#Open the IDE
#The first program for any programming language is “Hello World”
print ("Hello World")
# Execute
Hello World
# Integer
# int 5 56 69 0
int = 5 56 69 0
# Float
# float 9.45 0.55
float = 9.45 0.55
# Boolean
# bool True False
# String
# str "One" "Ahsan"
str = "One" , "Ahsan"
# Declaring a variable
# Whenever you use = you are assigning a value to some variable
#For example we use an integer
a = 1
print (a)
# Execute
1
# Re-assigning string to the same variable
a = "Ahsan"
print (a)
# Execute
Ahsan
#Concatenate Variables a & b
a = "Ahsan"
b = 1989
print (a+b)
# Execute
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "python", line 4, in <module>
TypeError: must be str, not int
# We got an error becasue we cannot add an integer & a string
# Hence we will convert integer to a string
# Use str function
print (a+str(b))
# Execute
Ahsan1989
# If we want to add a space between an integer and string
# Use " "
print (a+" "+str(b))
# Execute
Ahsan 1989
#Deleting a variable
# Delete b
del b
print (a+" "+str(b))
# Execute
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "python", line 8, in <module>
NameError: name 'b' is not defined
# b gets deleted hence the above NameError
#Accessing value in strings
a = "Ahsan"
print(a[0])
# Execute
A
# 0 is the first position in the variable
# Same can be done with multiple variables
a = "Ahsan"
b = "Will be teaching you python"
c = "How cool is that?"
print(a[0:5],b[0:20],c[0:8])
# Execute
Ahsan Will be teaching you How cool
# A list is a container type for storing different base types in Python
# also called an array
# List can be changed
list1 = [1, 2, 4]
list2 = ["Ahsan", "Anis", 1989]
# Accessing different values in a list
print(list1[1])
# Execute
2
print(list2[0:1])
# Execute
['Ahsan']
# Tuples are like lists but are immutable meaning they cannot be changed
tuple1 = (1, 2, 4)
tuple2 = ("Ahsan", "Anis", 1989)
print(tuple2[0:1])
# Execute
('Ahsan',)
# Dictionary is an immutable data type such as strings, numbers, or tuples
dict = {'Name': 'Ahsan', 'Age': 28, 'Position': 'Data Scientist'}
print (dict['Name'], dict['Age'], dict['Position'])
# Execute
Ahsan 28 Data Scientist
# Can also be written like this
dict = {'Name': 'Ahsan', 'Age': 28, 'Position': 'Data Scientist'}
print ("dict['Name']: ", dict['Name'])
print ("dict['Age']: ", dict['Age'])
print("dict['Position']:", dict['Position'])
# Execute
dict['Name']: Ahsan
dict['Age']: 28
dict['Position']: Data Scientist
# An array is a 1 dimensional data structure also known as a scalar
arr = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500]
print (arr[1:4])
# Execute
[200, 300, 400]
# A A matrix is a 2 dimensional data structure
matrix = [['Ahsan',8,8,8,8,8],
['Anis',9,9,9,9,9],
['Data',0,0,0,0,0],
['Scientist',1,1,1,1,1]]
print (matrix)
# Execute
[['Ahsan', 8, 8, 8, 8, 8], ['Anis', 9, 9, 9, 9, 9], ['Data', 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], ['Scientist', 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]
# Addition
a = 100
b = 10
print (a+b)
# Execute
110
