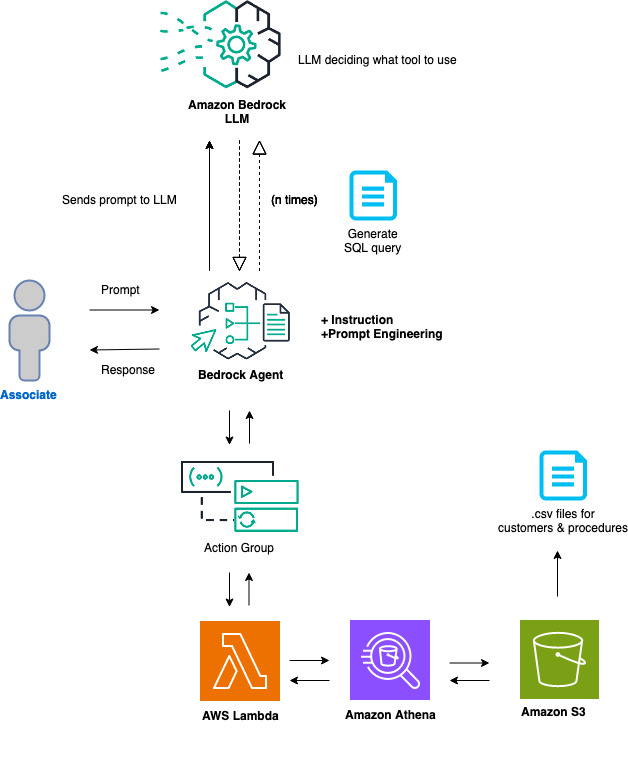
We will setup an Amazon Bedrock agent with an action group that will be able to translate natural language to SQL queries. In this project, we will be querying an Amazon Athena database, but the concept can be applied to most SQL databases.
- An active AWS Account.
- Familiarity with AWS services like Amazon Bedrock, Amazon S3, AWS Lambda, Amazon Athena, and Amazon Cloud9.
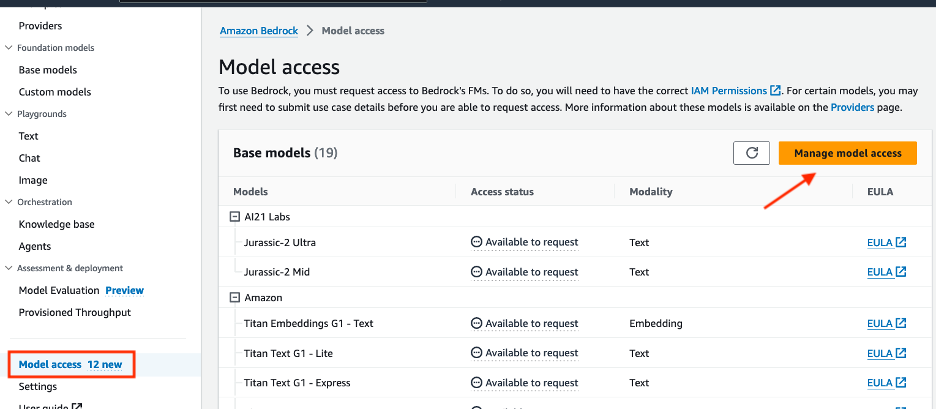
- Access will need to be granted to the Anthropic: Claude 3 Haiku model from the Amazon Bedrock console.
- We will need to grant access to the models that will be needed for our Bedrock agent. Navigate to the Amazon Bedrock console, then on the left of the screen, scroll down and select Model access. On the right, select the orange Manage model access button.
-
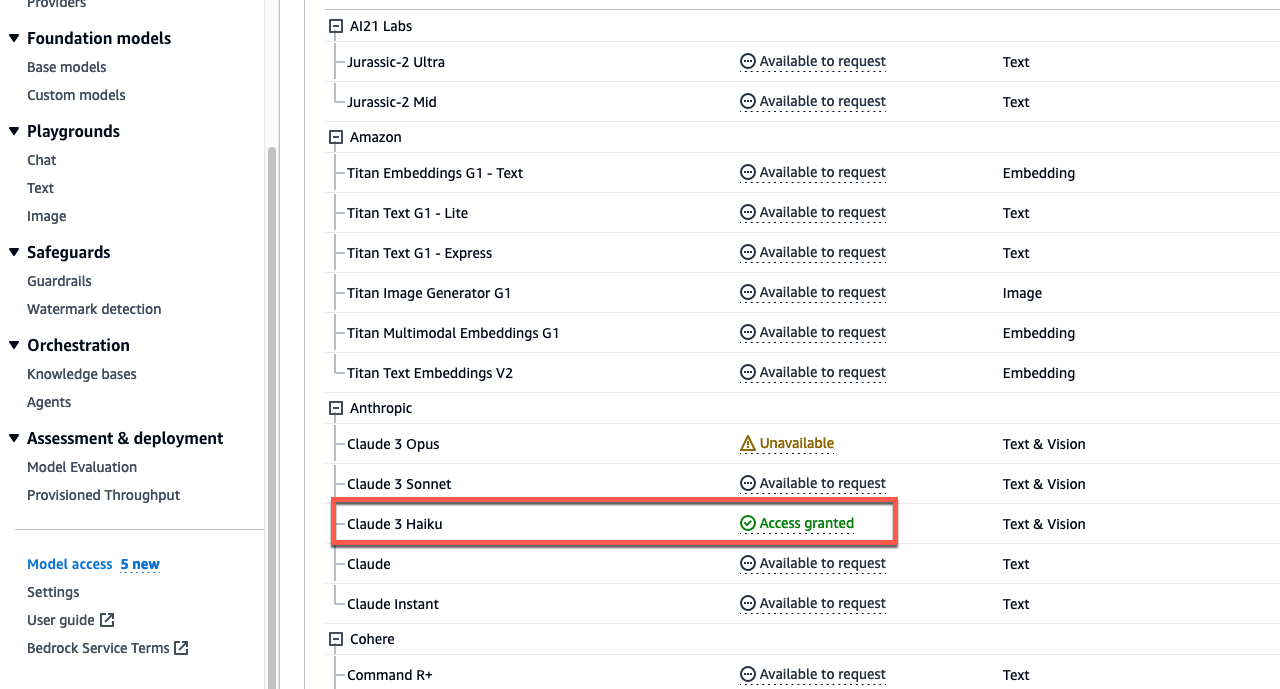
Select the checkbox for the base model column Anthropic: Claude 3 Haiku. This will provide you access to the required models. After, scroll down to the bottom right and select Request model access.
-
After, verify that the Access status of the Models are green with Access granted.
- Make sure that you are in the us-west-2 region. If another region is required, you will need to update the region in the
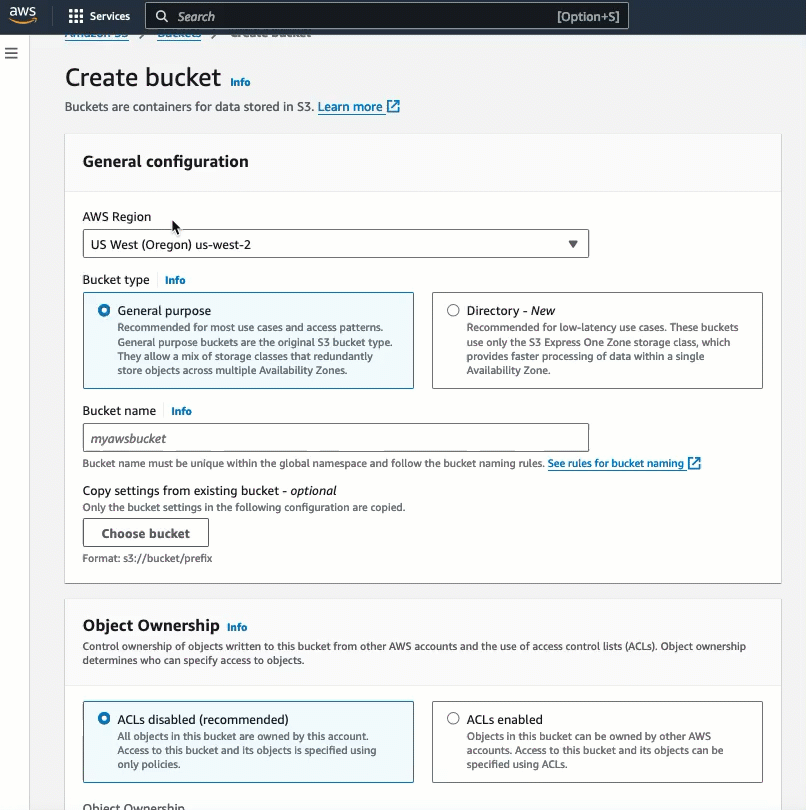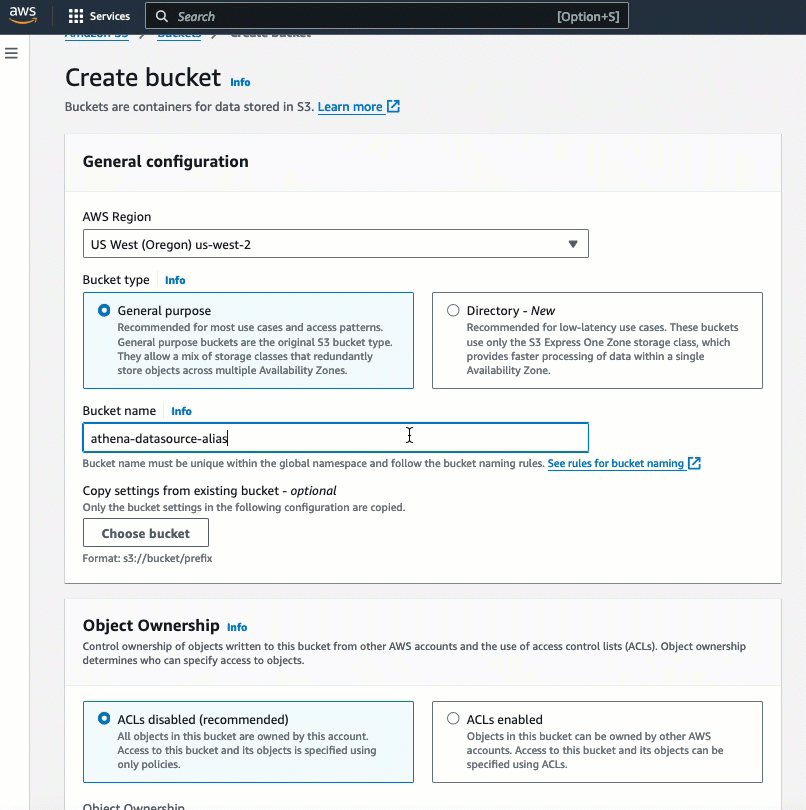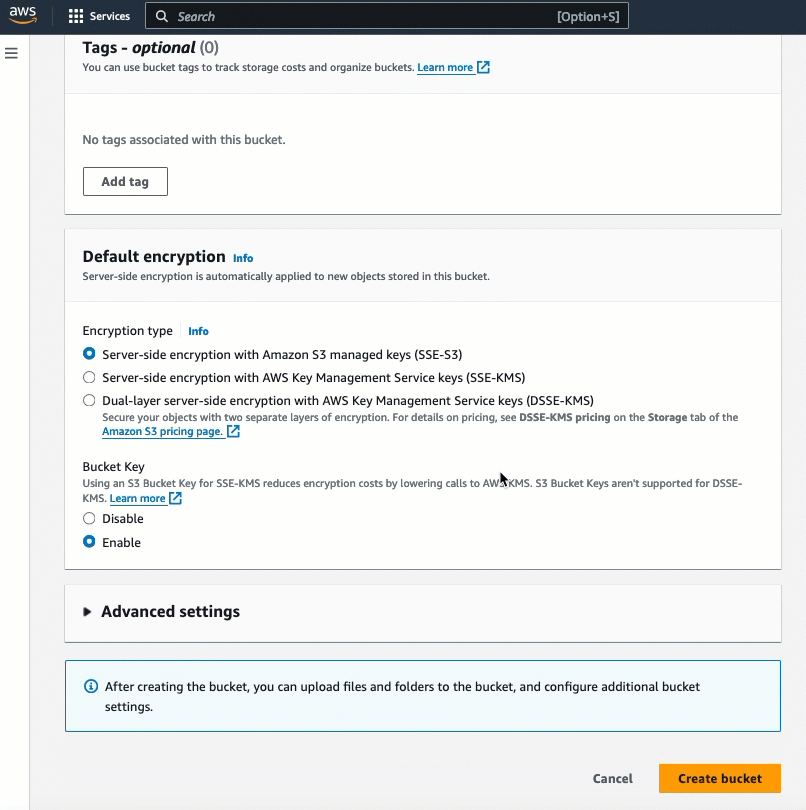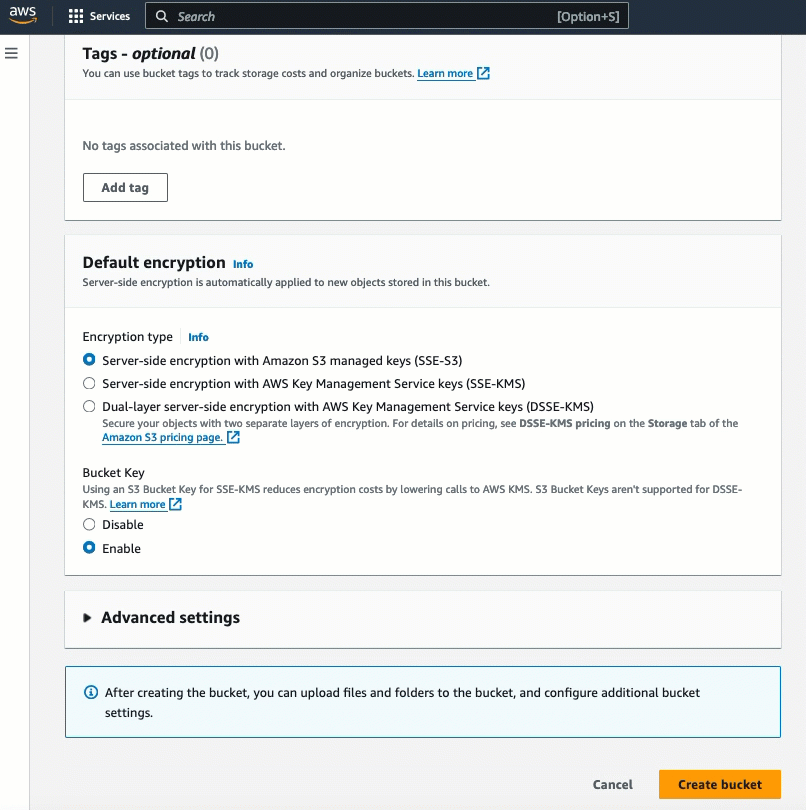
InvokeAgent.pyfile on line 24 of the code. - Domain Data Bucket: Create an S3 bucket to store the domain data. For example, call the S3 bucket
athena-datasource-{alias}. We will use the default settings. (Make sure to update {alias} with the appropriate value throughout the README instructions.)
