3levelmemcache
Overview
All modern server side applications use memcached as fast caching technology. Memcached comes with multiple languages clients including java. The client provides you an ability to gain access to the memcached servers and perform operations you need. All these operations a low level and require you to have control over synchronous/asynchronous execution of your request, require you to specify serializer to use, require you to manage data at low level. One more challenge any app faces with memcached. Memcached is in memory storage, if server crashes - data is lost. To avoid this kind of issues we write/read data from 2 identical memcached storages. Even if one crashes the other still able to server traffic and application do not see the problem. No outage for application.
Data.com has built own caching framework on top of provided memcached low level client. The distinguishing part of this framework:
- it allows you to operate data at higher level. No worries about serialization, about sync/async execution.
- it allows you to write into 2 memcached storages
- it adds local or JVM cache on top of memcached storages. That gives a huge boost in performance in some cases.
3levelmemcache uses spring but it also possible to instantiate objects manually
Supported memcached providers
- Couchbase or Membase
- plain memcached
Levels
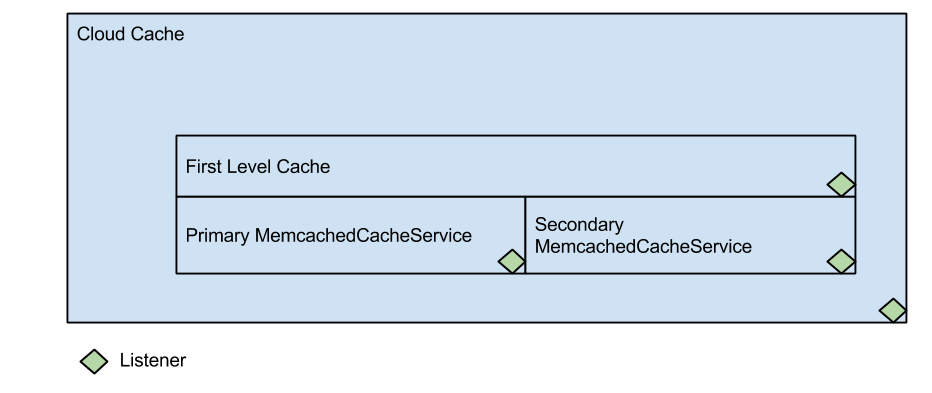
Data.com cache infrastructure has 3 levels of caching.
-
FirstLevelCache - this is jvm based caching for hot objects. Works as FIFO cache. Size is controlled by a property. See properties section.
-
PrimaryCache - the master memcached server. All requests that could not be found in FirstLevelCache are redirected to this cache.
-
SecondaryCache - the backup memcached server. All requests that could not be found/ or executed on PrimaryCache are redirected to this cache Any level of cache could be disabled except PrimaryCache. PrimaryCache is required.
Each level has an option to assign an interceptor/listener to listen for events.
Connection pools
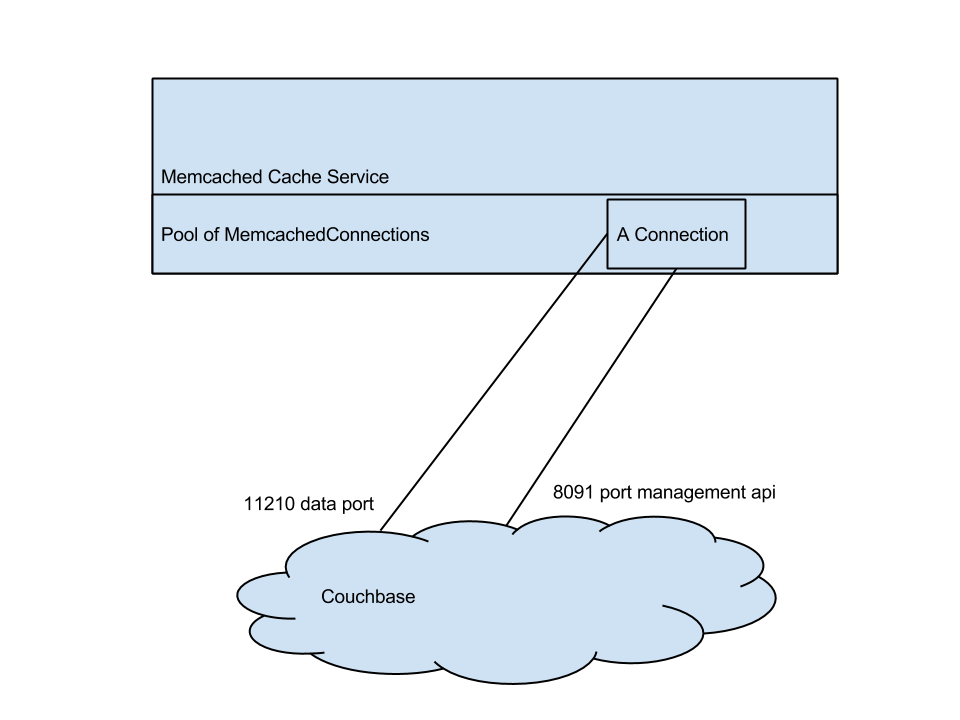
PrimaryCacheService and SecondaryCacheService maintain connection pool with keep alive mechanism. Each connection is a MemcachedConnection or CouchbaseConnection
CouchbaseConnection
Sockets:
- 8091 - couchbase "management port", which is used for cluster topology changes
- 11210 - data port. Port is used for data transmitting. Called "Data port"
- Optional [11211 - xxxxx] - bucket specific port Algorithm: Each connection has 2-3 threads behind. One thread for async processing of writes. One for listening 8091 management port.
