Check out FILO2, a more scalable version of FILO.
This repository and COBRA contain source code and support material associated with the paper A Fast and Scalable Heuristic for the Solution of Large-Scale Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problems
-
Build and install the COBRA library
-
Clone the repository and build the algorithm
git clone https://github.com/acco93/filo.git
cd filo
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DENABLE_VERBOSE=ON
make -j
The are a number of build options that are disabled by default.
In order to enable an option XYZ, add -DXYZ=ON to the cmake command before calling make
Available options
ENABLE_VERBOSEoutput some information during the resolution.ENABLE_GUIcreates a GLFW window showing a graphical representation of the best found solution along with some information regarding move generators and recently accessed vertices, and another GLFW window showing the algorithm search trajectory. Some additional packages, e.g.libglfw3-dev, may be necessary to compile the code when this option is enabled.TIMEBASED_TERMINATIONallows you to specify a termination criterion based on a maximum number of seconds.
Once filo has been built, you can run it by giving as first mandatory argument the path to a compatible instance file.
As an example, if the executable is in the build directory and both cobra and filo projects are into a git directory in the user home
cd /home/user/git/filo/build
./filo /home/user/git/cobra/instances/X/X-n936-k151.vrp
An help menu explaining available optional command line arguments can be read by executing filo --help.
More examples on how to run the code can be found in the scripts directory.
How can I exactly reproduce the results shown in the results directory?
- Drop me an email and I will send you a link you can use to donwload a copy of the Ubuntu environment we used to run the code
- Unzip
env.tar.zipto obtainenv.tar docker image load -i env.tardocker run -t -i filo:20200804 /bin/bash- Executable and instances can be found in
/data
Note that filo executed within docker will not be as fast as filo executed on the native OS, however, this is the safest way if you want to check our results. For any other reason, consider using a native build.
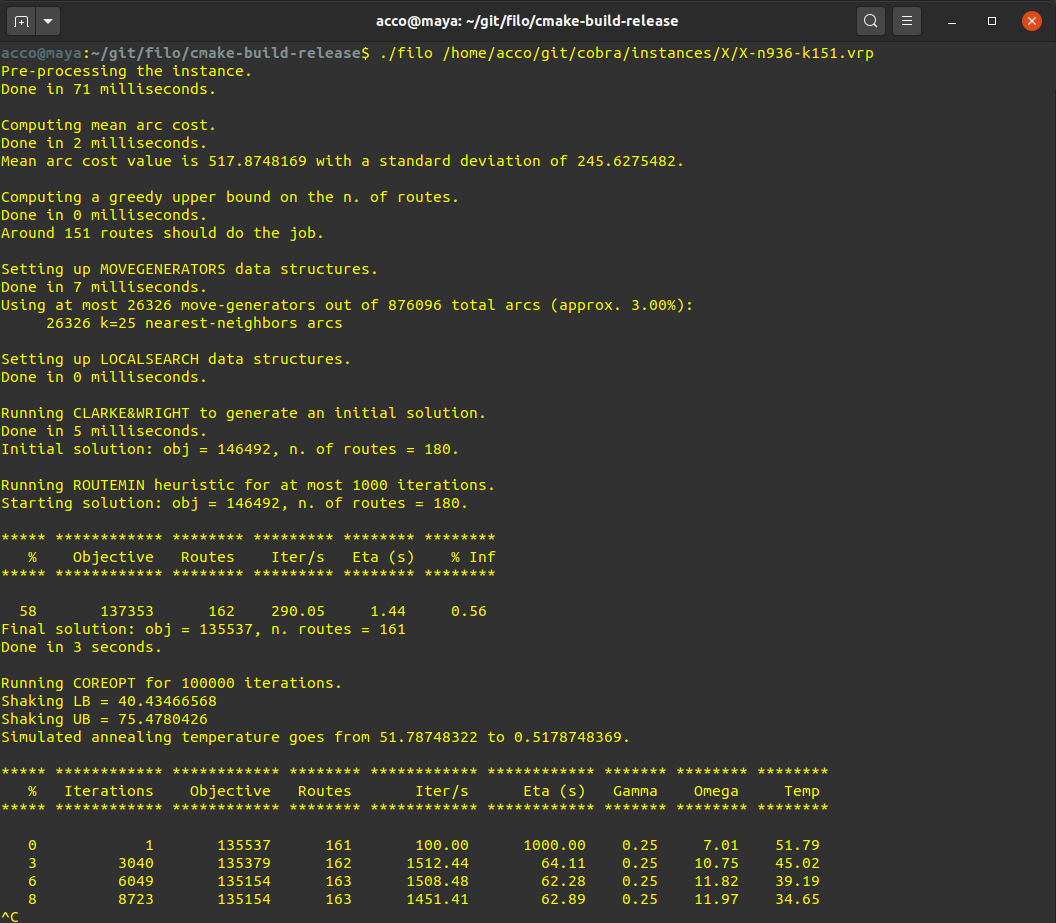
Console output (ENABLE_VERBOSE=ON). ROUTEMIN: % Inf = n. infeasible solution over number of performed iterations. COREOPT: Gamma = average sparsification factor, Omega = average shaking intensity.