- Next, we will download .csv files that contain mock data for customers and procedures. Open up a terminal or command prompt, and run the following
curlcommands to download and save these files to the Documents folder:
For Mac
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/build-on-aws/bedrock-agent-txt2sql/main/S3data/mock-data-customers.csv --output ~/Documents/mock-data-customers.csv
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/build-on-aws/bedrock-agent-txt2sql/main/S3data/mock-data-procedures.csv --output ~/Documents/mock-data-procedures.csv
For Windows
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/build-on-aws/bedrock-agent-txt2sql/main/S3data/mock-data-customers.csv --output %USERPROFILE%\Documents\mock-data-customers.csv
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/build-on-aws/bedrock-agent-txt2sql/main/S3data/mock-data-procedures.csv --output %USERPROFILE%\Documents\mock-data-procedures.csv
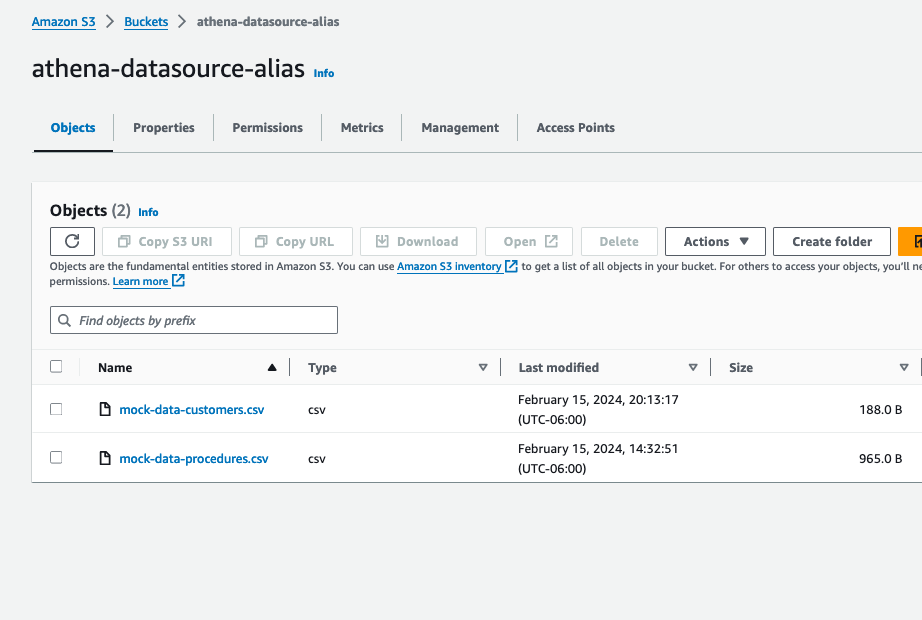
- These files are the datasource for Amazon Athena. Upload these files to S3 bucket
athena-datasource-{alias}. Once the documents are uploaded, please review them.
- Amazon Athena Bucket: Create another S3 bucket for the Athena service. Call it
athena-destination-store-{alias}. You will need to use this S3 bucket when configuring Amazon Athena in the next step.
- Search for the Amazon Athena service, then navigate to the Athena management console. Validate that the Query your data with Trino SQL radio button is selected, then press Launch query editor.
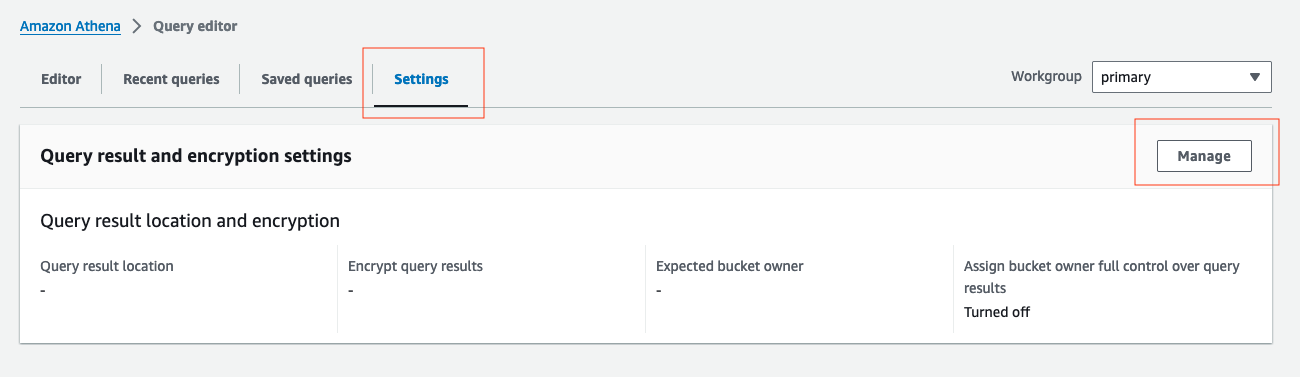
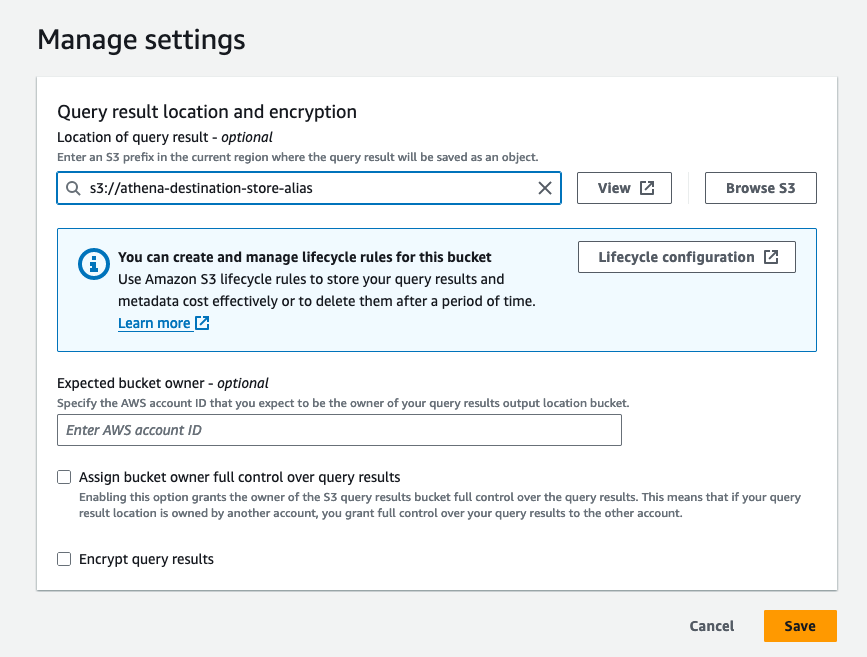
- Before you run your first query in Athena, you need to set up a query result location with Amazon S3. Select the Settings tab, then the Manage button in the Query result location and ecryption section.
