- 📄 Voice Chat with PDFs
- ⚙️ Prerequisites
- 🔮 Features
- 🏗️ Architecture
- 🔑 OpenAI API Key
- 🚀 Performance Improvements
⚠️ Important Notices- 🛠️ Setup Guide
- ❓ Facing Issues or Have Suggestions?
Voice Chat with PDFs is an open-source extension of run-llama/voice-chat-pdf, integrating advanced features like a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline with Supabase, Qdrant, Cohere, and OpenAI Realtime API for enhanced document interaction.
The project requires an OpenAI API key (user key or project key) that has access to the Realtime API.
Most features are free, even for commercial use.
-
User Authentication
- Sign up and sign in with user credentials for secure access.
-
Document Upload
- Upload documents for interaction.
- Preview mode to review documents before uploading.
-
Retrieval
- Generate embeddings for uploaded documents.
- Set top-n for similarity searches to find the most relevant chunks.
- Machine searches through generated embeddings to return relevant chunks.
- Set top-k for reranking results using Cohere to enhance relevance.
-
Interactive Playground
- Engage with documents using voice commands.
- Choose between Push-to-Talk or Open Mic interaction modes.
- Receive voice responses from the machine for a seamless experience.
-
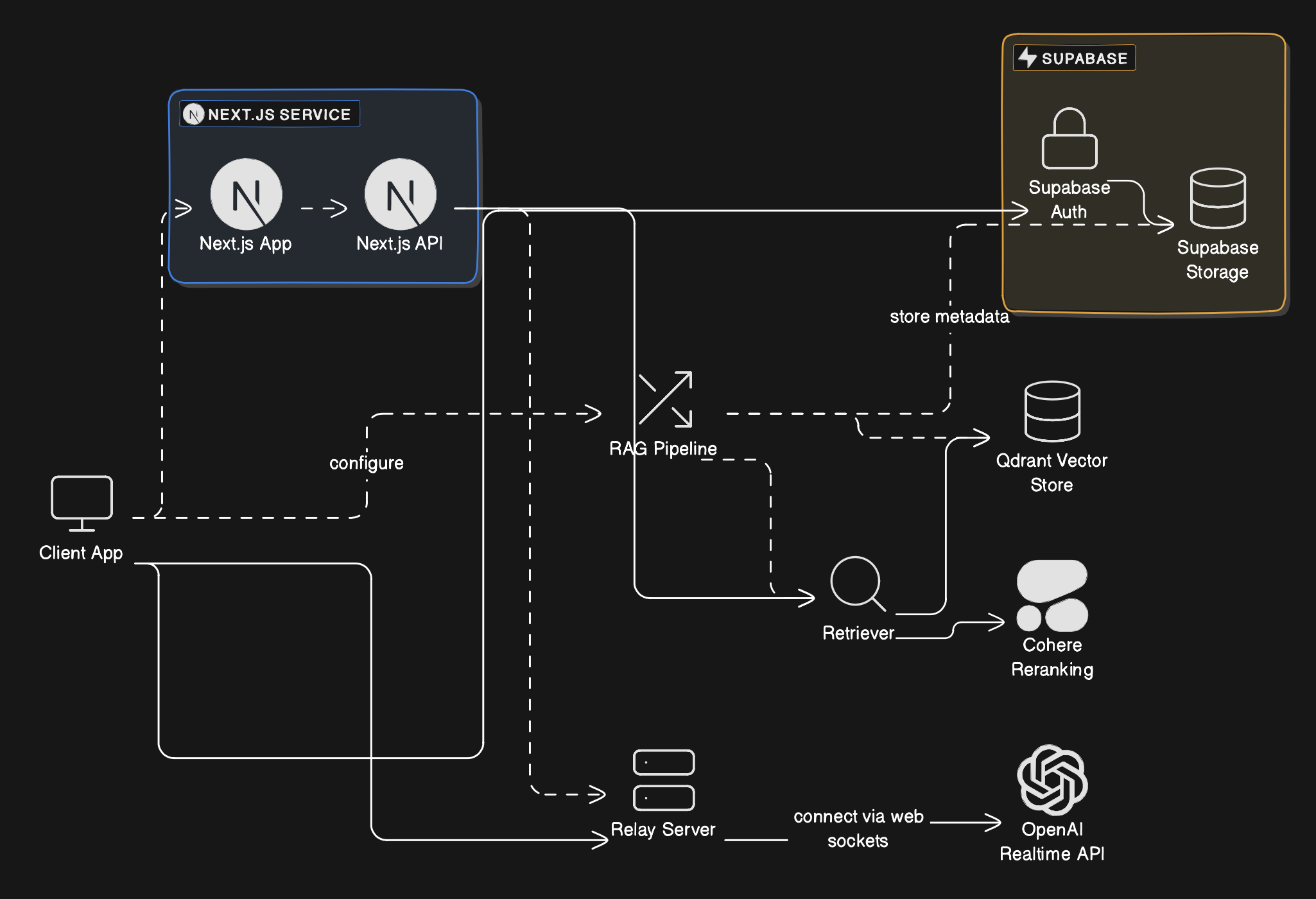
- Next.js App: This is the frontend layer, which provides the user interface where users can interact with the system, including uploading documents and querying them via voice interaction.