# Subtraction a-b = 90
# Multiplication a * b = 1000
# Division a / b = 10
# Modulus a % b = 0 , b % a = 10
# Exponent a**b = 100000000000000000000
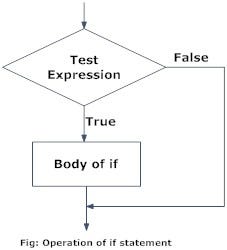
# If statetemnt is a boolean expression followed by one or more statements
# Boolean statement are either True or False
a = 100
if a > = 10:
print ("Thats a big number")
# Execute
Thats a big number
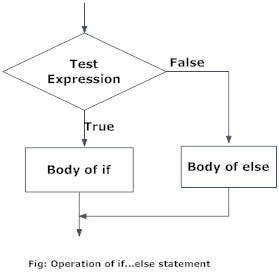
#If statement runs like usual, Else statement run if the first statement is False
a = 9
if a >= 10:
print ("Thats a big number")
else:
print ("Not a big number")
# Execute
Not a big number
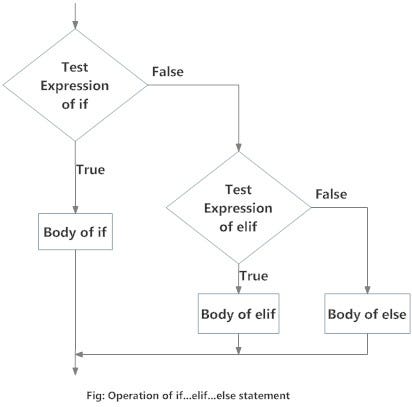
# Elif statement is a statement which you put after if statement
a = 1
if a > 0:
print ("Thats a big number")
elif a == 0:
print ("Not a big number")
else:
print ("Put another number")
# Execute
Thats a big number
a = 0
if a > 0:
print ("Thats a big number")
elif a == 0:
print ("Not a big number")
else:
print ("Put another number")
# Execute
Not a big number
a = -2
if a > 0:
print ("Thats a big number")
elif a == 0:
print ("Not a big number")
else:
print ("Put another number")
# Execute
Put another number
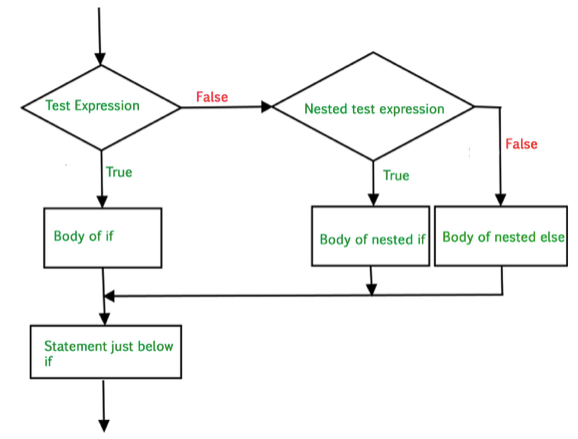
# An if, else, elif statement within an if, else, elif statement is called a nested if statement
num = float(input("Enter a number: "))
if num >= 0:
if num == 0:
print("Zero")
else:
print("Positive number")
else:
print("Negative number")
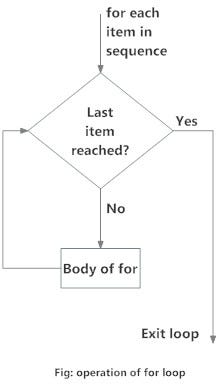
# a for loop executes till the last statement is reached
numbers = [1, 2, 2, 8, 4]
sum = 0
for val in numbers:
sum = sum+val
print("The sum is", sum)
# Execute
('The sum is', 17)
# Exactly like for loop, just that the else statement is printed at the end
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
for i in numbers:
print(i)
else:
print("All numbers printed.")
# Execute
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
All numbers printed.
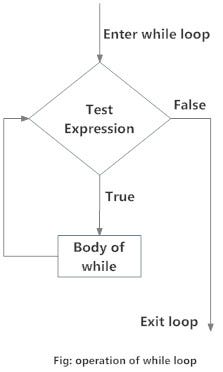
# a while loop iterates the statement as long as the statement is True
number = 0
while (number <= 10):
print 'The count is:', number
number = number + 1
print "All numbers printed"
# Execute
The count is: 0
The count is: 1
The count is: 2
The count is: 3
The count is: 4
The count is: 5
The count is: 6
The count is: 7
The count is: 8
The count is: 9
The count is: 10
All numbers printed
# Same as while loop, else statement is executed when logic is false
counter = 0
while counter <= 10:
print("loop")
counter = counter + 1
else:
print("end loop")
# Execute
loop
loop
loop
loop
loop
loop
loop
loop
loop
loop
loop
end loop
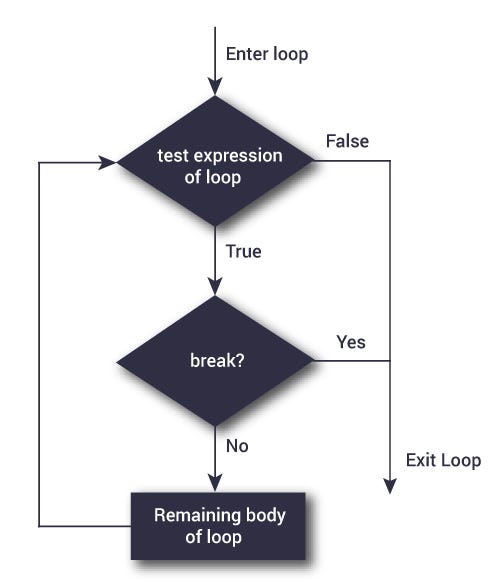
# Break statement is used to stop the loop in its tracks
for val in "Ahsan":
if val == "n":
break
print(val)
print("loop end")
# Execute
A
h
s
a
loop end
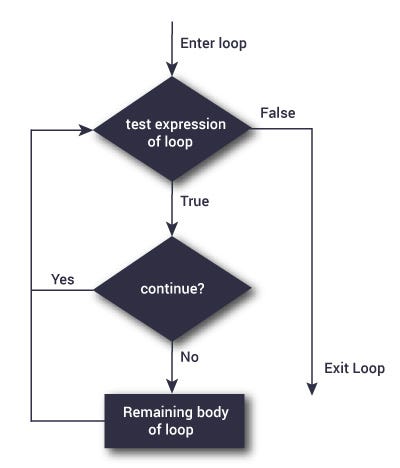
# Continue statement unlike break continues to print the statement till it finishes
for val in "Ahsan":
if val == "a":
continue
print(val)
print("loop end")
# Execute
A
h
s
n
loop end







