Read these instructions carefully. Understand exactly what is expected before starting this Sprint Challenge.
This challenge allows you to practice the concepts and techniques learned over the past sprint and apply them in a concrete project. This sprint explored some advanced React topics ⚛️. During this sprint, you studied class components, the component lifecycle and class component lifecycle methods, custom hooks, and React Testing Library 🐙.
In your challenge this week, you will demonstrate your mastery of these skills by creating an app that will fetch data from an internal server using a class component, displaying that data, using a custom hook, and writing tests for your app.
This is an individual assessment. All work must be your own. All projects will be submitted to codegrade for automated review. You will also be given feedback by code reviewers the Monday after challenge submissions. For more information on the review process click here.
You are not allowed to collaborate during the sprint challenge. However, you are encouraged to follow the twenty-minute rule and seek support by dropping a 👋 in your help channel when needed.
Sprint challenges open at Midnight PST on Thursday and close at 5pm PST on Friday. You will receive feedback on what you have finished and submitted by 5pm when the submissions will be closed. No retakes will be accepted.
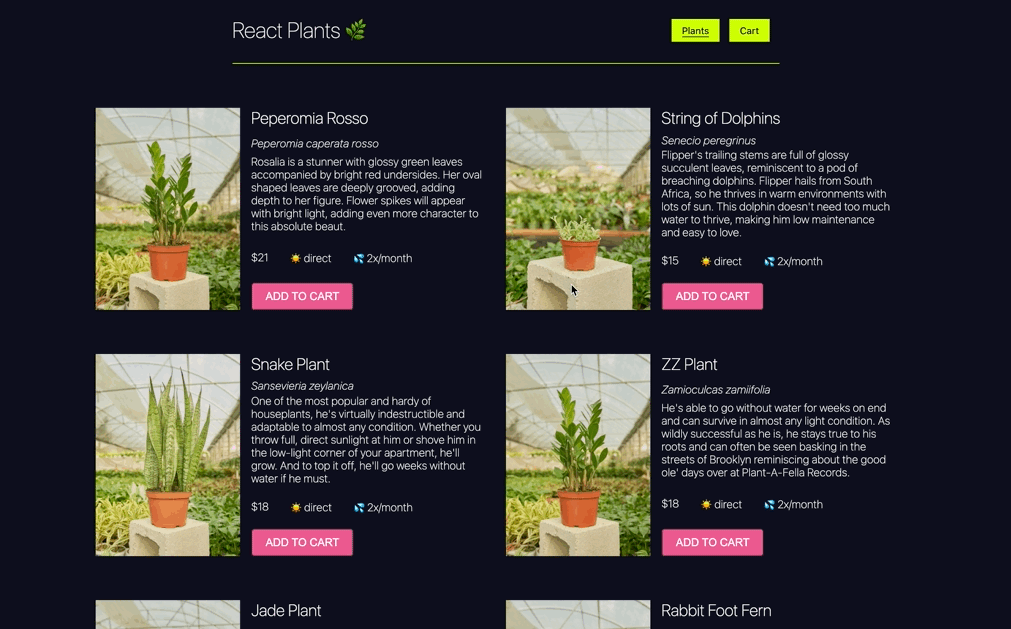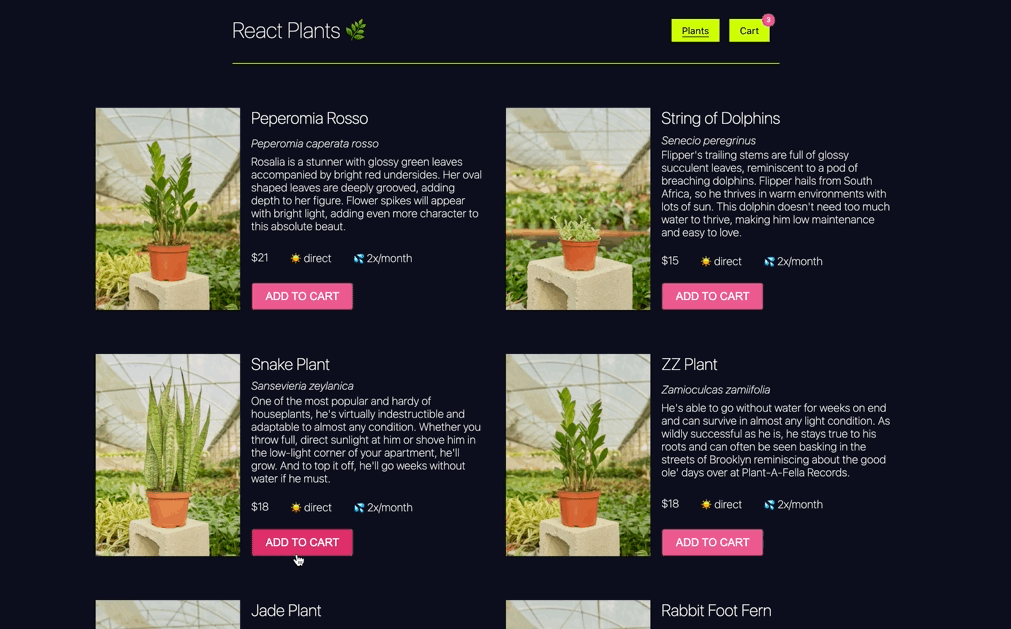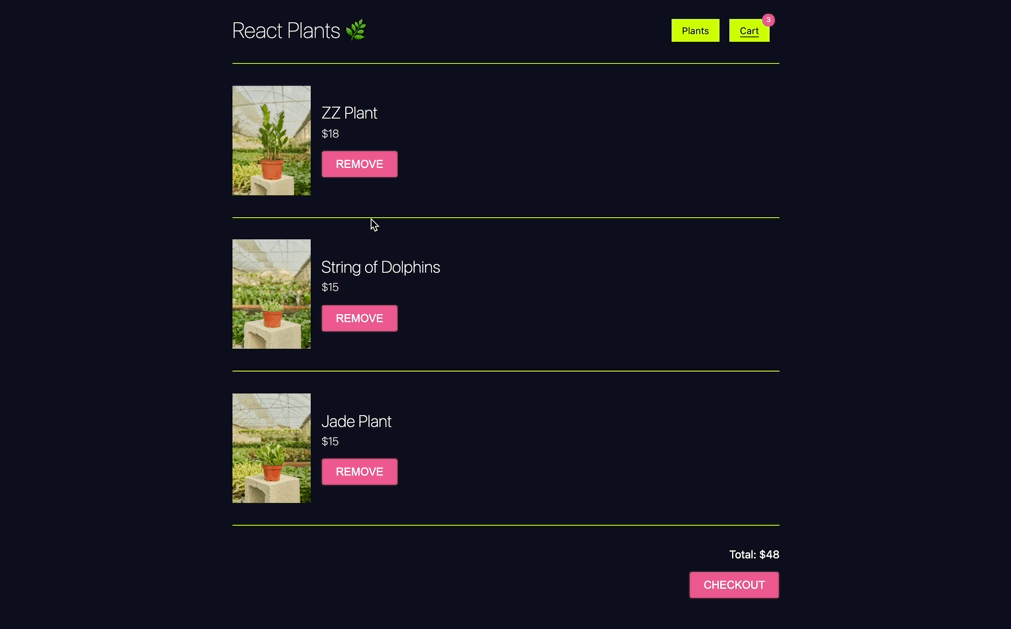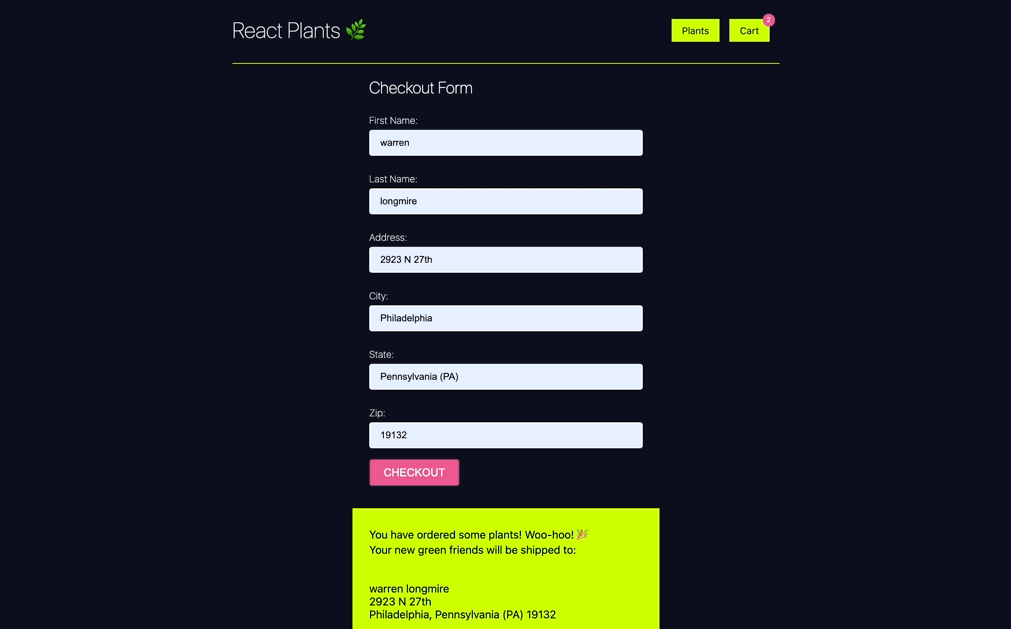
In this challenge, you will add class components to your a basic ecommerce site that allow you to request product data from a server and render that data. You will also implement the ablitity to add products to a shopping cart.
