FixCache is a github app implementation of FixCache with git commit history.
FixCache can be useful for prioritizing verification, validation and testing resources on the most fault-prone files.
It keeps track of bug fix commits pushed to a configurable tracked branch of a repository and maintains a fix-sized cache of file entities most prone to bugs. The bug fix commits are identified by the fix keywords provided in the configuration.
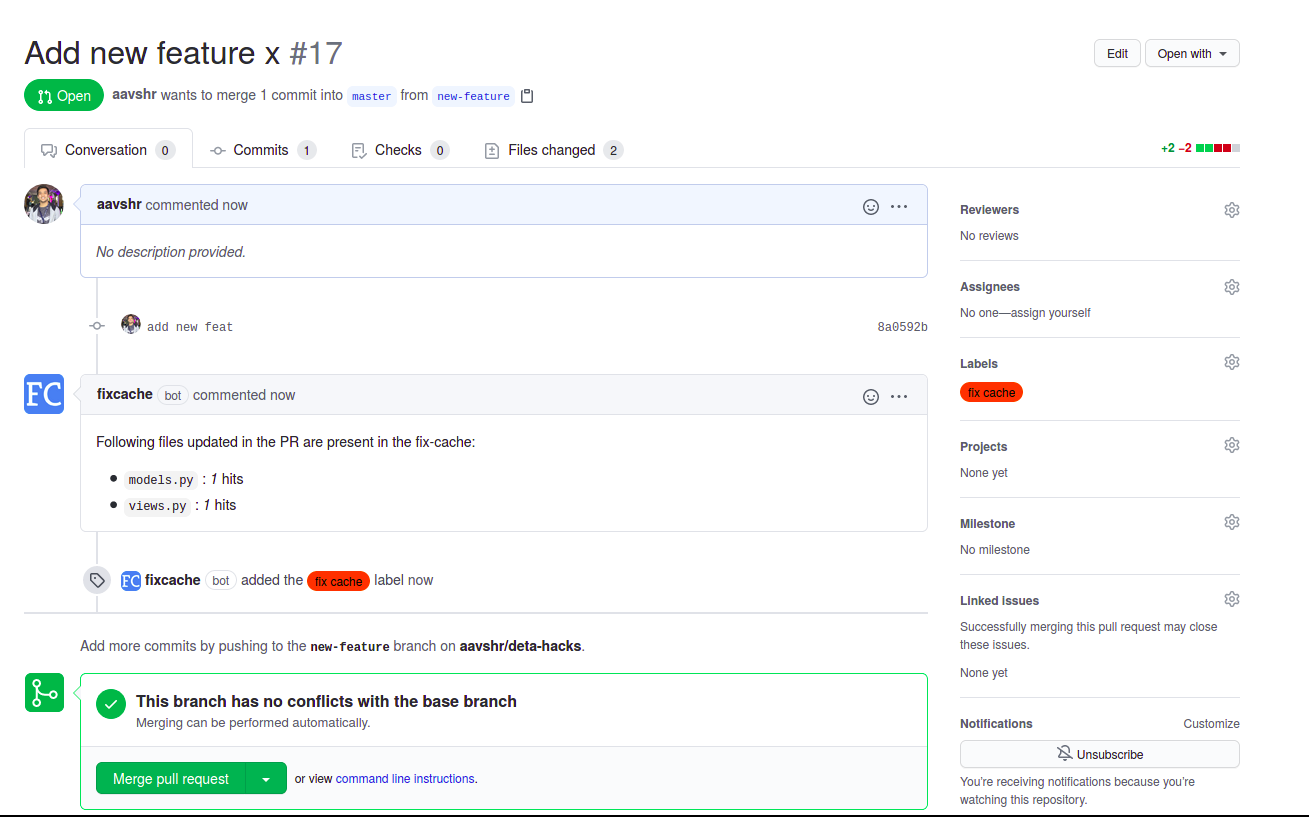
On pull requests, it fetches the cache and updates the pull requests with information about the files present in the cache if the pull request updates these files.
- it adds a label
fix cacheto the pull request. - it adds a comment with the filenames present in the cache and the respective number of cache hits.