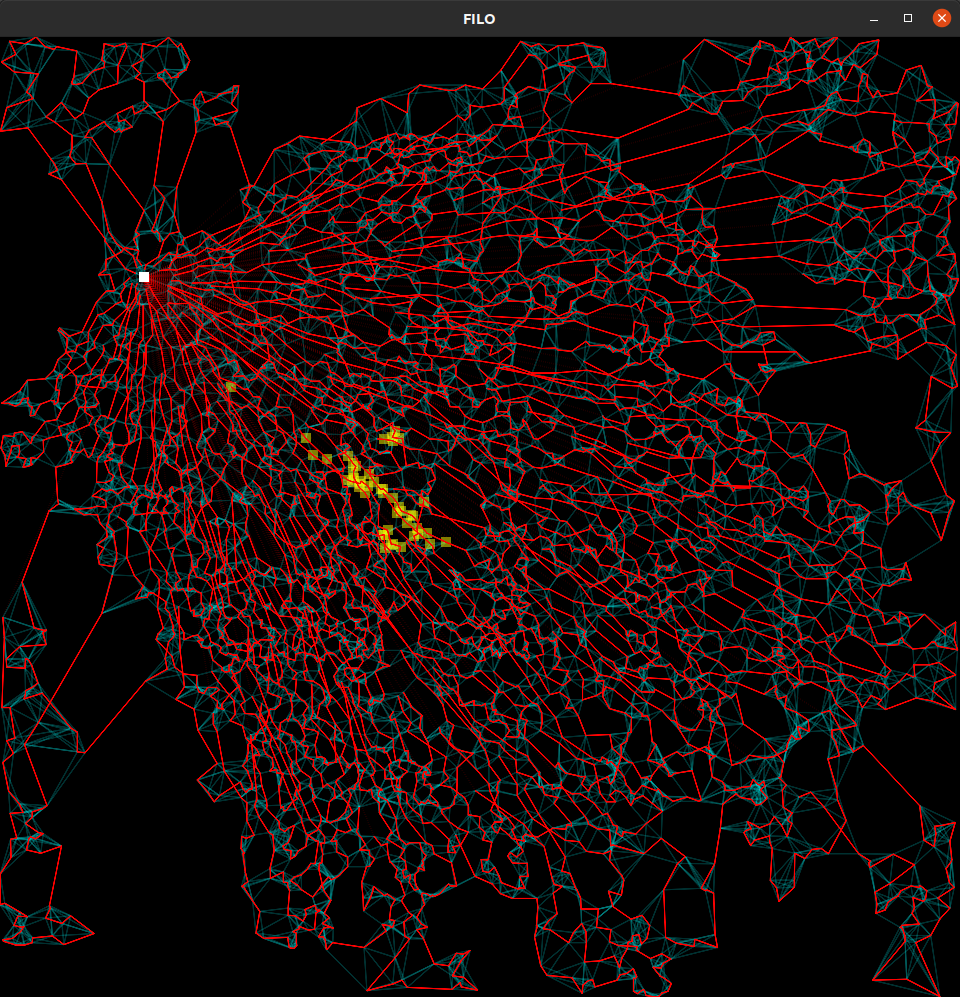
Solution representation (ENABLE_GUI=ON). Routes are shown in green-to-red shades, the redder the loaded.