MemcachedConnection
Sockets:
- [11211-xxxx] - data port for plain memcached connection Algorithm: Each connection has 1 thread behind, for async processing of writes.
Pool Algorithm
Pool is a "Round robin pool" hidden behind JDK dynamic proxy.
Keep alive
Keep alive was implemented for cases where your app connects to cache through firewall, some firewall software might stale the connection without breaking it after some non-active time. To prevent this there is a keep-alive logic. Pooling connection allows to increase the bandwidth primarily because of increasing the amount of worker threads. 1 connection has 1 worker thread and queue, that is not enough sometimes. We identified that having multiple queues with multiple worker threads - improves the performance on multi CPU hardware.
Algorithm
Here are basic algorithms
Action: PUT
Algorithm:
- if data is allowed* to be cached in FirstLevelCache - put/update data into FirstLevelCache
- if PrimaryCache is connected and healthy - put data to the PrimaryCache
- if SecondaryCache is connected and healthy - put data to the SecondaryCache Concept: "Last write wins"
*Allowed means that some data by nature could be sensitive to caching in JVM. There is a way to prevent FirstLevelCache from caching that type of data.
Action: GET
Algorithm:
- if data exists in FirstLevelCache - return data from FirstLevelCache and stop
- if data was not found on step 1, return data from PrimaryCache if it's healthy and connected
- if data was not found on step 2, return data from SecondaryCache if it's healthy and connected Concept: "First found data is served."
Action: APPEND
Algorithm:
- if key exists in FirstLevelCache - append data there
- if PrimaryCache is connected and healthy - append data to the PrimaryCache
- if SecondaryCache is connected and healthy - append data to the SecondaryCache Concept: "Append everywhere"
Action: DELETE
Algorithm:
- if key exists in FirstLevelCache - delete data there
- if PrimaryCache is connected and healthy - delete data to the PrimaryCache
- if SecondaryCache is connected and healthy - delete data to the SecondaryCache Concept: "Delete everywhere"
Properties
Your application should have following properties
cache.l1.size
Value: [0-Integer.MaxInt]
Desc: Size of firstlevelcache. Where 0 means it's disabled.
Required: yes
memcached.pool.size
Value: [1-100]
Desc: Size of the memcached connections pool, usually 10-20 connections should be enough for most of the applications
Required: yes
memcached.pool.timeBetweenKeepAliveRunsSecs
Value: [0-..)
Desc: Keep alive time intervals
Required: yes
memcached.operationTimeOutMsec
Value: [2500-xx]
Desc: Time out for single operation(get/put/append)
Required: optional, default 3000
memcached.operationQueueMaxBlockTimeMsec
Value: [200-xx]
Desc: If queue is overfull, thread will be waiting for queue, and after this amount timeouts
Required: optional, default 6000
memcached.operationQueueSize
Value: [16000--xxx]
Desc: One connection has an internal queue for operations, this property controls size of this queue
Required: yes
memcached.protocol.binary
Value: [true/false]
Desc: Used only for plain memcached provider. Note: dev memcached.exe works only with false.
Required: yes
memcached.membase.primary.URL
Value: comma separated URLs
Desc: Couchbase cluster comma separated URLs. Example: http://mb01:8091/pools,http://mb02:8091/pools
Required: conditional*
memcached.membase.primary.bucketName
Value: Couchbase bucket name
Required: conditional*
memcached.membase.secondary.URL
Value: comma separated URLs.
Desc: Couchbase cluster comma separated URLs. Example: http://mb01:8091/pools,http://mb02:8091/pools
Required: conditional*
memcached.membase.secondary.bucketName
Value: Couchbase bucket name
Required: conditional*
memcached.primary.nodeAddresses
Value:comma separated socket adresses
Desc: For plain memcached only. Example: mb01:11211,mb02:11211
Required: conditional*
memcached.secondary.nodeAddresses
Value: comma separated socket adresses
Desc: For plain memcached only.Example: mb01:11211,mb02:11211
Required: conditional*
Conditional*:
since you cannot connect to both plain memcached and couchbase server you should specify one of them.
RULE: Primary Cache: memcached.primary.nodeAddresses OR [memcached.membase.primary.URL + memcached.membase.secondary.bucketName]
RULE: Secondary Cache: EMPTY OR memcached.secondary.nodeAddresses OR [memcached.membase.secondary.URL + memcached.membase.secondary.bucketName]
If you set memcached.primary.nodeAddresses AND [memcached.membase.primary.URL + memcached.membase.secondary.bucketName] the membase configs has higher priority and will be taken.
Customizations/observers/hooks
This section describes possible customization you can do per component.
Put a listener at any cache level.
Implement custom listener by implementing com.salesforce.ddc.threlevelmemcache.exposed.listener.CacheListener interface
Put custom listener as spring bean
Annotate your listener with required annotation
- @CloudCacheListener - to make it listen CloudCache
- @FirstLevelCacheListener - to make it listen FirstLevelCache
- @MemcachedPrimaryCacheListener - to make it listen PrimaryCache
- @MemcachedSecondaryCacheListener - to make it listen SecondaryCache
Example: ListenersTestNG.java
Customize FirstLevel cache caching strategy
Default caching strategy can be found here DefaultAnnotationBasedCachingStrategy.java you can define what to cache in JVM what not.
You can add custom strategy per application by implementing com.salesforce.ddc.threlevelmemcache.exposed.strategy.CachingStrategy Expose it as spring bean and annotate with @FirstLevelCacheStrategy