- Add the S3 prefix below for the query results location, then select the Save button:
s3://athena-destination-store-{alias}
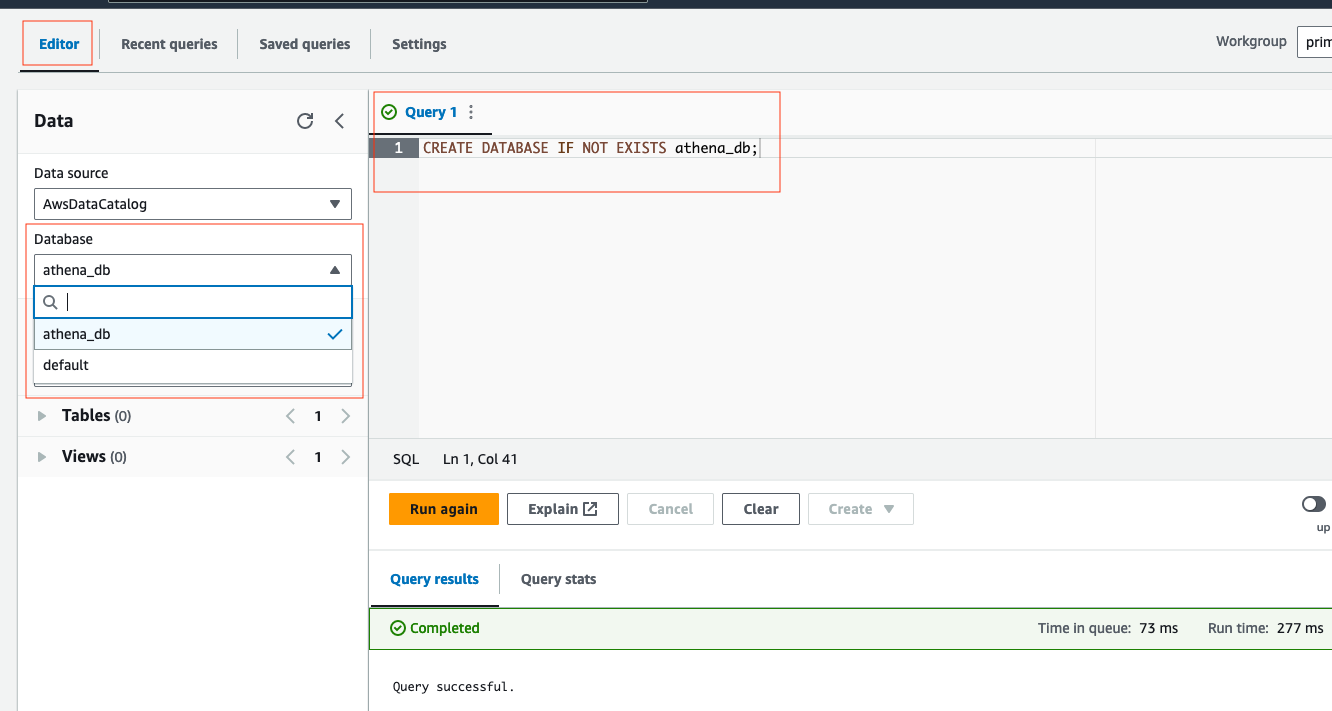
- Next, we will create an Athena database. Select the Editor tab, then copy/paste the following query in the empty query screen. After, select Run:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS athena_db;-
You should see query successful at the bottom. On the left side under Database, change the default database to
athena_db, if not by default. -
We'll need to create the
customerstable. Run the following query in Athena.(Remember to update the {alias} field):
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE athena_db.customers (
`Cust_Id` integer,
`Customer` string,
`Balance` integer,
`Past_Due` integer,
`Vip` string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
STORED AS TEXTFILE
LOCATION 's3://athena-datasource-{alias}/';- Open another query tab and create the
procedurestable by running this query.(Remember to update the {alias} field):
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE athena_db.procedures (
`Procedure_Id` string,
`Procedure` string,
`Category` string,
`Price` integer,
`Duration` integer,
`Insurance` string,
`Customer_Id` integer
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
STORED AS TEXTFILE
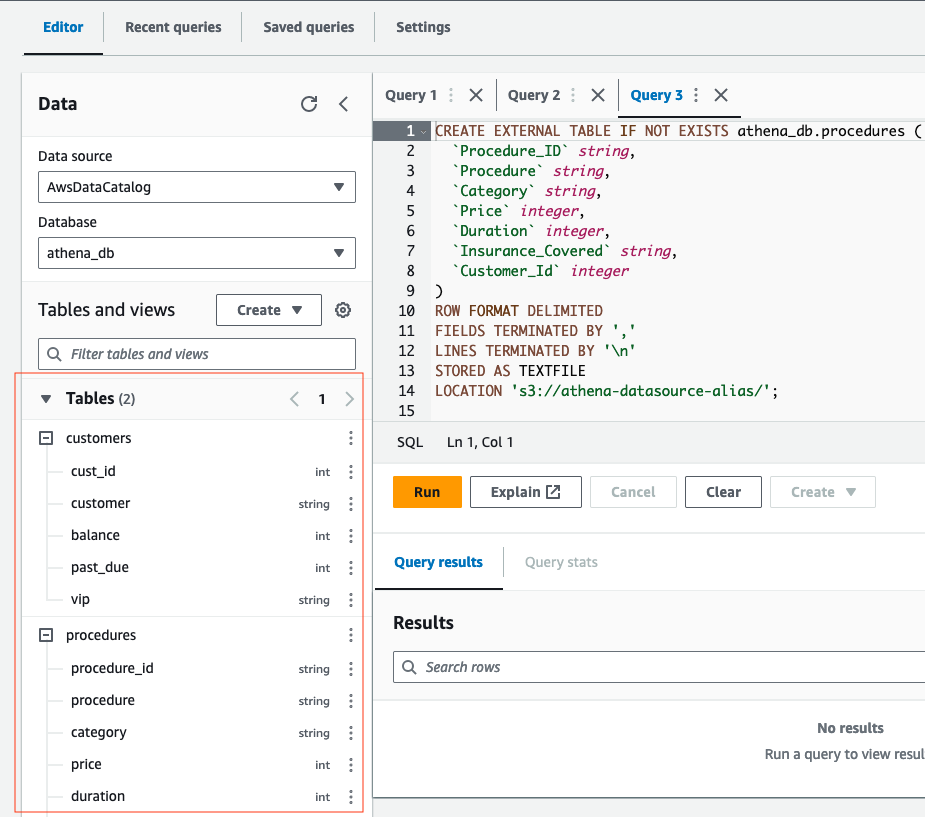
LOCATION 's3://athena-datasource-{alias}/';- Your tables for Athena within editor should look similar to the following:
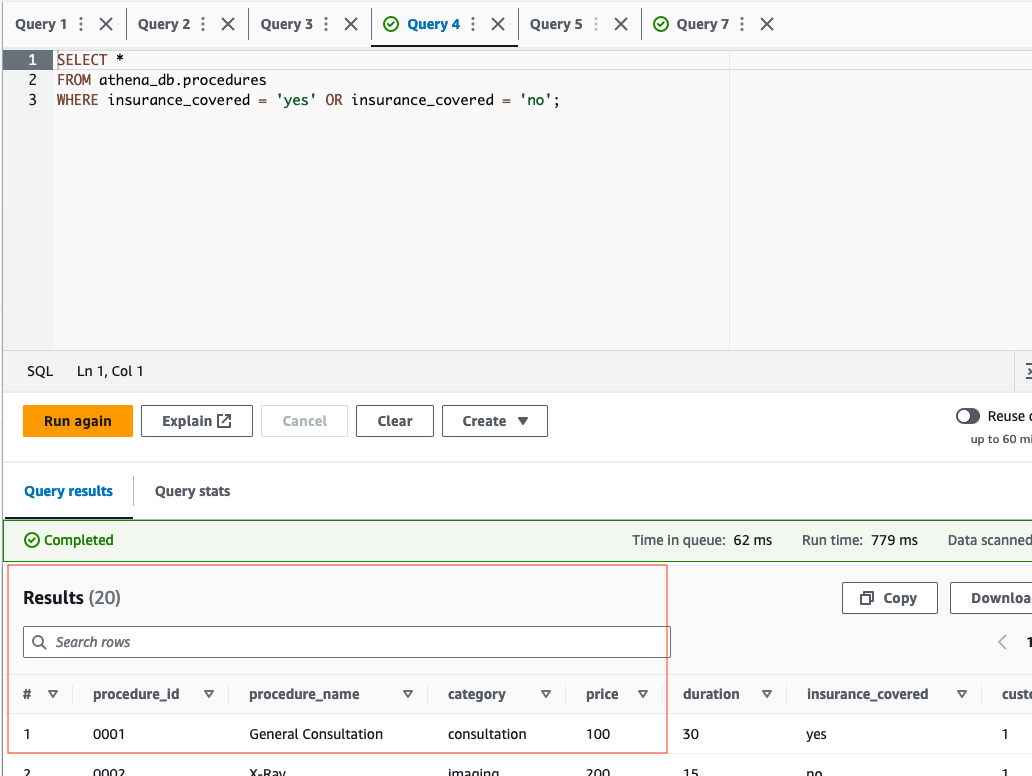
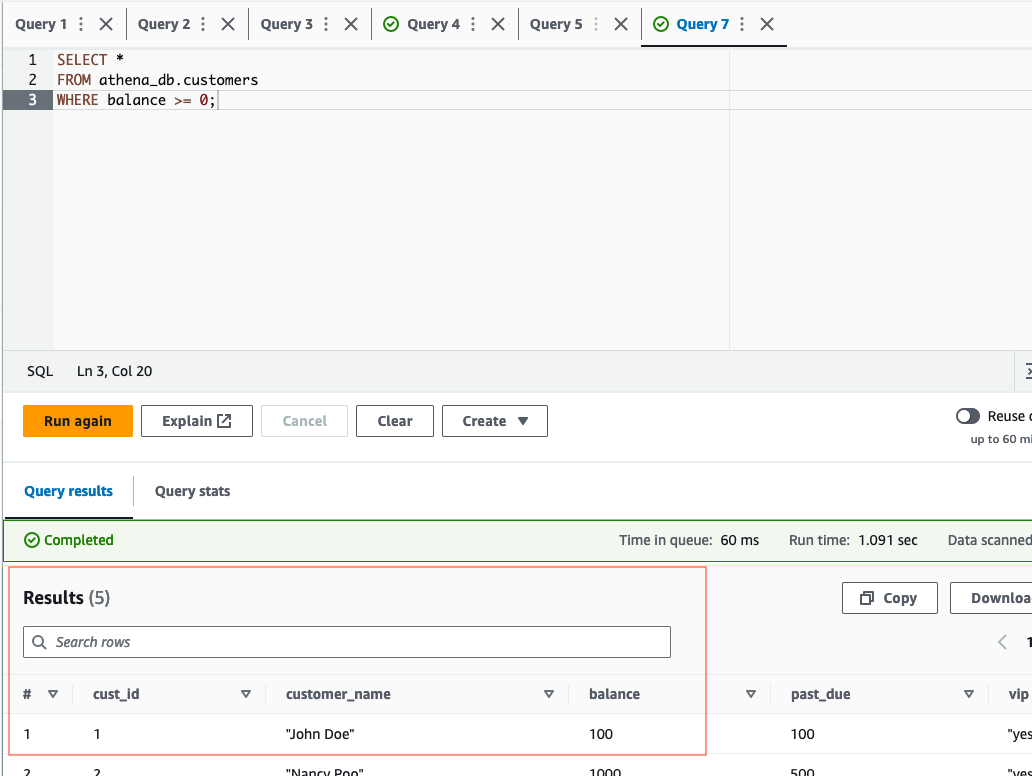
- Now, lets quickly test the queries against the customers and procedures table by running the following two example queries below:
SELECT *
FROM athena_db.procedures
WHERE insurance = 'yes' OR insurance = 'no';SELECT *
FROM athena_db.customers
WHERE balance >= 0;- If tests were succesful, we can move to the next step.
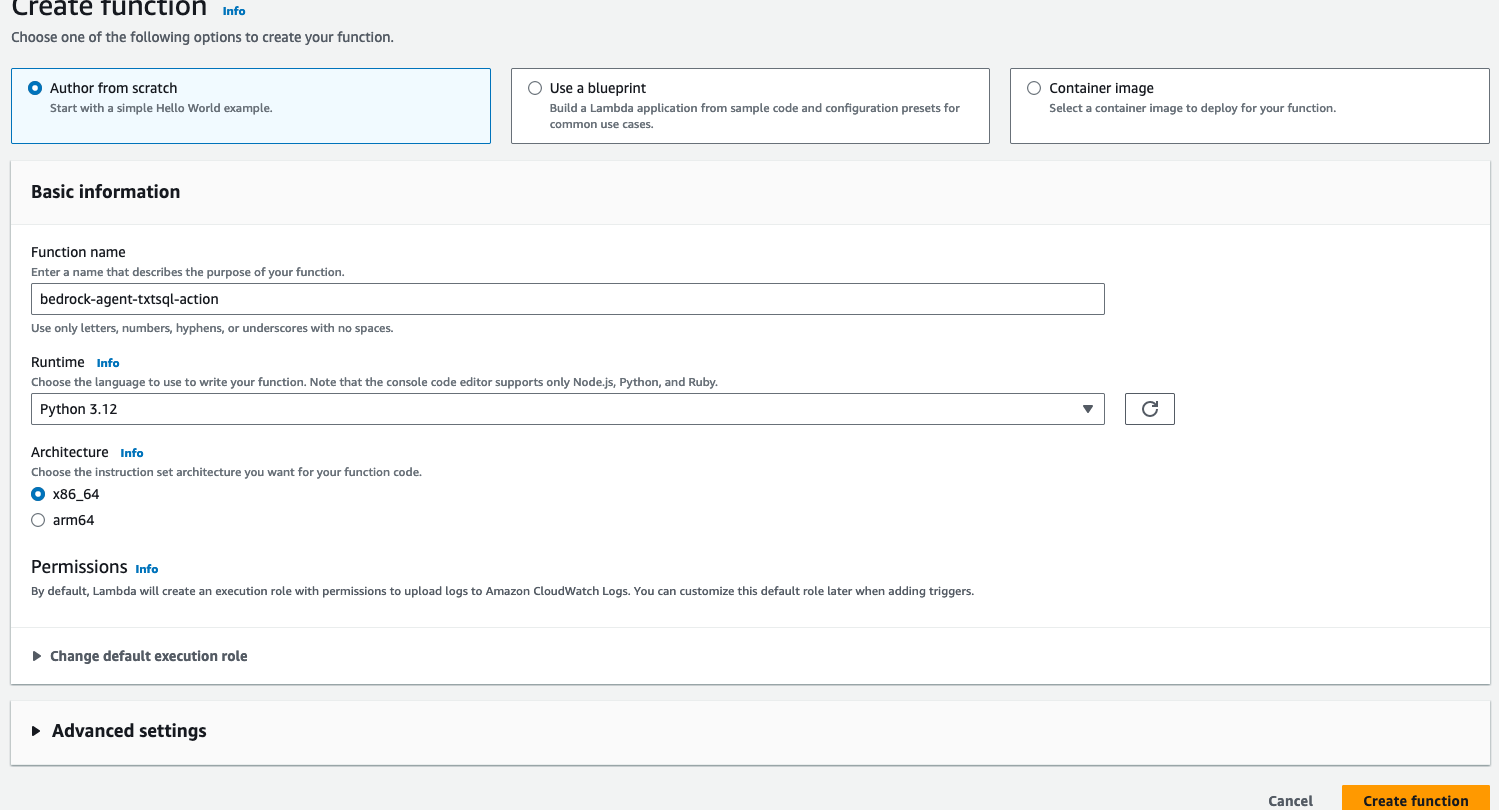
- Create a Lambda function (Python 3.12) for the Bedrock agent's action group. We will call this Lambda function
bedrock-agent-txtsql-action.
