Realtime Geolocation with Firestore & RxJS
npm install geofirex
# peer dependencies
npm install rxjs firebaseThe library is a lightweight client for the Firebase Web SDK that provides tools for wrangling geolocation data in Firestore. You need a Firebase project to get started.
// Init Firebase
import * as firebase from 'firebase/app';
firebase.initializeApp(yourConfig);
// Init GeoFireX
import * as geofirex from 'geofirex';
const geo = geofirex.init(firebase);Next, add some geolocation data in your database. A collection creates a reference to Firestore (just like the SDK), but with some extra geolocation tools. The point method returns a class that helps you create geolocation data.
const cities = geo.collection('cities');
const point = geo.point(40, -119);
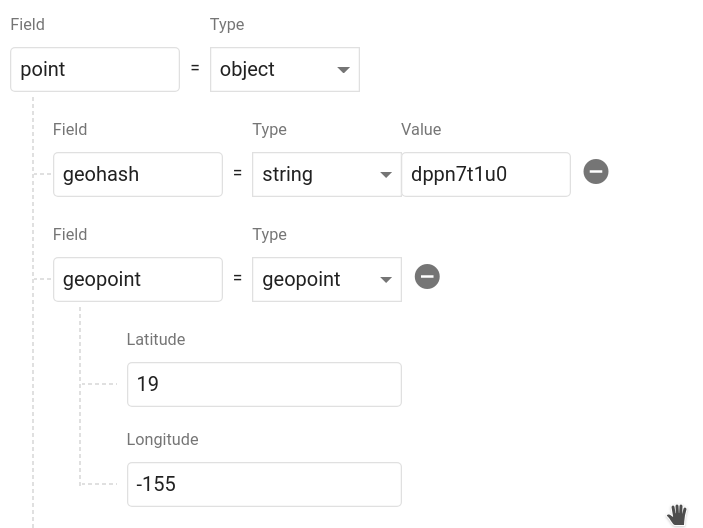
cities.add({ name: 'Phoenix', position: point.data });Calling point.data returns an object that contains a geohash string and a Firestore GeoPoint. It should look like this in your database. You can name the object whatever you want and even save multiple points on a single document.
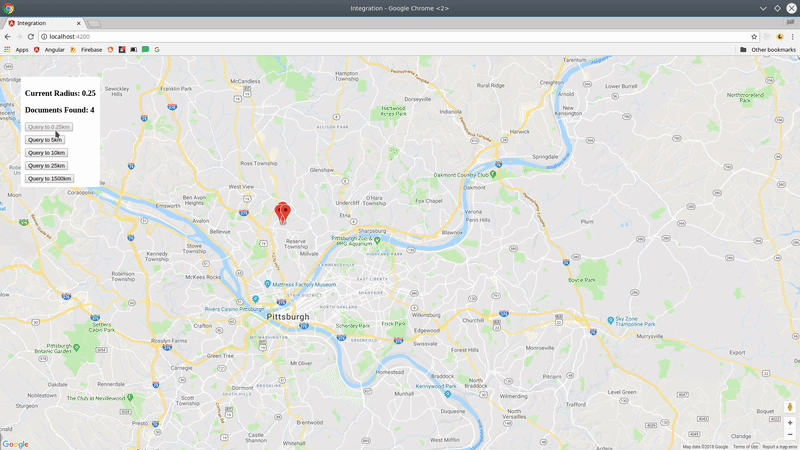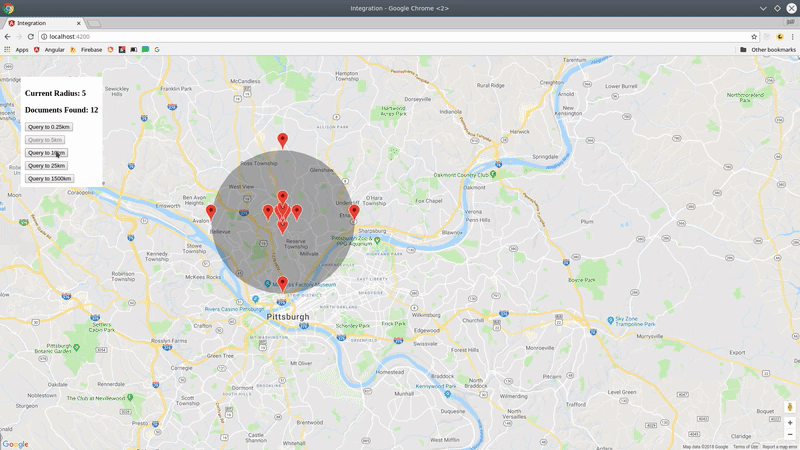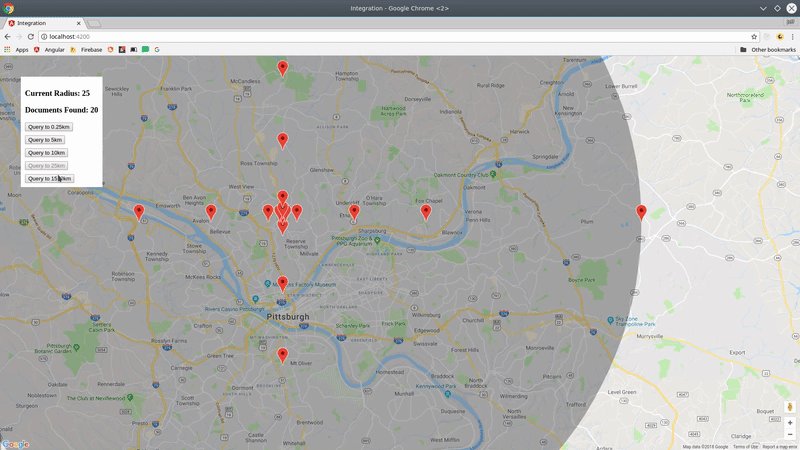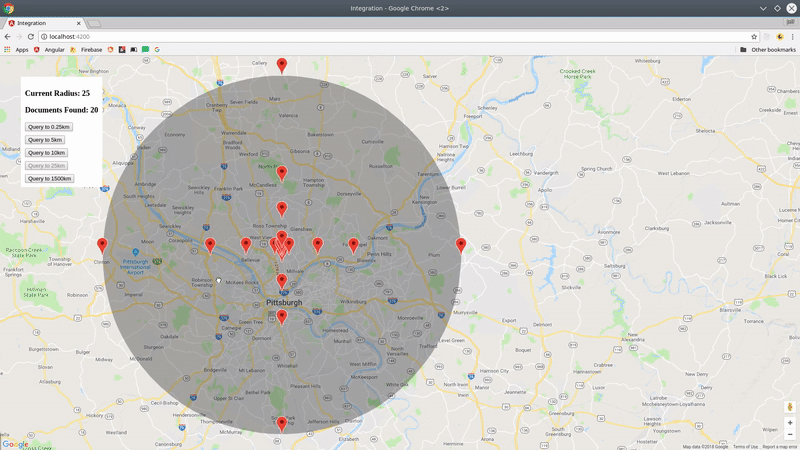
Now let's query Firestore for cities.position within 100km radius of a centerpoint.
const center = geo.point(40.1, -119.1);
const radius = 100;
const field = 'position';
const query = cities.within(center, radius, field);The query returns a realtime Observable of the document data, plus some useful metadata like distance and bearing from the query centerpoint.
query.subscribe(console.log);
// [{ ...documentData, queryMetadata: { distance: 1.23232, bearing: 230.23 } }]You now have a realtime stream of data to visualize on a map.
Creates reference to a Firestore collection that can be used to make geo-queries and perform writes If you pass an optional Firestore query function, all subsequent geo-queries will be limited to this subset of documents
Example:
const collection = geo.collection('cities');collection.within(center: GeoFirePoint, radius: number, field: string)
Query the parent Firestore collection by geographic distance. It will return documents that exist within X kilometers of the centerpoint.
Each doc also contains returns distance and bearing calculated on the query on the queryMetadata property.
Returns: Observable<object[]>
Write data just like you would in Firestore
collection.add(data)
Or use one of the client's conveniece methods
collection.setDoc(id, data)- Set a document in the collection with an ID.collection.setPoint(id, field, lat, lng)- Add a geohash to an existing doc
In addition to Geo-Queries, you can also read the collection like you would normally in Firestore, but as an Observable
collection.data()- Observable of document datacollection.snapshot()- Observable of Firestore QuerySnapshot
