Advance Lane Detection
The goals / steps of this project are the following:
- Compute the camera calibration matrix and distortion coefficients given a set of chessboard images.
- Apply a distortion correction to raw images.
- Use color transforms, gradients, etc., to create a thresholded binary image.
- Apply a perspective transform to rectify binary image ("birds-eye view").
- Detect lane pixels and fit to find the lane boundary.
- Determine the curvature of the lane and vehicle position with respect to center.
- Warp the detected lane boundaries back onto the original image.
- Output visual display of the lane boundaries and numerical estimation of lane curvature and vehicle position.
Camera Calibration
The code for this step is contained in the first code cell of the IPython notebook located in "./code/pipeline.ipynb"
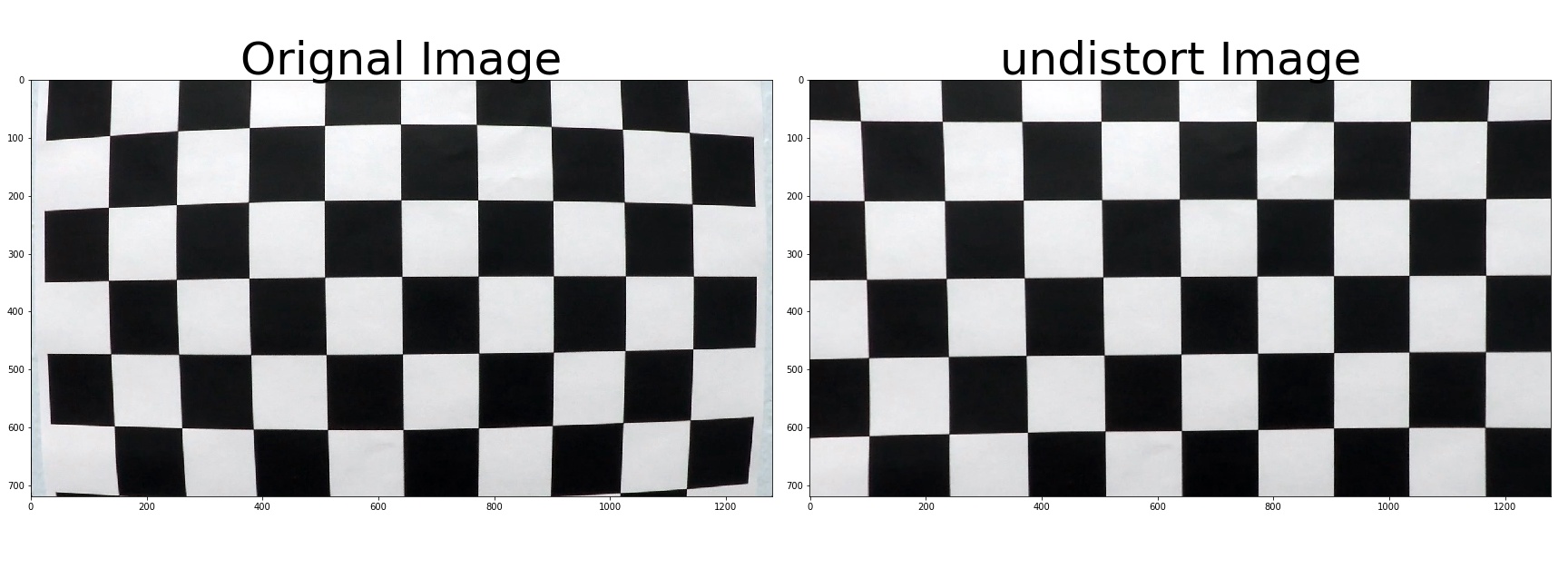
I start by preparing "object points", which will be the (x, y, z) coordinates of the chessboard corners in the world. Here I am assuming the chessboard is fixed on the (x, y) plane at z=0, such that the object points are the same for each calibration image. Thus, objp is just a replicated array of coordinates, and objpoints will be appended with a copy of it every time I successfully detect all chessboard corners in a test image. imgpoints will be appended with the (x, y) pixel position of each of the corners in the image plane with each successful chessboard detection.
I then used the output objpoints and imgpoints to compute the camera calibration and distortion coefficients using the cv2.calibrateCamera() function. I applied this distortion correction to the test image using the cv2.undistort() function and obtained this result:
Pipeline (single images)
1. Provide an example of a distortion-corrected image.
To demonstrate this step, I will describe how I apply the distortion correction to one of the test images like this one:
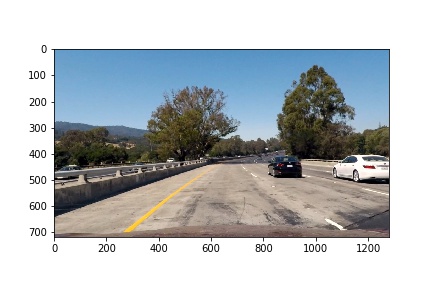
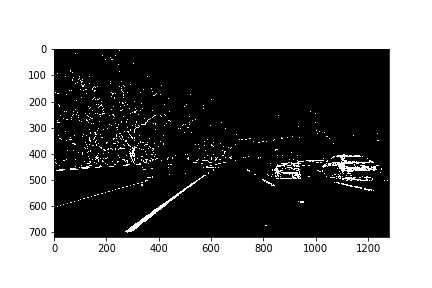
2. Threshold Binary Image
Under 'Gradient threshhold methods' section in ./code/pipeline.ipynb, I used a combination of the following threshold:
a. soble gradients of x, y
b. sobel gradient magitude of x,y
c. sobel gradient direction
d. s channel of HLS
Here's an example of my output for this step.