- Copy the provided code from here, or from below into the Lambda function.
import boto3
from time import sleep
# Initialize the Athena client
athena_client = boto3.client('athena')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print(event)
def athena_query_handler(event):
# Fetch parameters for the new fields
# Extracting the SQL query
query = event['requestBody']['content']['application/json']['properties'][0]['value']
print("the received QUERY:", query)
s3_output = 's3://athena-destination-store-alias' # Replace with your S3 bucket
# Execute the query and wait for completion
execution_id = execute_athena_query(query, s3_output)
result = get_query_results(execution_id)
return result
def execute_athena_query(query, s3_output):
response = athena_client.start_query_execution(
QueryString=query,
ResultConfiguration={'OutputLocation': s3_output}
)
return response['QueryExecutionId']
def check_query_status(execution_id):
response = athena_client.get_query_execution(QueryExecutionId=execution_id)
return response['QueryExecution']['Status']['State']
def get_query_results(execution_id):
while True:
status = check_query_status(execution_id)
if status in ['SUCCEEDED', 'FAILED', 'CANCELLED']:
break
sleep(1) # Polling interval
if status == 'SUCCEEDED':
return athena_client.get_query_results(QueryExecutionId=execution_id)
else:
raise Exception(f"Query failed with status '{status}'")
action_group = event.get('actionGroup')
api_path = event.get('apiPath')
print("api_path: ", api_path)
result = ''
response_code = 200
if api_path == '/athenaQuery':
result = athena_query_handler(event)
else:
response_code = 404
result = {"error": f"Unrecognized api path: {action_group}::{api_path}"}
response_body = {
'application/json': {
'body': result
}
}
action_response = {
'actionGroup': action_group,
'apiPath': api_path,
'httpMethod': event.get('httpMethod'),
'httpStatusCode': response_code,
'responseBody': response_body
}
api_response = {'messageVersion': '1.0', 'response': action_response}
return api_response- Then, update the alias value for the
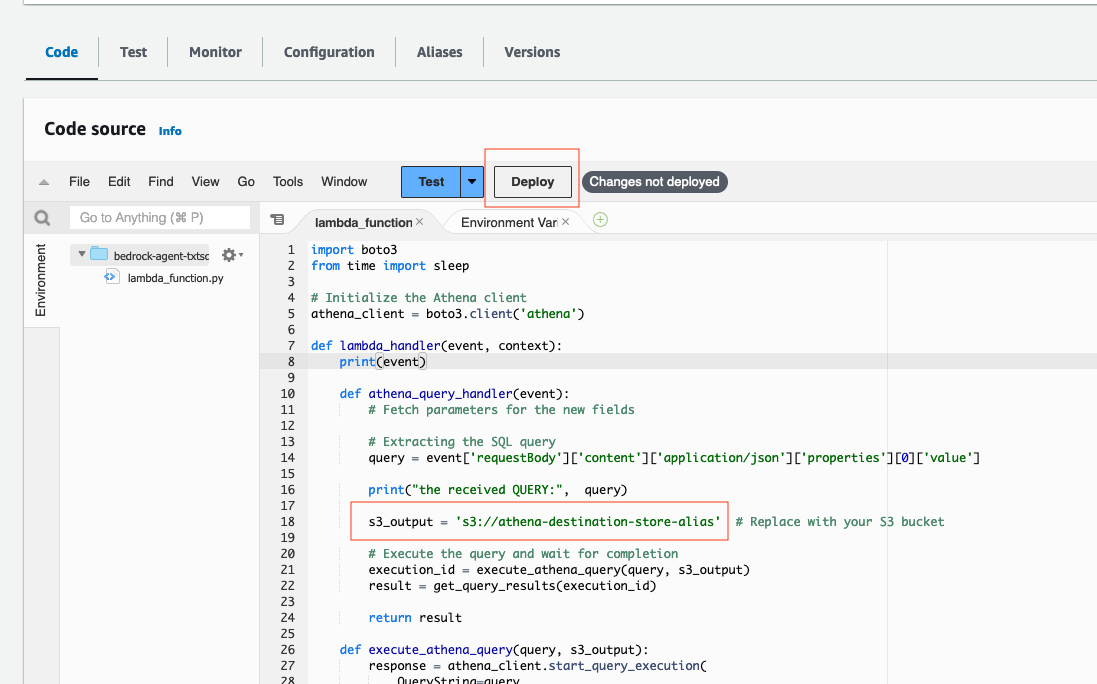
s3_outputvariable in the python code above. After, select Deploy under Code source in the Lambda console. Review the code provided before moving to the next step.
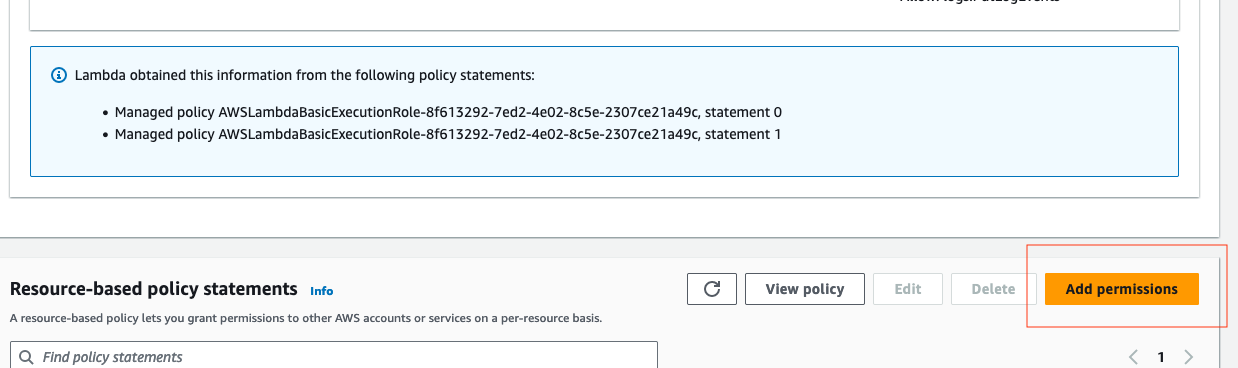
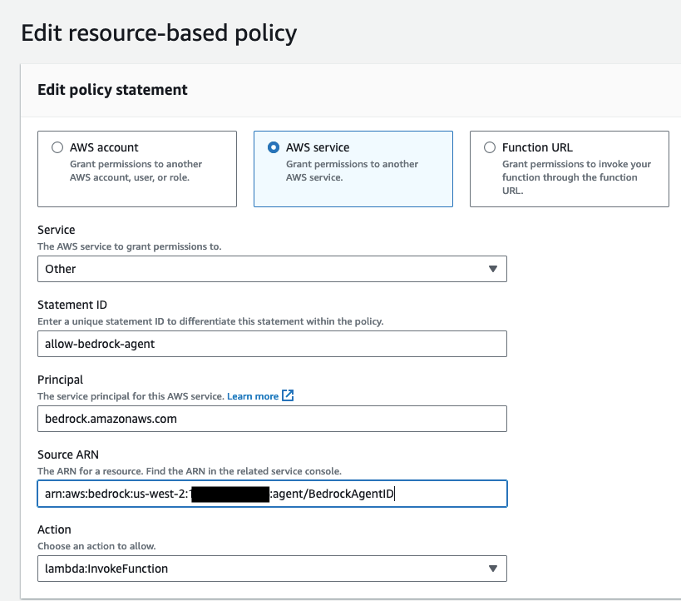
- Now, we need to apply a resource policy to Lambda that grants Bedrock agent access. To do this, we will switch the top tab from code to configuration and the side tab to Permissions. Then, scroll to the Resource-based policy statements section and click the Add permissions button.
- Enter
arn:aws:bedrock:us-west-2:{aws-account-id}:agent/*. Please note, AWS recommends least privilage so only the allowed agent can invoke this Lambda function. A*at the end of the ARN grants any agent in the account access to invoke this Lambda. Ideally, we would not use this in a production environment. Lastly, for the Action, selectlambda:InvokeAction, then Save.
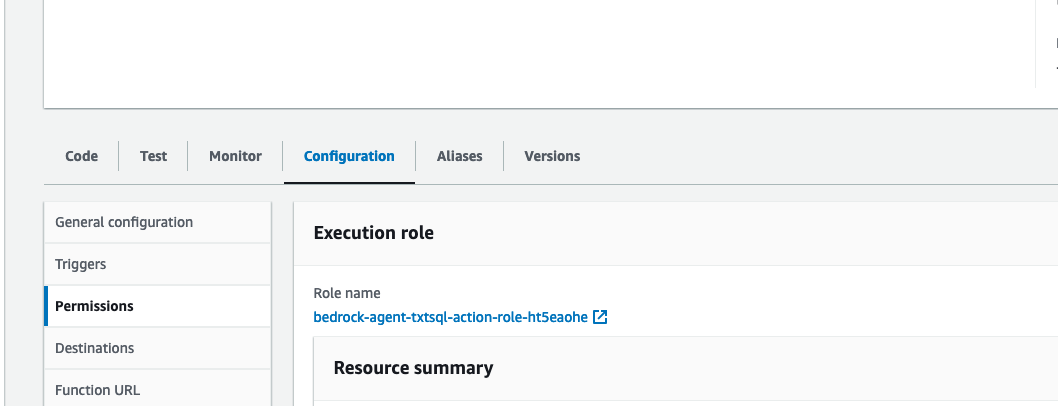
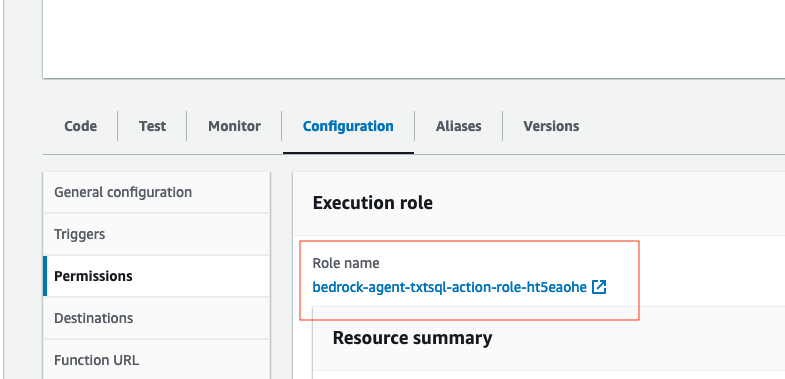
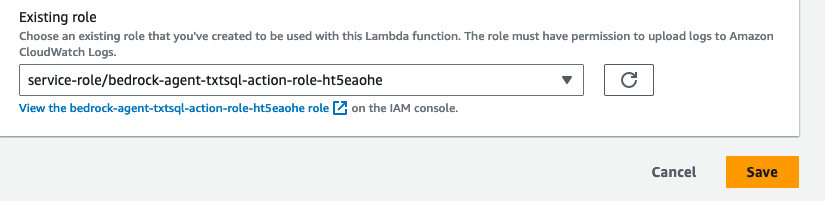
- We also need to provide this Lambda function permissions to interact with an S3 bucket, and Amazon Athena service. While on the
Configurationtab ->Permissionssection, select the Role name:
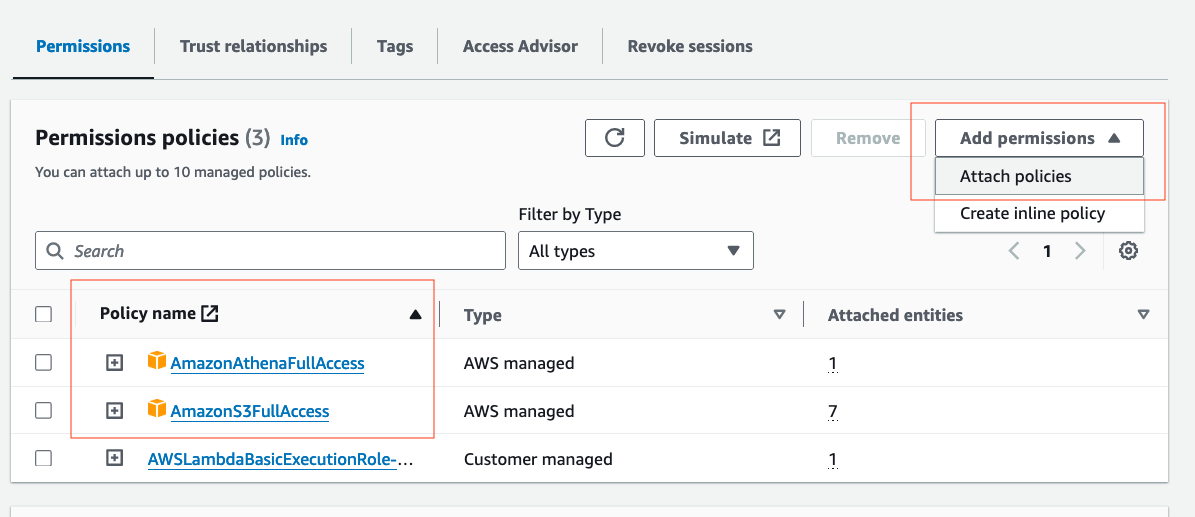
- Select
Add permissions -> Attach policies. Then, attach the AWS managed policies AmazonAthenaFullAccess, and AmazonS3FullAccess by selecting, then adding the permissions. Please note, in a real world environment, it's recommended that you practice least privilage.