Returns a GeoFirePoint allowing you to create geohashes, format data, and calculate relative distance/bearing.
Example: const point = geo.point(38, -119)
point.hashReturns a geohash string at precision 9point.geoPointReturns a Firestore GeoPointpoint.geoJSONReturns data as a GeoJSONFeature<Point>point.coordsReturns coordinates as[latitude, longitude]point.dataReturns data object suitable for saving to the Firestore database
point.distance(latitude, longitude)Haversine distance to a pointpoint.bearing(latitude, longitude)Haversine bearing to a point
The goal of this package is to facilitate rapid feature development with tools like MapBox, Google Maps, and D3.js. If you have an idea for a useful feature, open an issue.
A custom RxJS operator that transforms a collection into a GeoJSON FeatureCollection. Very useful for tools like MapBox that can use GeoJSON to update a realtime data source.
const query = geo.collection('cars').within(...)
query.pipe( toGeoJSON() )
// Emits a single object typed as a FeatureCollection<Geometry>
{
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [...]
}Don't need a realtime stream? Convert any query observable to a promise by wrapping it with get.
import { get } from 'geofirex';
async function getCars {
const query = geo.collection('cars').within(...)
const cars = await get(query)
}It's possibe to build Firestore collections with billions of documents. One of the main motivations of this project was to make geoqueries possible on a queried subset of data. You can make a regular Firestore query on collection by passing a callback as the second argument, then all geoqueries will scoped these contstraints.
Note: This query requires a composite index, which you will be prompted to create with an error from Firestore on the first request.
Example:
const users = geo.collection('users', ref =>
ref.where('status', '==', 'online')
);
const nearbyOnlineUsers = users.within(center, radius, field);This package requires RxJS 6.2, but you can still use it with older versions without blowing up your app by installing rxjs-compat.
Example:
npm i rxjs@latest rxjs-compatFirestore writes cannot use custom classes, so make sure to call the data getter on the point.
const point = geo.point(40, -50);
// This is an ERROR
ref.add({ location: point });
// This is GOOD
ref.add({ location: point.data });const radius = new BehaviorSubject(1);
const cities = geo.collection('cities');
const points = this.radius.pipe(
switchMap(rad => {
return cities.within(center, rad, 'point');
})
);
// Now update your query
radius.next(23);The GeoJSON spec formats coords as [Longitude, Latitude] to represent an X/Y plane. However, the Firebase GeoPoint uses [Latitude, Longitude]. For consistency, this libary will always require you to use the latter format.