- Next.js API: The backend service that handles API requests from the frontend, processes user requests (like document uploads), and interacts with other services such as the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) pipeline.
-
- Supabase Auth: Manages user authentication and authorization for secure access to document-related features.
- Supabase Storage: Stores uploaded documents and associated metadata, ensuring secure access and scalability for user data.
-
RAG Pipeline (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
- The RAG pipeline is the core of the system's retrieval capabilities. It processes user queries, searches through stored embeddings (generated from uploaded documents), and fetches relevant document chunks to provide a context-aware response. This is done via:
- Retriever: Fetches relevant document sections based on the query.
- Cohere Reranking: Enhances the relevance of retrieved document sections to provide more accurate results.
- The RAG pipeline is the core of the system's retrieval capabilities. It processes user queries, searches through stored embeddings (generated from uploaded documents), and fetches relevant document chunks to provide a context-aware response. This is done via:
-
- Qdrant Vector Store: This is where document embeddings are stored after the document upload. Embeddings are numerical representations of document chunks that allow the system to efficiently search and retrieve relevant information based on user queries.
-
- Provides AI-driven responses by interacting with the user’s queries in real time. The system sends the retrieved context from the document (via the RAG pipeline) to OpenAI’s API, which generates voice responses based on the document content.
- Client App (Frontend): The user uploads a document and interacts with it through the app.
- Document Storage (Supabase): The document is stored securely, and metadata is captured.
- Embedding Generation (RAG Pipeline): The document is processed, embeddings are generated, and stored in the Qdrant Vector Store.
- Query Handling (Retriever & Reranking): When a user queries the document, relevant chunks are retrieved using the embeddings.
- Response Generation (OpenAI API): The retrieved chunks are passed to the OpenAI API, which generates a response that is returned to the user through the Client App.
This architecture ensures seamless interaction, real-time voice responses, and efficient document handling, making DocTalk a robust platform for document-based AI interactions.
- Required for Document Interaction
- An OpenAI API key is necessary for generating embeddings and enabling voice interactions.
- Enter your API key in the interactive playground to start using voice commands with your documents.
Our goal is to continuously enhance the interaction experience between the user and the model by reducing inference time and improving overall responsiveness.
- Optimized Model Inference
We’ve made significant optimizations to reduce the time it takes for the model to process user queries and return responses. These improvements are aimed at providing a smoother, near real-time interaction experience.
When uploading documents, users should be aware that the responsibility of the content lies entirely with them. Please exercise caution while uploading sensitive or confidential documents. Ensure that you have the necessary permissions to share and process the document before interacting with this platform.
This project supports deployment through Vercel and running the application locally. It uses Supabase for authentication and database storage, and Qdrant for vector storage. Follow these steps for a seamless setup:
Set up a Supabase project for authentication and database functionalities. This includes:
- Creating a Supabase project and linking it.
- Configuring Supabase authentication (email verification or disabling confirmation emails).
- Setting up a database table and storage buckets.
Once your Supabase project is set up, run the following command to create storage buckets and database tables:
npm run setup:supabaseFor step-by-step instructions, refer to the Supabase Setup Guide.
Qdrant is used as a vector database for storing and searching embeddings. Set up a free Qdrant cluster and configure its environment variables.
Detailed instructions can be found in the Qdrant Setup Guide.
Add the following environment variables to your .env file:
# Supabase settings
NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_BUCKET_NAME=<bucket-name>
NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_BUCKET_FILE_SIZE_LIMIT=<file-size>
NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_BUCKET_ALLOWED_MIME_TYPES=<type>
NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_USER_TABLE_NAME=<table-name>
NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_URL=https://<project_id>.supabase.co
NEXT_PUBLIC_SUPABASE_ANON_KEY=<anon_key>
# Qdrant settings
QDRANT_URL=https://<instance>.europe-west3-0.gcp.cloud.qdrant.io
QDRANT_API_KEY=<qdrant_api_key>You can run the application in two ways:
- On Vercel
- Deploy the application to Vercel.
- Add the
.envvariables in the Vercel environment settings.
- Locally
- Install the required dependencies:
pnpm install
- Start the development server:
pnpm run dev
If you encounter any problems while running or using DocTalk or have suggestions for improvements, we encourage you to utilize our templates to streamline communication:
- 🐞 Bug Report: Found a bug? Help us fix it by providing detailed information using our bug report template.
- 🌟 Feature Request: Have an idea for a new feature? Share your thoughts using our feature request template.
- ❓ General Queries: Have a question or need help? Submit your query using our query template.