The algorithm is executed over the commit history of the project. The paper assumes four kinds of localities that bugs occur in:
- Changed-entity locality : if an entity was changed recently, it will tend to introduce faults soon
- New-entity locality: if an entity has been added recently, it will tend to introduce faults soon
- Temporal locality: if an entity introduced a fault recently, it will tend to introduce other faults soon
- Spatial locality: if an entity introduced a fault recently, "nearby" entities will also tend to introduce faults soon
- Install it to your repositories from here
The app has access to the following repository permissions:
- Contents:
Read-only - Metadata :
Read-only - Pull requests:
Read & write
The app is subscribed to the following events:
Pull requestPush
The app (for now) uses a .env file for configuration. A sample config is shown in env.sample.
GITHUB_APP_ID: the github application idPRIVATE_KEY_PATH: the path to the private keyWEBHOOK_SECRET: the webhook secret for the app's webhook
CACHE_SIZE: the size of the fix cache i.e number of files stored in the cacheHISTORY_SIZE: the number of days to load commit history from on installationFIX_KEY_WORDS: Keywords in a fix commit eg. fix,fixedTRACKED_BRANCH: the main branch to track pushes onSKIP_PATHS: paths to skip/not store in the fix cache like test files
Following default values are used in the current version of the app:
CACHE_SIZE:25HISTORY_SIZE:30FIX_KEY_WORDS:fixTRACKED_BRANCH:masterSKIP_PATHS:test,.md
If this configuration is not suitable for your repositories, you can deploy your own FixCache with the required configuration.
FixCache is deployed on Deta micros. The following steps show how to deploy your own FixCache as a github app with custom configuration.
- Clone the repository with
git clone https://github.com/aavshr/fixCache.git.
This deployment is for Deta micros. You will need to have signed up for deta and the deta cli installed.
If you want to deploy on another platform, you will need to modify the code slightly and then set up the respective configuration for deployment to other platforms.
- After you have cloned the repository, change the directory to the cloned directory and enter in your terminal
$ deta newYou should see the output that the application has been created and the dependencies have been installed.
- After installing the app, enter
$ deta detailsYou should see details about your application in your output. The endpoint shown will be needed later to add as the webhook url in our github app.
- Lastly disable auth by entering:
$ deta auth disableWe will use a webhook secret to verify that the events are coming from github on our webhook endpoint.
A comprehensive guide on creating a github app is available here.
- Go to your developer settings (it's under settings on the dropdown menu when you click your profile on github) and create a new github app. Provide a name (and description if you want).
In Webhook URL, type the endpoint from the output to deta details.
Generate a long secure random string (there are services online that do this) and use that as the Webhook Secret. Keep hold of this secret as you will need it to set up the configuration later.
When choosing the permissions for the app, you will need to provide the app with following repository permissions:
- Contents:
Read-only - Metadata :
Read-only - Pull requests:
Read & write
The app is subscribed to the following events:
Pull requestPush
After creating the github app, go to your app's General settings and generate a private key.
Save the private key in the your cloned directory in a file. This is required for authentication.
Make sure you do not commit this file to a public repository.
App configuration (for now) is simply done through environment variables. Create a new file .env in the cloned directory and provide it with the following variables.
A sample env.sample is present in the repository to see the format of the file. Make sure you do not expose your .env file publicly.
GITHUB_APP_ID: the github app id, you can find this in your github app's general settings.PRIVATE_KEY_PATH: the path to the private key file you saved in the earlier step.WEBHOOK_SECRET: the webhook secret for the app's webhookCACHE_SIZE: the size of the fix cache i.e number of files stored in the cacheHISTORY_SIZE: the number of days to load commit history from on installationFIX_KEY_WORDS: Keywords in a fix commit separated by commas eg. fix,fixedTRACKED_BRANCH: the main branch to track pushes onSKIP_PATHS: paths to skip/not store in the fix cache like test files
First change the directory to the root of the cloned directory (if you are not there already) and deploy the changes with,
$ deta deployNext, deploy the configuration in the .env with,
$ deta update -e .envYou should see that the environment variables have been successfully updated.
The FixCache should be now be deployed completely and ready to function. You can install the app to your repositories in the Install App page of your github app.