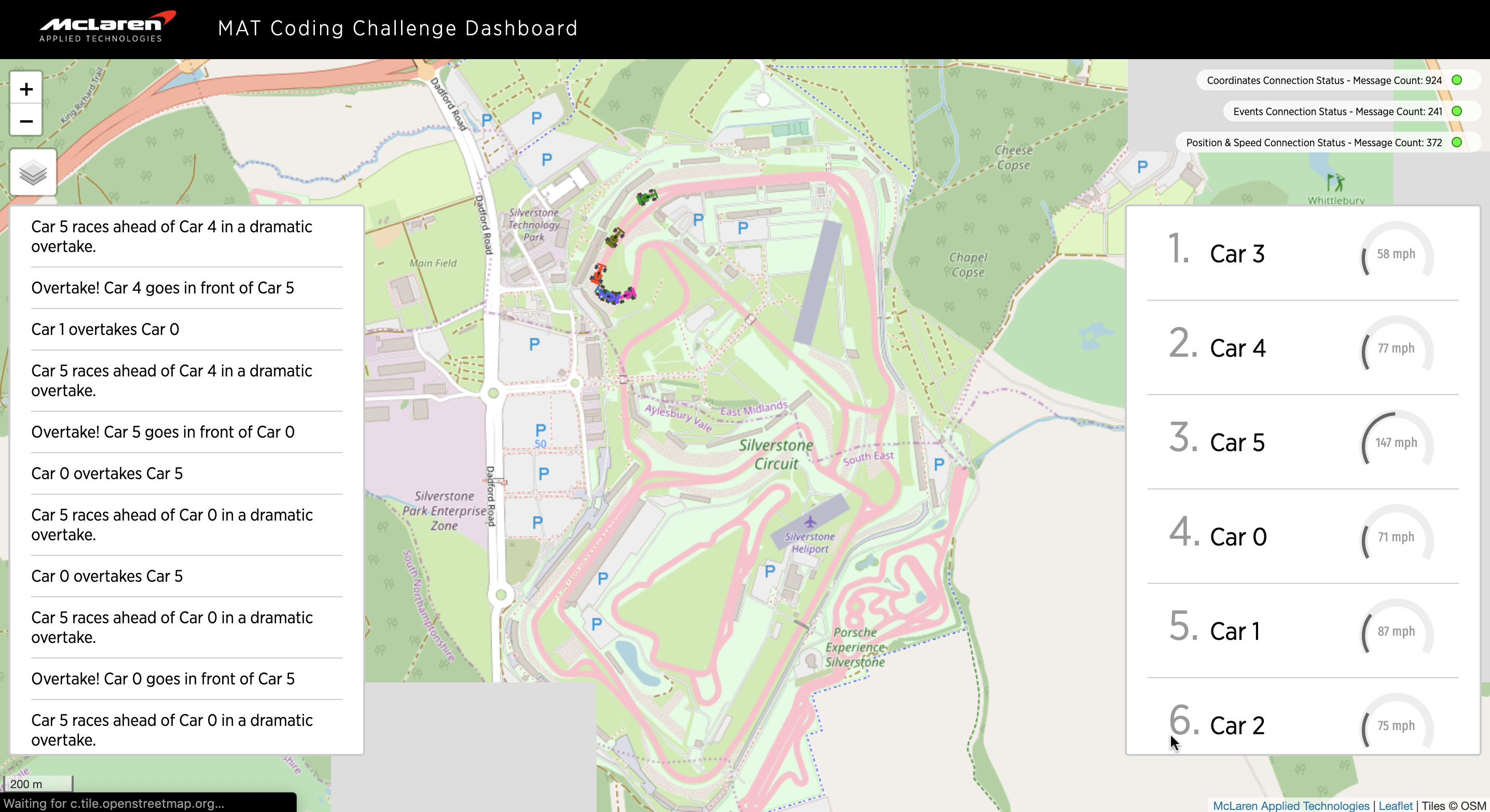
- The client susbcribes to the
carCoordinatestopic - The race class updates all the cars
- If the car does not exist, a car is created and then updated
- Car Position is determined by calculating total distance travelled
- The speed (mph) is calculated by using two consectuive
carCoordinateupdates. The distance is calculated by using thegeodesicfunction which takes in two coordinates. - Race class exposes a callback to the car class which publishes messages to the MQTT Client.
- Every time, all six the cars are updated, the speed and position of each car is published
- An event is published by tracking car positions and is sent when two cars swaped places
- All cars are following a racing line so I can calculate position by using total distance travelled
- No cars will be going in reverse
- All cars start at the same location
The purpose of this challenge is for you to demonstrate
- write and structure a simple backend application in an appropriate language of your choice
- parse and transform streamed telemetry data
- deliver a component to integrate into a stack of technologies
Feel free to use any libraries, frameworks or dependencies you want in order to achieve the task.
Please include instructions on how to build and run your code, any tests you've written and some text explaining what you did.
If you are already familiar with the underlying technologies we hope that it won't take you more than a couple of hours to get your application up and running.
Real-time data from a Formula 1 race has been recorded and streamed into our system. We want to use that data in order to increase fan engagement by providing a live visualisation.
Raw telemetry data is arriving via MQTT. A basic front-end application has been developed to visualise F1 cars going around a track. It can also display an event stream and car status information such as speed and position, but currently it is not receiving this information.
Please develop a data processing application which subscribes to the provided MQTT broker and consumes data from the following MQTT topic with the format shown:
-
carCoordinates
{ timestamp: number, carIndex: number, location: { lat: float, long: float } }
e.g.
{ "timestamp": 1541693114862, "carIndex": 2, "location": { "lat": 51.349937311969725, "long": -0.544958142167281 } }
It should then publish aggregated and enriched data on the following MQTT topics using the format described:
-
carStatus
{ timestamp: number, carIndex: number, type: string<SPEED|POSITION>, value: number }
e.g.
{ "timestamp": 1541693114862, "carIndex": 2, "type": "POSITION", "value": 1 } -
events
{ timestamp: number, text: string }
e.g.
{ "timestamp": 1541693114862, "text": "Car 2 races ahead of Car 4 in a dramatic overtake." }
All these topics will then be forwarded via a gateway-like MQTT-to-WebSocket service to the frontend application.
Start all components:
$ docker-compose pull
$ docker-compose up -d
Creating network "mat-coding-challenge_default" with the default driver
Creating broker ... done
Creating source_gps ... done
Creating mqtt-to-websocket ... done
Creating webapp ... doneOpen (http://localhost:8084)
Test the setup with mosquitto_pub or a similar MQTT client:
$ mosquitto_pub -t events -f examples/event.json
$ mosquitto_pub -t carStatus -f examples/position.json
$ mosquitto_pub -t carStatus -f examples/speed.jsonYou should now see a car's position and an event in the webapp.