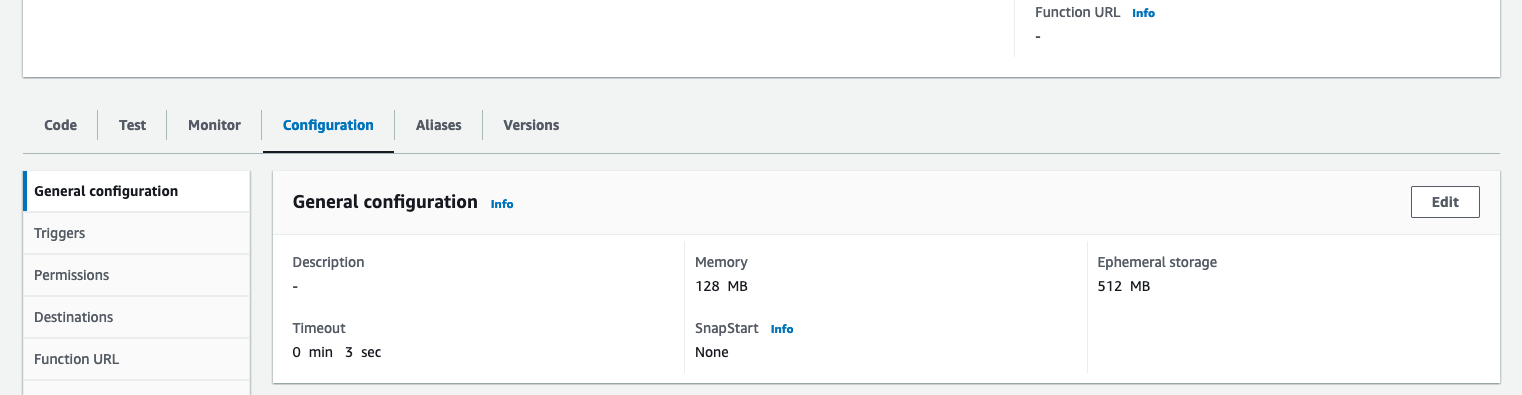
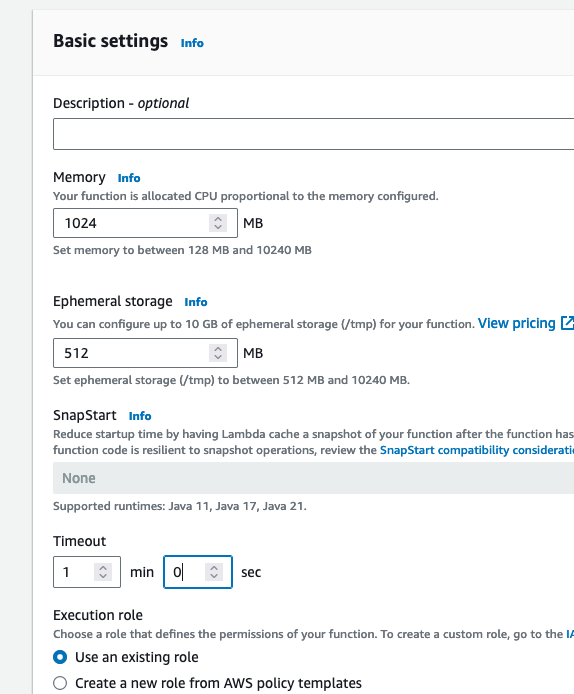
- The last thing we need to do with the Lambda is update the configurations. Navigate to the
Configurationtab, thenGeneral Configurationsection on the left. From here select Edit.
- Update the memory to 1024 MB, and Timeout to 1 minute. Scroll to the bottom, and save the changes.
- We are now done setting up the Lambda function
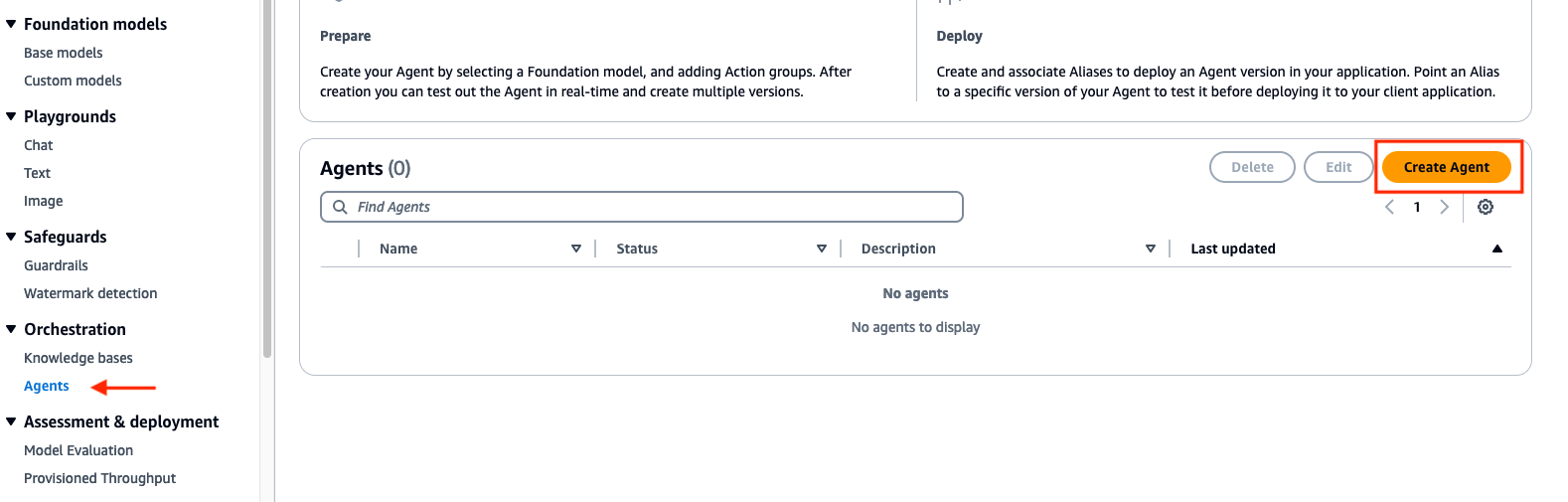
- Navigate to the Bedrock console. Go to the toggle on the left, and under Orchestration select Agents, then Create Agent. Provide an agent name, like
athena-agentthen Create.
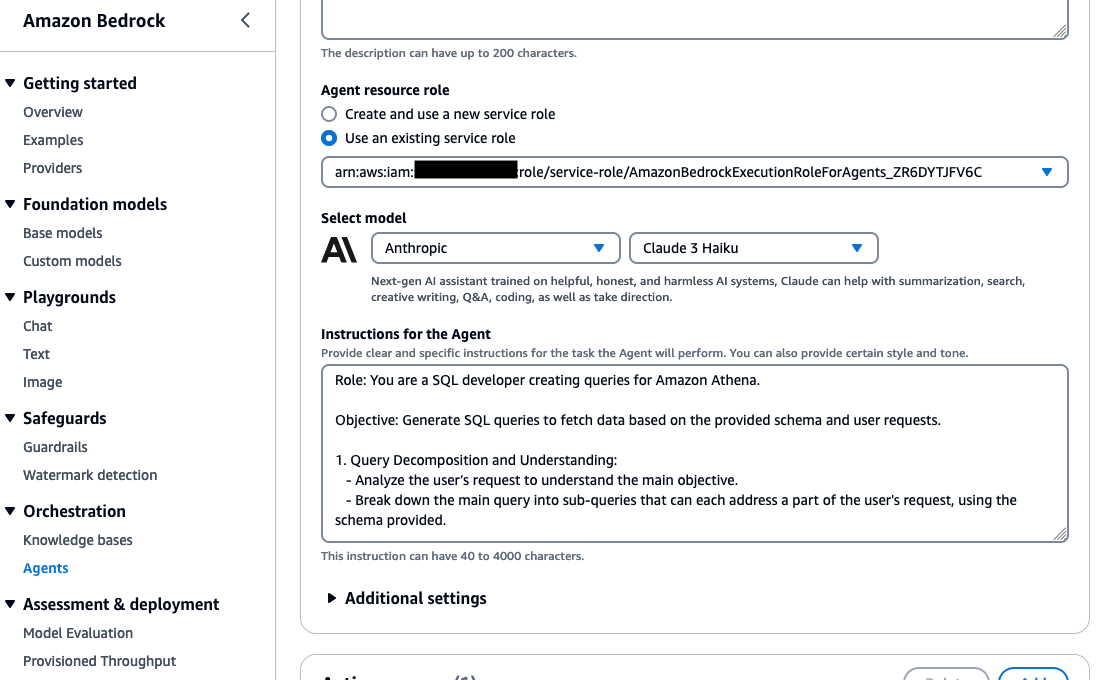
- The agent description is optional, and use the default new service role. For the model, select Anthropic Claude 3 Haiku. Next, provide the following instruction for the agent:
Role: You are a SQL developer creating queries for Amazon Athena.
Objective: Generate SQL queries to return data based on the provided schema and user request. Also, returns SQL query created.
1. Query Decomposition and Understanding:
- Analyze the user’s request to understand the main objective.
- Break down reqeusts into sub-queries that can each address a part of the user's request, using the schema provided.
2. SQL Query Creation:
- For each sub-query, use the relevant tables and fields from the provided schema.
- Construct SQL queries that are precise and tailored to retrieve the exact data required by the user’s request.
3. Query Execution and Response:
- Execute the constructed SQL queries against the Amazon Athena database.
- Return the results exactly as they are fetched from the database, ensuring data integrity and accuracy. Include the query generated and results in the response.
It should look similar to the following:
-
Scroll to the top, then select Save.
-
Keep in mind that these instructions guide the generative AI application in its role as a SQL developer creating efficient and accurate queries for Amazon Athena. The process involves understanding user requests, decomposing them into manageable sub-queries, and executing these to fetch precise data. This structured approach ensures that responses are not only accurate but also relevant to the user's needs, thereby enhancing user interaction and data retrieval efficiency.
