A practical example of how to use RedisTimeSeries with Apache Kafka for analyzing time series data.
The blog post is coming soon. Meanwhile, here is a talk from RedisConf 2021 which covers this topic as well
Individual services:
-
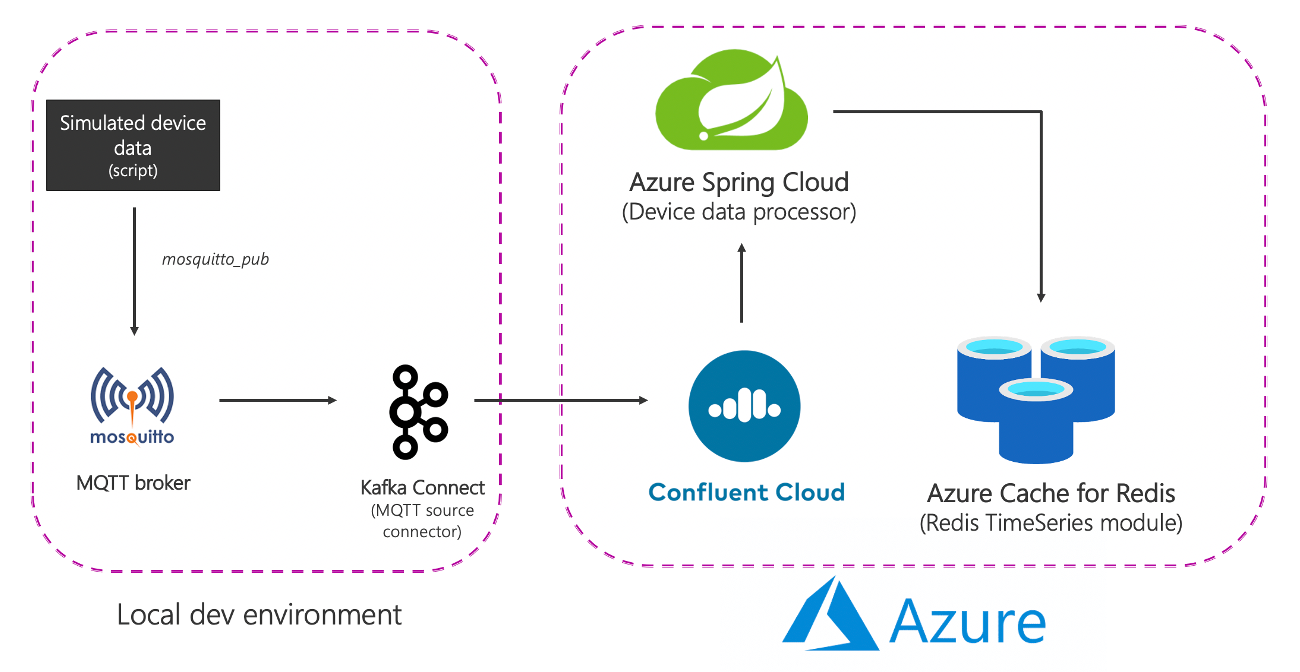
Source (local) components
- MQTT broker (mosquitto): MQTT is a de-facto protocol for IoT use cases. The scenario we will be using is a combination of IoT and Time Series - more on this later.
- Kafka Connect: The MQTT source connector is used to data from MQTT broker to a Kafka cluster.
-
Azure services
- Azure Cache for Redis Enterprise Tiers: The Enterprise tiers are based on Redis Enterprise, a commercial variant of Redis from Redis Labs. In addition to RedisTimeSeries, Enterprise tier also supports RediSearch and RedisBloom.
- Confluent Cloud on Azure: A fully-managed offering that provides Apache Kafka as a service, thanks to an integrated provisioning layer from Azure to Confluent Cloud.
- Azure Spring Cloud: Deploying Spring Boot microservices to Azure is easier, thanks to Azure Spring Cloud, which does all the heavy lifting so developers can focus on their code.
Imagine there are many locations, each of them has multiple devices and you're tasked with the responsibility to monitor device metrics - we will consider temperature and pressure. These metrics will be stored in RedisTimeSeries (of course!) and use the following naming convention for keys - <metric name>:<location>:<device>. For e.g. temperature for device 1 in location 5 will be represented as temp:5:1. Each time series data point will also have the following Labels (key value pairs) - metric, location, device. This is to allow for flexible querying as you will see in the upcoming sections.
Here are a couple of examples to give you an idea of how you would add data points using the TS.ADD command:
# temperature for device 2 in location 3 along with labels
TS.ADD temp:3:2 * 20 LABELS metric temp location 3 device 2
# pressure for device 2 in location 3
TS.ADD pressure:3:2 * 60 LABELS metric pressure location 3 device 2- A script produces simulated device data that is sent to the local MQTT broker.
- This data is picked up by the MQTT Kafka Connect source connector and sent to a topic in the Confluent Cloud Kafka cluster running in Azure.
- It is further processed by the Spring Boot application hosted in Azure Spring Cloud which then persists it to the Azure Cache for Redis instance.