Move generators are shown in cyan. The current area in which filo is working is identified by the yellow squares.
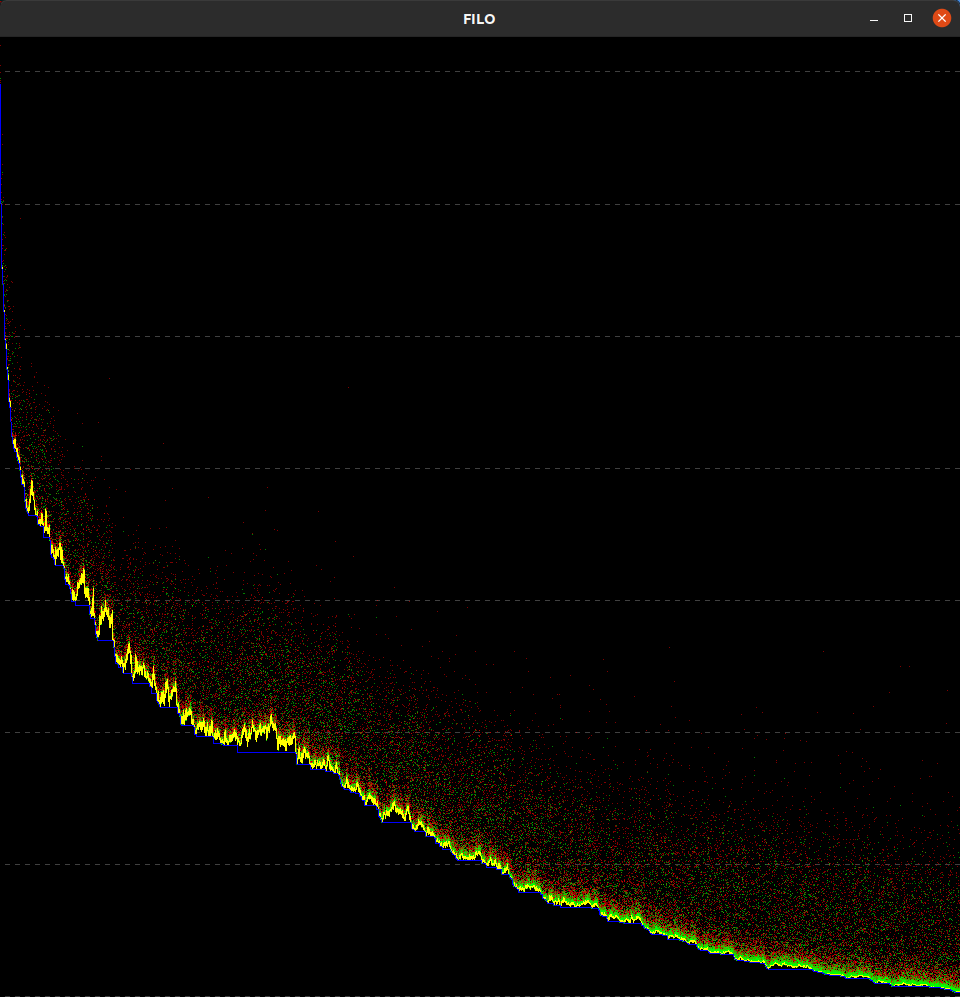
Search trajectory (ENABLE_GUI=ON). The best solution value is represented by the blue line while the current solution value by the yellow line. Red and green dots represent the value of the shaken solution and the re-optimized local optima respectively. Each horizontal dashed line identifies a 1% improvement of the gap with respect to the initial solution value.