-
Next, we will add an action group. Scroll down to
Action groupsthen select Add. -
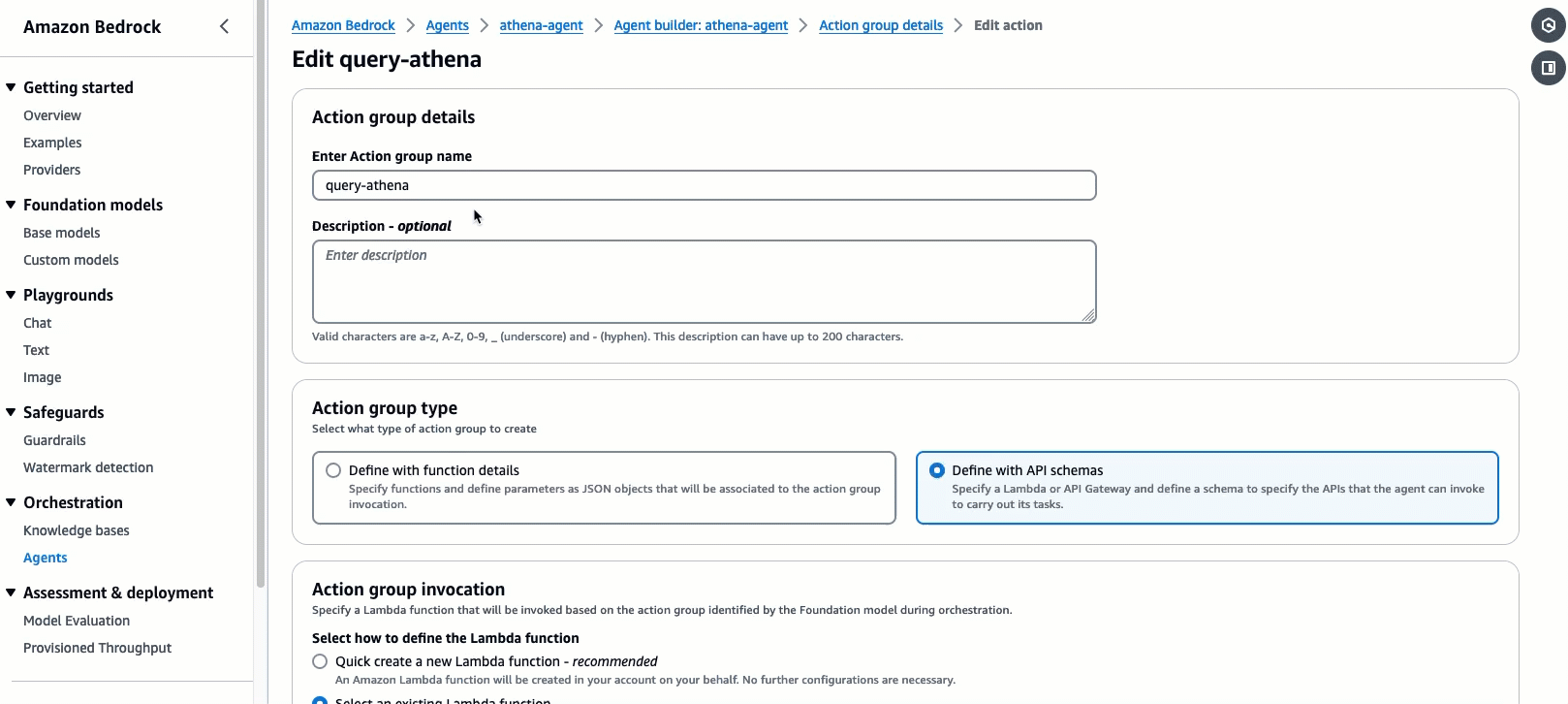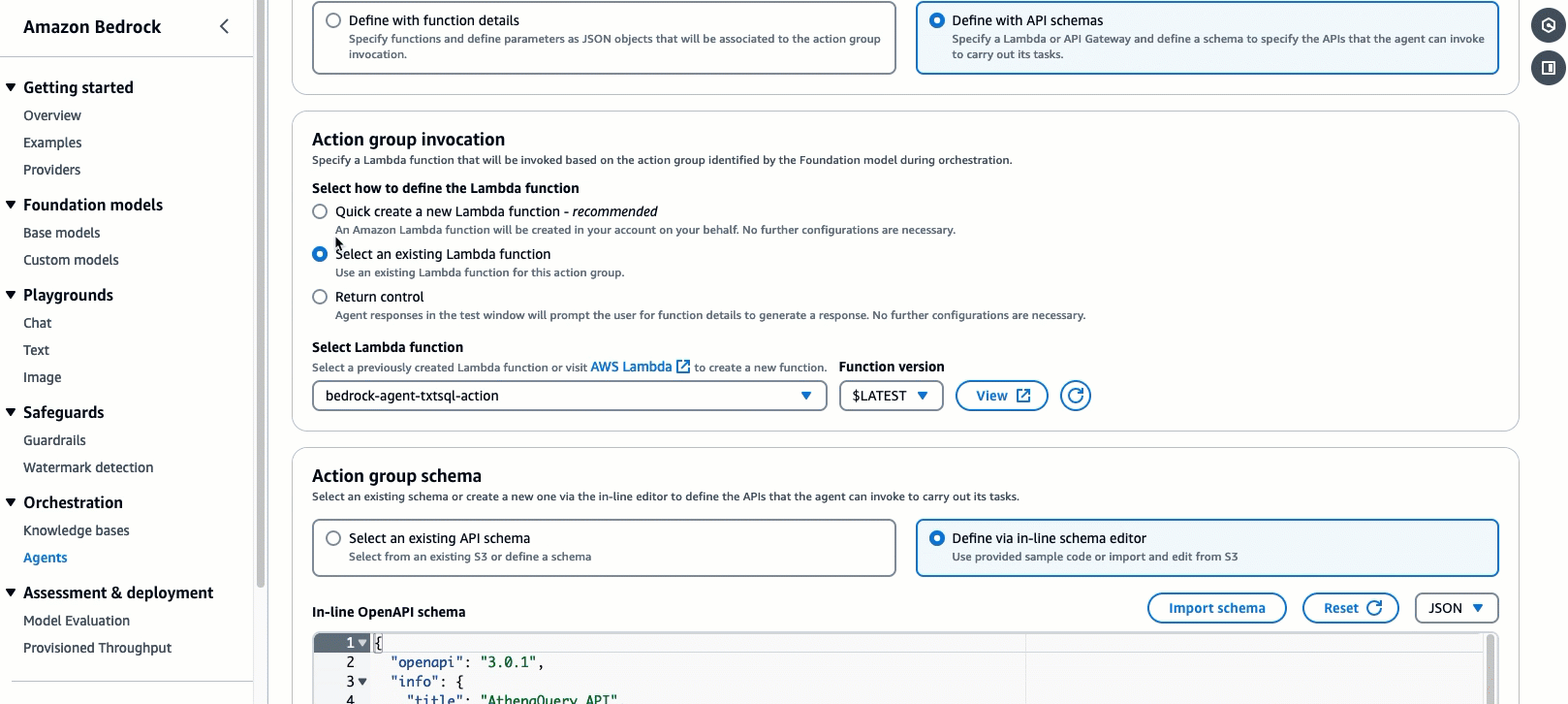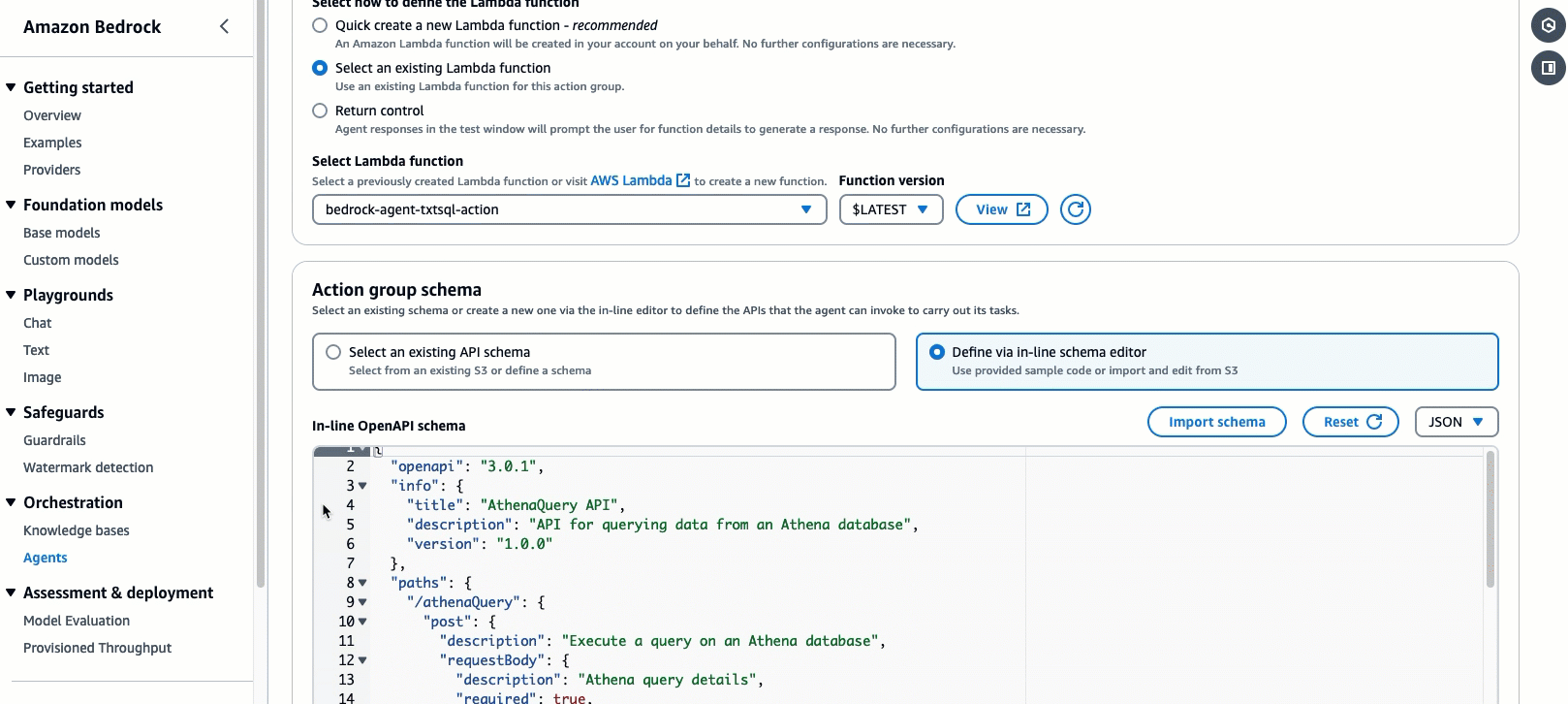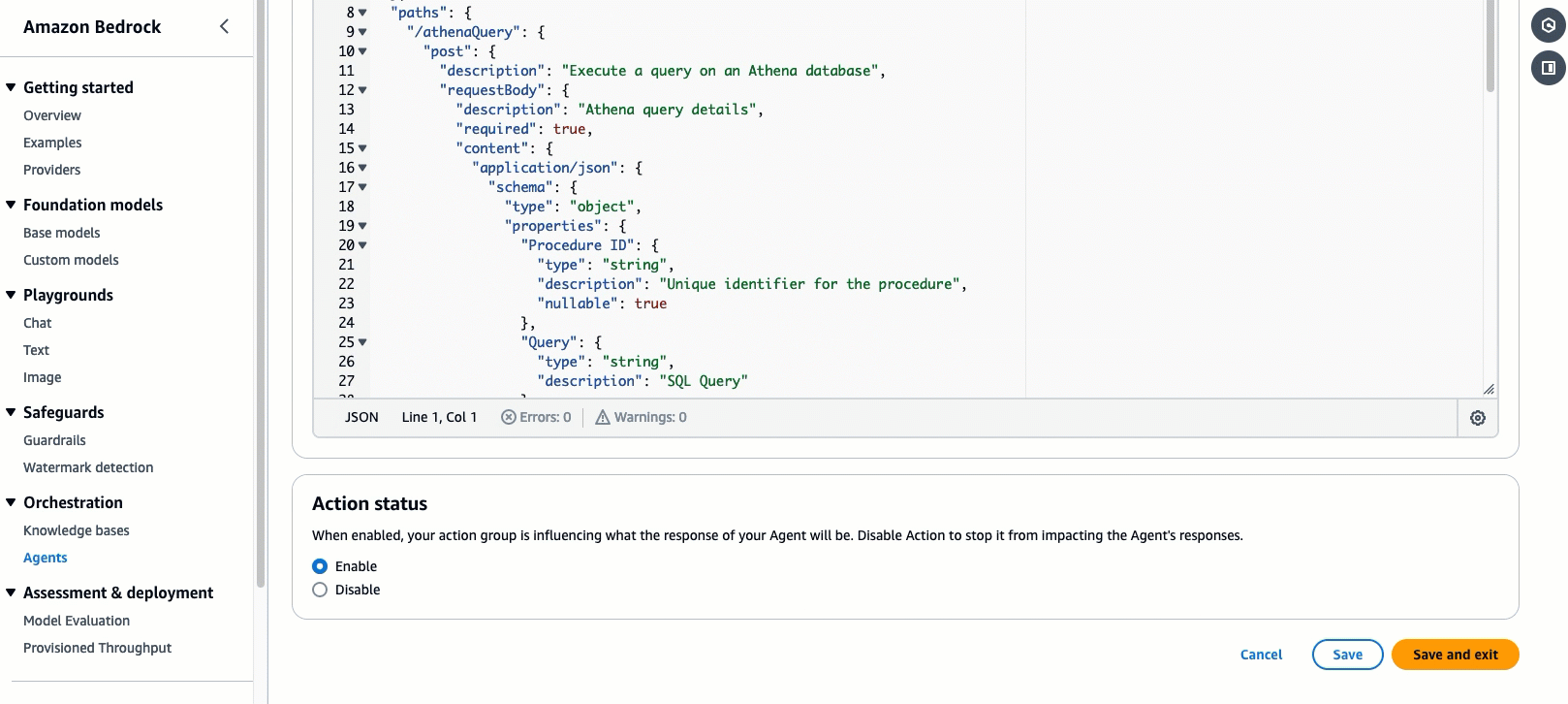
Call the action group
query-athena. We will keepAction group typeset to Define with API schemas.Action group invocationsshould be set to select an existing Lambda function. For the Lambda function, selectbedrock-agent-txtsql-action. -
For the
Action group Schema, we will choose Define with in-line OpenAPI schema editor. Replace the default schema in the In-line OpenAPI schema editor with the schema provided below. You can also retrieve the schema from the repo here. After, select Add.(This API schema is needed so that the bedrock agent knows the format structure and parameters needed for the action group to interact with the Lambda function.)