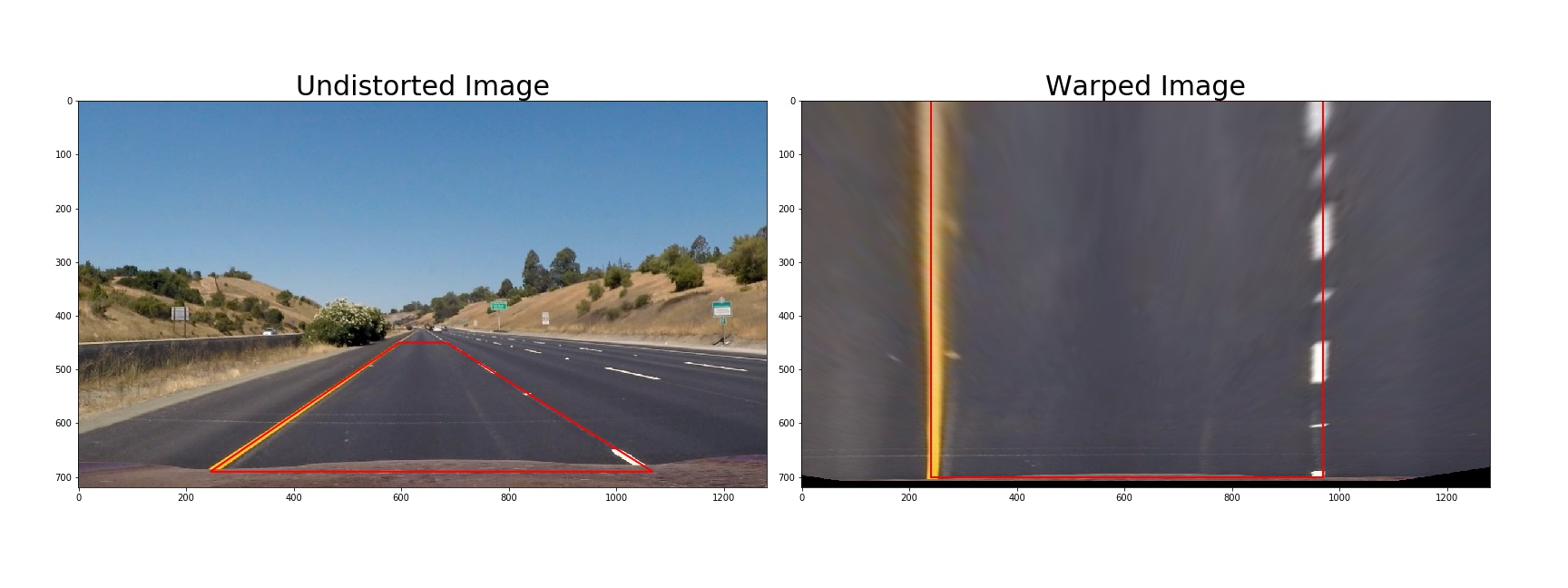
3. Perspective Transform
Under 'Image perspective transform' in ./code/pipeline.ipynp. The warperImage() function takes as inputs an image (image).
The source source and destination points are predefined and hardcoded.
The following source and destination points: source_points = np.float32([[245, 690],[596, 450], [685, 450], [1068, 690]]) dest_points = np.float32([[240, 700], [240, 0], [970, 0], [970, 700]])
| Source | Destination |
|---|---|
| 245, 690 | 240, 700 |
| 596, 450 | 240, 0 |
| 685, 450 | 970, 0 |
| 1068, 690 | 9670, 700 |
I verified that my perspective transform was working as expected by drawing the source and destination points onto a test image and its warped counterpart to verify that the lines appear parallel in the warped image.
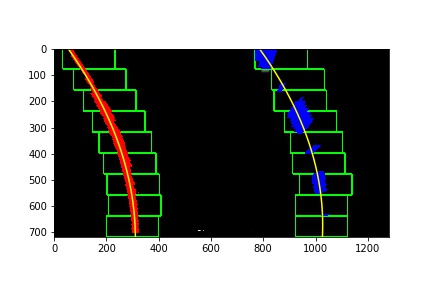
4. Identify lane lines and fit with a polynomial
Under 'Implement Sliding Windows and Fit a Polynomial' Section, method 'init_frame' is uesed to detect lane lines of image. First, we used histogram to find the base x position of lane lines, then using a sliding window (100, image.height/9) to search the line points. After searching all the interesting area, we polyfit the lane line points, then get the fit coefficients. A example of image looks like this:
5. Curature of lane lines
The following code section is used to caculate the curvature of lane lines once
y_eval = np.max(ploty)
left_curverad = ((1 + (2*left_fit[0]*y_eval + left_fit[1])**2)**1.5) / np.absolute(2*left_fit[0])6. Final lane detection
After the lanes of first frame of a video is detected, then we can use 'processing_frame' method to process each frame. A example of lane detected images looks like:
Pipeline (video)
Final video processing is under 'Video process pipeline' and 'Pipeline frame processing' section.
Discussion
- Noticed the lane detection is easily fail at the road surface where is not clean(misleading tree shadows, dust cover the lane lines...), a more robust gradient threshhold method is needed to filter out these noises.
- The solution is unable to detect road which is not flat. Maybe the slope of road data is needed in order to transform the road images into a flatten 2D space.