Wiki | Gallery | Quickstart | Status
Fablish is deprecated (and not maintained atm) in favor of aardvark.media.
This library provides utilities for building Elm-style [1] applications in .NET. In contrast to Fable [2], which uses a F# to JS compiler, this library runs directly in your favorite CLR. To stay compatible, we reused Fable-arch's API and replaced the virtualdom backend with a custom code generator, which creates the HTML DOM via React [3].
Fablish is useful if your use case looks like:
- you want purely functional user interfaces
- you want to profit from web technology and tooling
- you want solid technology for rendering your ui - browsers are superfast ;)
- you still want native .net programs since your application state cannot be run in the broser alone (e.g. you are rendering several GBs of data, as we do in other projects, based on the Aardvark rendering platform [10].
module TestApp =
type Model = int
type Action = Inc | Dec
let update (env : Env<Action>) (m : Model) (a : Action) =
match a with
| Inc -> m + 1
| Dec -> m - 1
let view (m : Model) : DomNode<Action> =
div [] [
text (sprintf "current content: %d" m)
br []
button [onMouseClick (fun _ -> Inc)] [text "increment"]
button [onMouseClick (fun _ -> Dec)] [text "decrement"]
]
let app =
{
initial = 0
update = update
view = view
onRendered = Script.ignore
subscriptions = Subscriptions.none
}
The overall architecture is:
- Elm architecture similar to fable-arch [8]
- Fable-style API for building views
- JavaScript code generator for building React DOM
- WebSocket via Suave [7] provides DOM to static webpage
- the webpage utilizes WebSocket and React to update and render the DOM
- the overall application can either be fully hosted inside a browser, or by using a chromium window (which is included).
Differences to Fable:
- altough the signature is very similar to fable-arch (in fact i copied the Fable.Helpers.Virtualdom and changed some bits), some features of fable-arch are implemented differently (mostly for historical reasons). Still, fablish should feel quite similar to fable-arch and learning fablish is therefore much easier,
Differences to elm:
- instead of returning commands, in fablish commands can be pushed into a environment which is passed into the update function. The effects of this change are not totally clear yet, however for the moment it works quite good.
ChromiumUtilities.unpackCef() // downloads CEF build if not already present
Chromium.init argv // initialize CEF runtime (mind argv being the executable arguments as usual)Either use application setup to spawn a window with embedded Chrome and your UI:
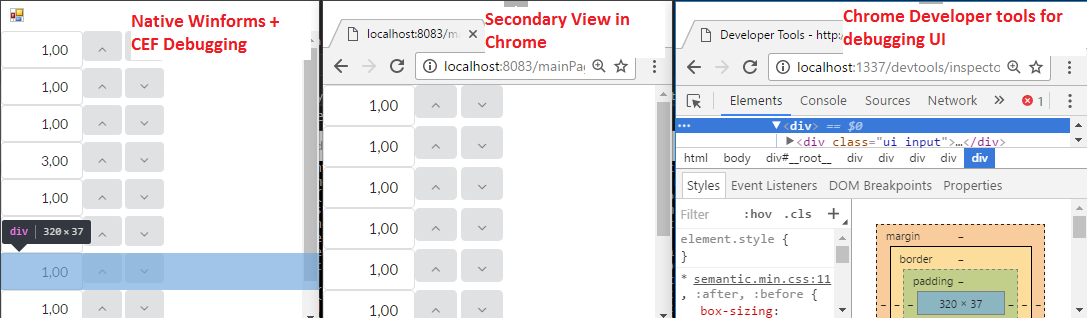
let browser = Chromium.runControl "8083" app // start websocket hosting app on port 8083, i.e. UI is available at localhost:8083/mainPage and can be debugged by using chrome on localhost:1337
use w = new Form()
w.Controls.Add browser
w.Width <- 800
w.Height <- 600
Application.Run(w) or use a stand-alone server:
Fablish.runLocally "8083" app // run websocket on port 8083 and serve website requests on localhost:8083 while a debug web page is available for chrome on localhost:1337In both cases your application can be debugged using Chrome debugging tools:
- run
build.cmdorbuild.sh(F# 4.0 [9] and .net or mono needs to be installed) - you can also use the prebuilt package currently available here: https://vrvis.myget.org/feed/aardvark_public/package/nuget/Fablish
Fablish-hmr [4] provides webpack-style [5] interactive programming by utilizing F# compiler services. The following video shows off this feature: youtube video on hmr