In meeting the minimum viable product (MVP) specifications listed below, your project should look like the solution examples below:
You will also need to build the two tests in the CheckoutForm.test.js file and make sure they are testing what the test title says they are.
- Run npm install to install your dependencies.
- Run npm start to run your frontend and backend code automatically.
- Note your backend code will run automatically when your run npm start. There is no need to seperately run a server.js file and no means to test the server through postman or the browser. Feel free to ignore any messages related to MSW or mock service workers.
In this project, you will build the retrieve data from a public api, add in a familiar custom hook and add in some tests.
- [GET] * to
http://localhost:3333/plants: returns an array of objects of the following form
{
name: "Peperomia Rosso",
id: 143,
scientificName: "Peperomia caperata rosso",
difficulty: "easy",
light: "direct",
img:
"https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/2781/9558/products/PEPEROMIA_ROSSO-1_800x.png?v=1587156590",
sizes: ["small"],
watering: 2,
description:
"Rosalia is a stunner with glossy green leaves accompanied by bright red undersides. Her oval shaped leaves are deeply grooved, adding depth to her figure. Flower spikes will appear with bright light, adding even more character to this absolute beaut.",
price: 21,
}Your finished project must include all of the following requirements.
Display a list of the plants from the server. This should be done in the class component PlantList. Unlike other projects, the local server used here can not be accessed through the browser. It is started automatically and without the need for starting a server.js file. Feel free to ignore any messages related to MSW or mock service workers. For this and the rest of your sprint challenges, test the functioning of the server directly through your axios calls.
- In the
PlantListclass component, fetch data from the server you now have running - the data can be fetched fromhttp://localhost:3333/plants. - Set the data to a state property called
this.state.plants. - The render function is already built and styled. Once the data is on the state, you will see the list of plants, and you will have the functionality to add a plant to the cart.
Nothing needs to be done here. You will have to navigate to the cart page in your app so you can go to the checkout form for the next step.
The form is working, but it is currently controlled by local stateful logic. We want to control this form with a custom hook.
-
Build a custom hook called
useForm, and use it in your CheckoutForm component to control the form's stateful logic. You do not need to use useLocalStorage to complete this task! localStorage is not necessary for this project. Simply reproduce all functionality for the in module 1 useForm custom hook to complete. -
Try and build it out first before you peek at the guided project. And do not copy/paste directly from the guided project!_
- Run the test runner and ensure that
src/components/CheckoutForm.test.jsis correctly called. - Fill out code necessary to test that that Checkout form renders without errors.
- Fill out code necessary to test that when all form inputs are filled with valid data, a success message appears.
- Make sure the tests are passing, and make sure you can cause the tests to fail purposefully, so that you know the tests are truly working.
- Again, unlike other projects, the local server used here can not be accessed through the browser. For this and the rest of your sprint challenges, test the functioning of the server directly through your axios calls.
- You are welcome to create additional files but do not move or rename existing files or folders.
- Do not alter your
package.jsonfile except to install extra libraries. - In your solution, it is essential that you follow best practices and produce clean and professional results.
- Schedule time to review, refine, and assess your work and perform basic professional polishing including spell-checking and grammar-checking on your work.
- It is better to submit a challenge that meets MVP than one that attempts too much and does not.
const plants = {{}, {}, {}} // with each object being a mock plant
test("displays plants in cart", () => {
const { getByText } = render(<ShoppingCart cart={plants} />)
...
})- Submit via Codegrade by committing and pushing any new changes to your main branch.
- Check Codegrade before the deadline to compare its results against your local tests.
- Check Codegrade on the days following the Sprint Challenge for reviewer feedback. For more information on how to access and read your feedback, check here
- New commits will be evaluated by Codegrade if pushed before the sprint challenge deadline.
Be prepared to demonstrate your understanding of this week's concepts by answering questions on the following topics. Add your answers below.
- What are the main differences between a class-based and a functional component?
The main differences is that a class-based component will require you to extend from React whereas functional components are basically plain javascript that can pass props. A class-based component can go more in depth in the components lifecycle.
- When does a componentWillMount function be called? What about a componentDidUpdate?
Component"Will/Did"Mount function will be called when a component first mounts onto the application and only then. Where as a componentDidUpdate function will be called on every time the application state changes.
- Define stateful logic.
Stateful logic is code within a component that stores, changes any state.
- What are the three step of creating a successful test? What is done in each phase?
The first step is making sure that the data that you are trying to test exists within the code and that it's referencing it correctly.
The second step is arranging/setting the values you'd like that data to be set to so that you can then conduct the actual test.
The third step, is setting the expectational result of the test. Whether that be if you are trying to get a fail message or a success message.