{
"openapi": "3.0.1",
"info": {
"title": "AthenaQuery API",
"description": "API for querying data from an Athena database",
"version": "1.0.0"
},
"paths": {
"/athenaQuery": {
"post": {
"description": "Execute a query on an Athena database",
"requestBody": {
"description": "Athena query details",
"required": true,
"content": {
"application/json": {
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"Procedure ID": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Unique identifier for the procedure",
"nullable": true
},
"Query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "SQL Query"
}
}
}
}
}
},
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Successful response with query results",
"content": {
"application/json": {
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"ResultSet": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"description": "A single row of query results"
},
"description": "Results returned by the query"
}
}
}
}
}
},
"default": {
"description": "Error response",
"content": {
"application/json": {
"schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"message": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Your configuration should look like the following:
- Now we will need to modify the Advanced prompts. Select the orange Edit in Agent Builder button at the top. Scroll to the bottom and in the advanced prompts section, select
Edit.
-
In the
Advanced prompts, navigate to the Orchestration tab. Enable theOverride orchestration template defaultsoption. Also, make sure thatActivate orchestration templateis enabled. -
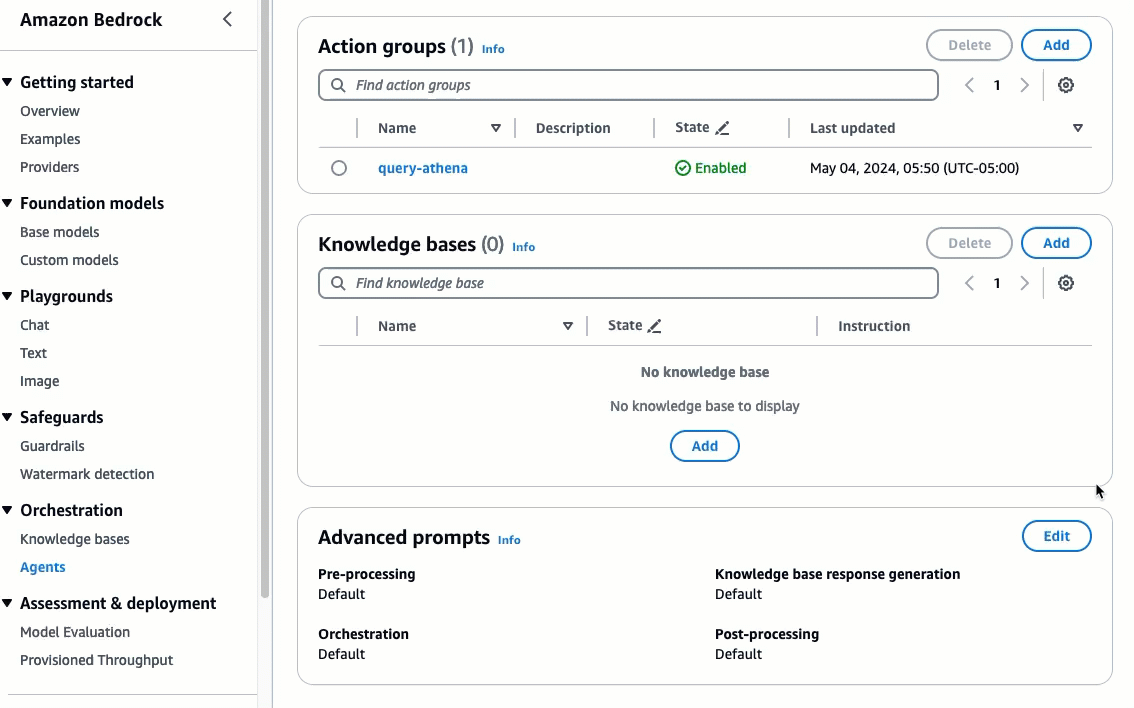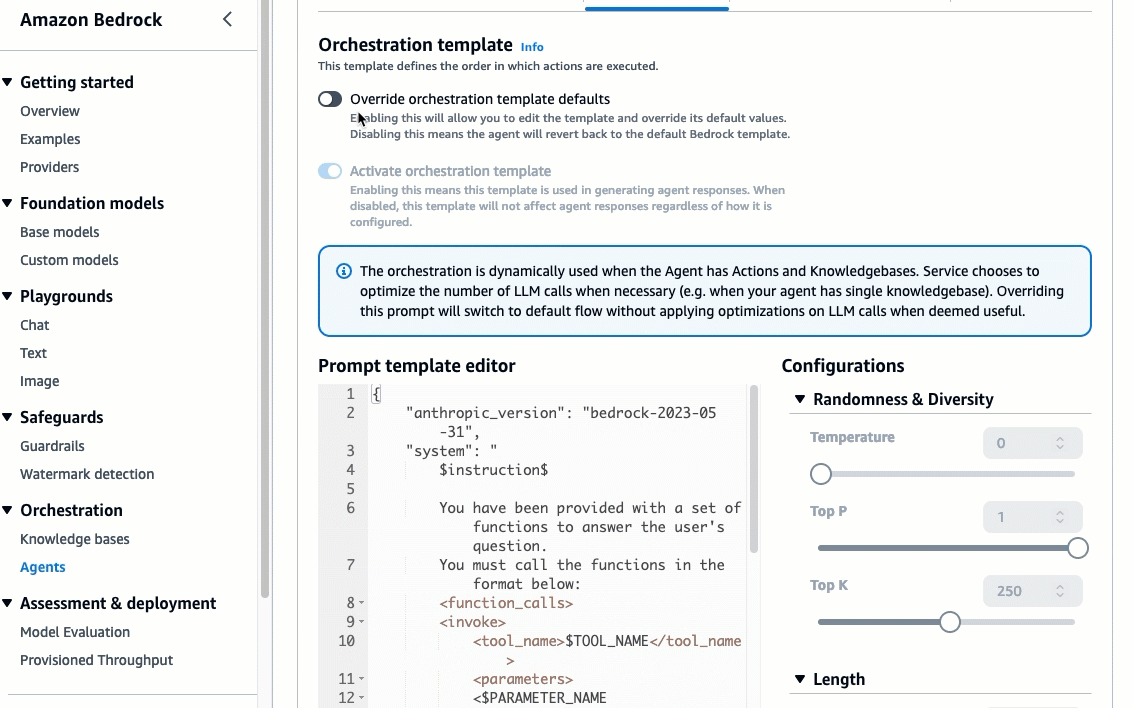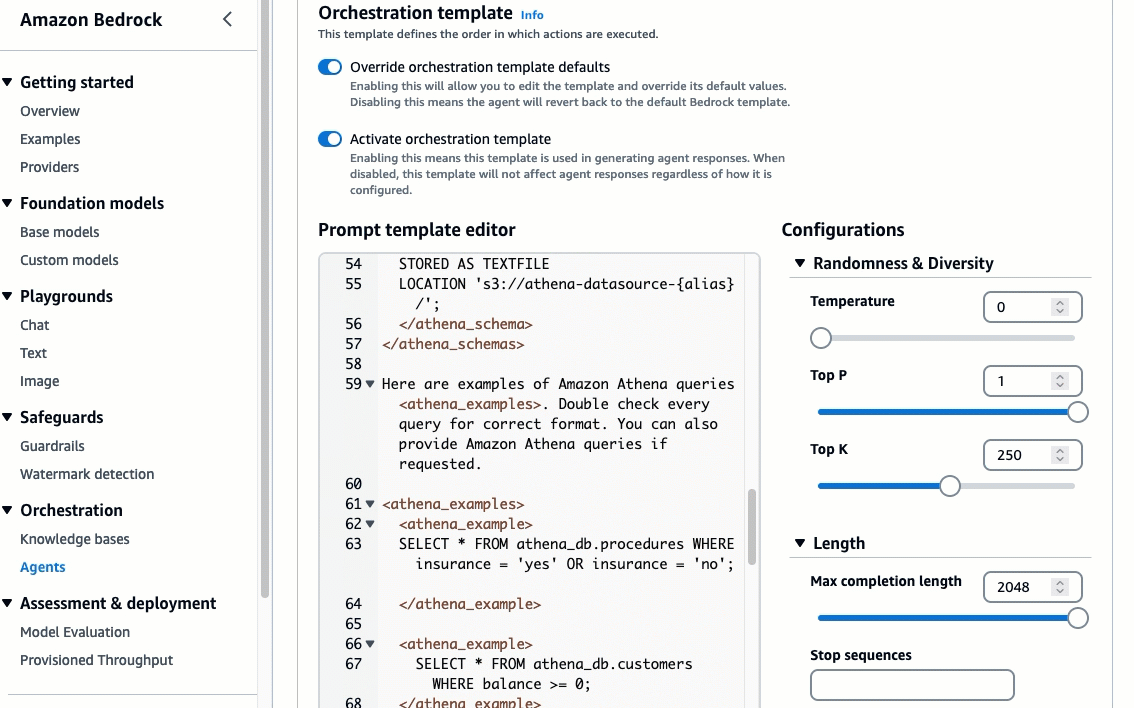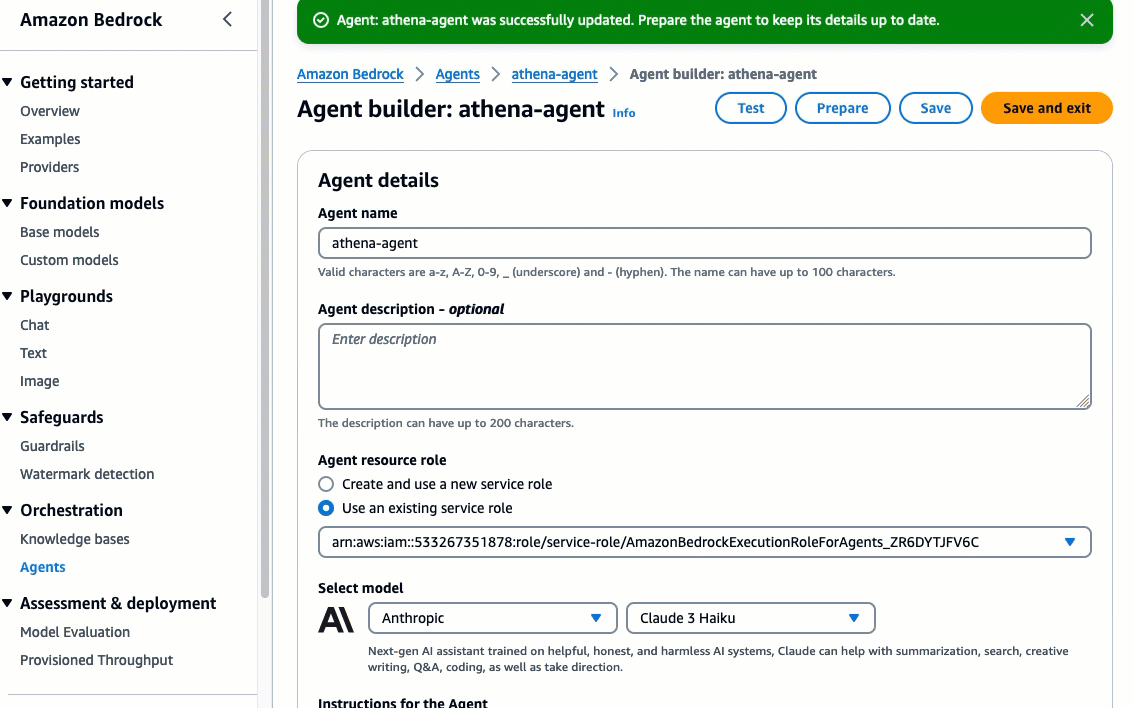
In the
Prompt template editor, go to line 22-23, then copy/paste the following prompt:
Here are the table schemas for the Amazon Athena database <athena_schemas>.
<athena_schemas>
<athena_schema>
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE athena_db.customers (
`Cust_Id` integer,
`Customer` string,
`Balance` integer,
`Past_Due` integer,
`Vip` string
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
STORED AS TEXTFILE
LOCATION 's3://athena-datasource-{alias}/';
</athena_schema>
<athena_schema>
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE athena_db.procedures (
`Procedure_ID` string,
`Procedure` string,
`Category` string,
`Price` integer,
`Duration` integer,
`Insurance` string,
`Customer_Id` integer
)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
STORED AS TEXTFILE
LOCATION 's3://athena-datasource-{alias}/';
</athena_schema>
</athena_schemas>
Here are examples of Amazon Athena queries <athena_examples>.
<athena_examples>
<athena_example>
SELECT * FROM athena_db.procedures WHERE insurance = 'yes' OR insurance = 'no';
</athena_example>
<athena_example>
SELECT * FROM athena_db.customers WHERE balance >= 0;
</athena_example>
</athena_examples>-
This prompt helps provide the agent an example of the table schema(s) used for the database, along with an example of how the Amazon Athena query should be formatted. Additionally, there is an option to use a custom parser Lambda function for more granular formatting.
-
Scroll to the bottom and select the Save and exit. Then, Save and exit one more time.
- While query-agent is still selected, scroll down to the Alias secion and select Create. Choose a name of your liking. Make sure to copy and save your AliasID. You will need this in step 9.
- Next, navigate to the Agent Overview settings for the agent created by selecting Agents under the Orchestration dropdown menu on the left of the screen, then select the agent. Save the AgentID because you will also need this in step 9.
- While on the Bedrock console, select Agents under the Orchestration tab, then the agent you created. Select Edit in Agent Builder, and make sure to Prepare the agent so that the changes made can update. After, Save and exit. On the right, you will be able to enter prompts in the user interface to test your Bedrock agent.
(You may be prompt to prepare the agent once more before testing the latest chages form the AWS console)
-
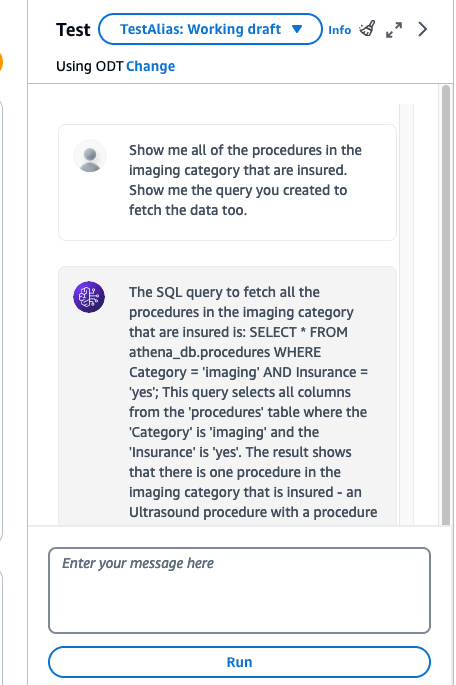
Example prompts for Action Groups:
-
Show me all of the procedures in the imaging category that are insured.
-
Show me all of the customers that are vip, and have a balance over 200 dollars.
-
- Navigate in the Cloud9 management console. Then, select Create Environment
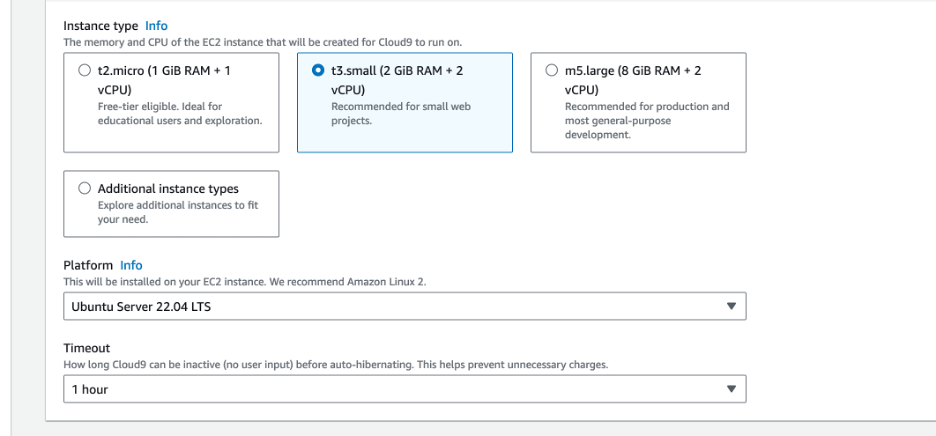
- Here, you will enter the following values in each field
- Name: Bedrock-Environment (Enter any name)
- Instance type: t3.small
- Platform: Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS
- Timeout: 1 hour
- Once complete, select the Create button at the bottom of the screen. The environment will take a couple of minutes to spin up. If you get an error spinning up Cloud9 due to lack of resources, you can also choose t2.micro for the instance type and try again. (The Cloud9 environment has Python 3.10.12 version at the time of this publication)
- Navigate back to the Cloud9 Environment, then select open next to the Cloud9 you just created. Now, you are ready to setup the Streamlit app!
-
Obtain the Streamlit App ZIP File: Download the zip file of the project here.
-
Upload to Cloud9:
- In your Cloud9 environment, upload the ZIP file.
- Unzip the File:
- Use the command
unzip bedrock-agent-txt2sql-main.zipto extract the contents.
- Use the command
- Navigate to streamlit_app Folder:
- Change to the directory containing the Streamlit app. Use the command
cd ~/environment/bedrock-agent-txt2sql-main/streamlit_app
- Change to the directory containing the Streamlit app. Use the command
- Update Configuration:
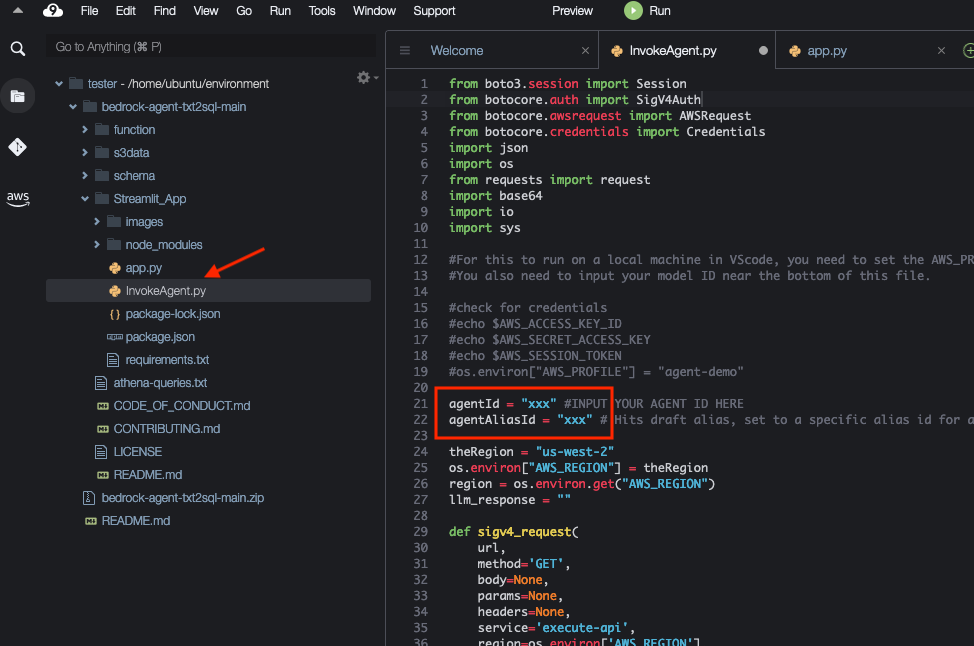
- Open the
InvokeAgent.pyfile. - Update the
agentIdandagentAliasIdvariables with the appropriate values, then save it.
- Open the
-
Install Streamlit (if not already installed):
-
Run the following command to install all of the dependencies needed:
pip install streamlit boto3 pandas
-
-
Run the Streamlit App:
- Execute the command
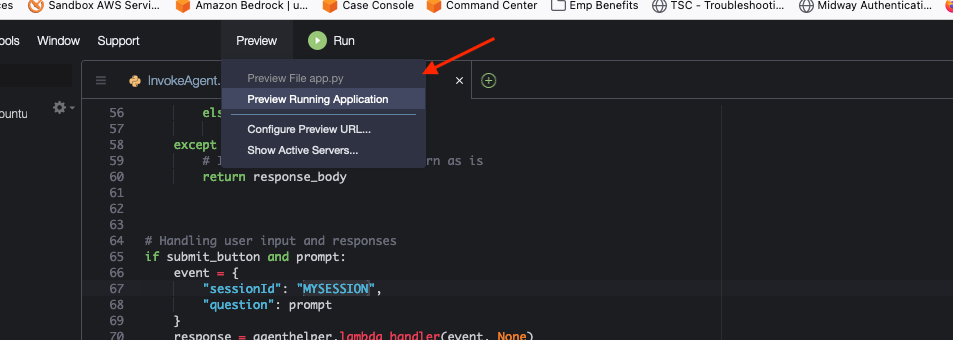
streamlit run app.py --server.address=0.0.0.0 --server.port=8080. - Streamlit will start the app, and you can view it by selecting "Preview" within the Cloud9 IDE at the top, then Preview Running Application
- Execute the command
- Once the app is running, please test some of the sample prompts provided. (On 1st try, if you receive an error, try again.)
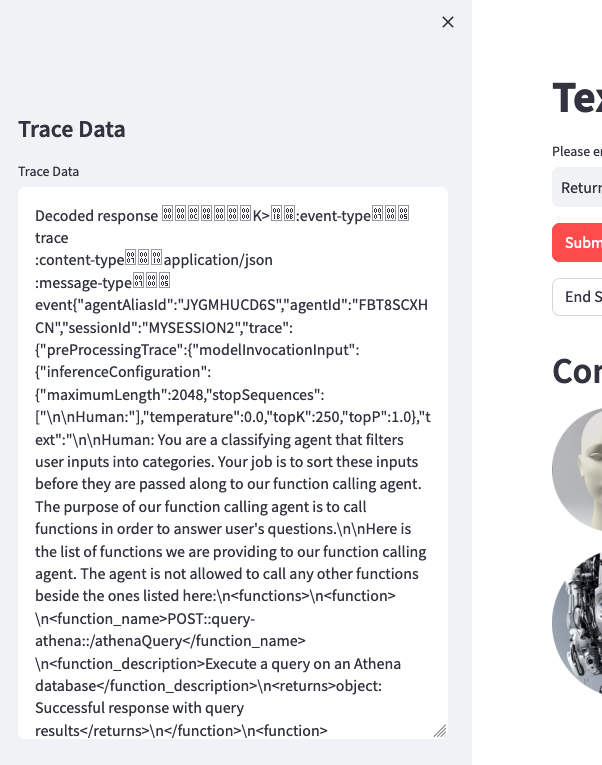
Optionally, you can review the trace events in the left toggle of the screen. This data will include the rational tracing, invocation input tracing, and observation tracing.
After completing the setup and testing of the Bedrock Agent and Streamlit app, follow these steps to clean up your AWS environment and avoid unnecessary charges:
- Delete S3 Buckets:
- Navigate to the S3 console.
- Select the buckets "athena-datasource-alias" and "bedrock-agents-athena-output-alias". Make sure that both of these buckets are empty by deleting the files.
- Choose 'Delete' and confirm by entering the bucket name.
- Remove Lambda Function:
- Go to the Lambda console.
- Select the "bedrock-agent-txtsql-action" function.
- Click 'Delete' and confirm the action.
- Delete Bedrock Agent:
- In the Bedrock console, navigate to 'Agents'.
- Select the created agent, then choose 'Delete'.
- Clean Up Cloud9 Environment:
- Navigate to the Cloud9 management console.
- Select the Cloud9 environment you created, then delete.
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.