This tutorial provides an introduction to Docker and covers the following topics:
- Introduction to Docker
- Installation
- Docker Basics
- Docker Images
- Docker Containers
- Docker Compose
- Docker Networking
- Docker Volumes
- Dockerfile
- Docker Best Practices
- Additional Resources
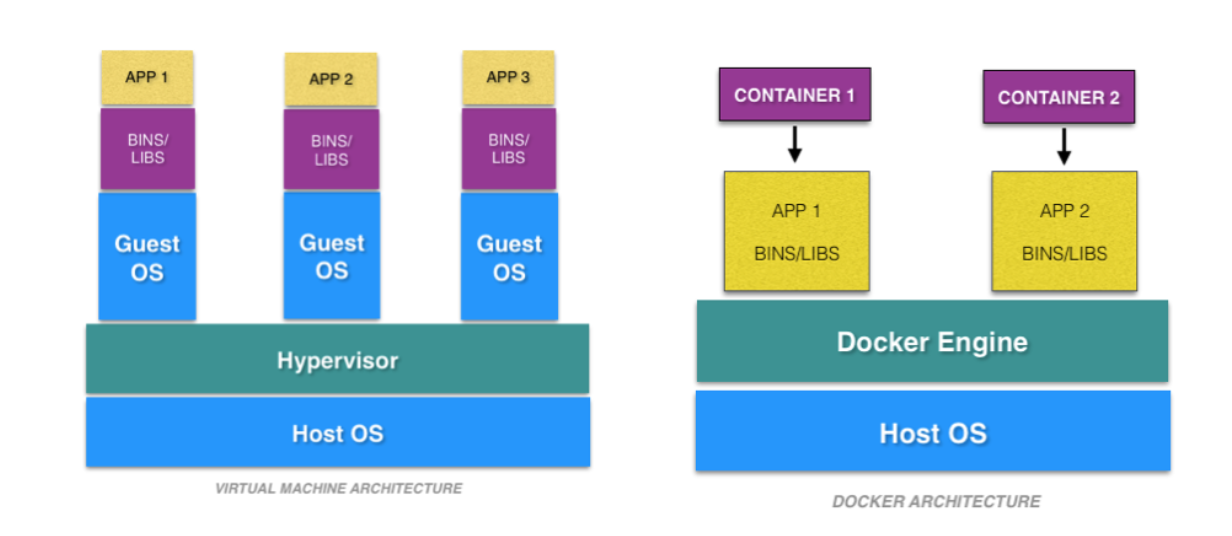
Docker is a platform that allows you to develop, ship, and run applications in containers. Containers are lightweight, portable, and self-sufficient units that contain everything needed to run an application, including the code, runtime, system tools, libraries, and settings. Docker provides tools and a platform to create, manage, and deploy containers easily and consistently across different environments.
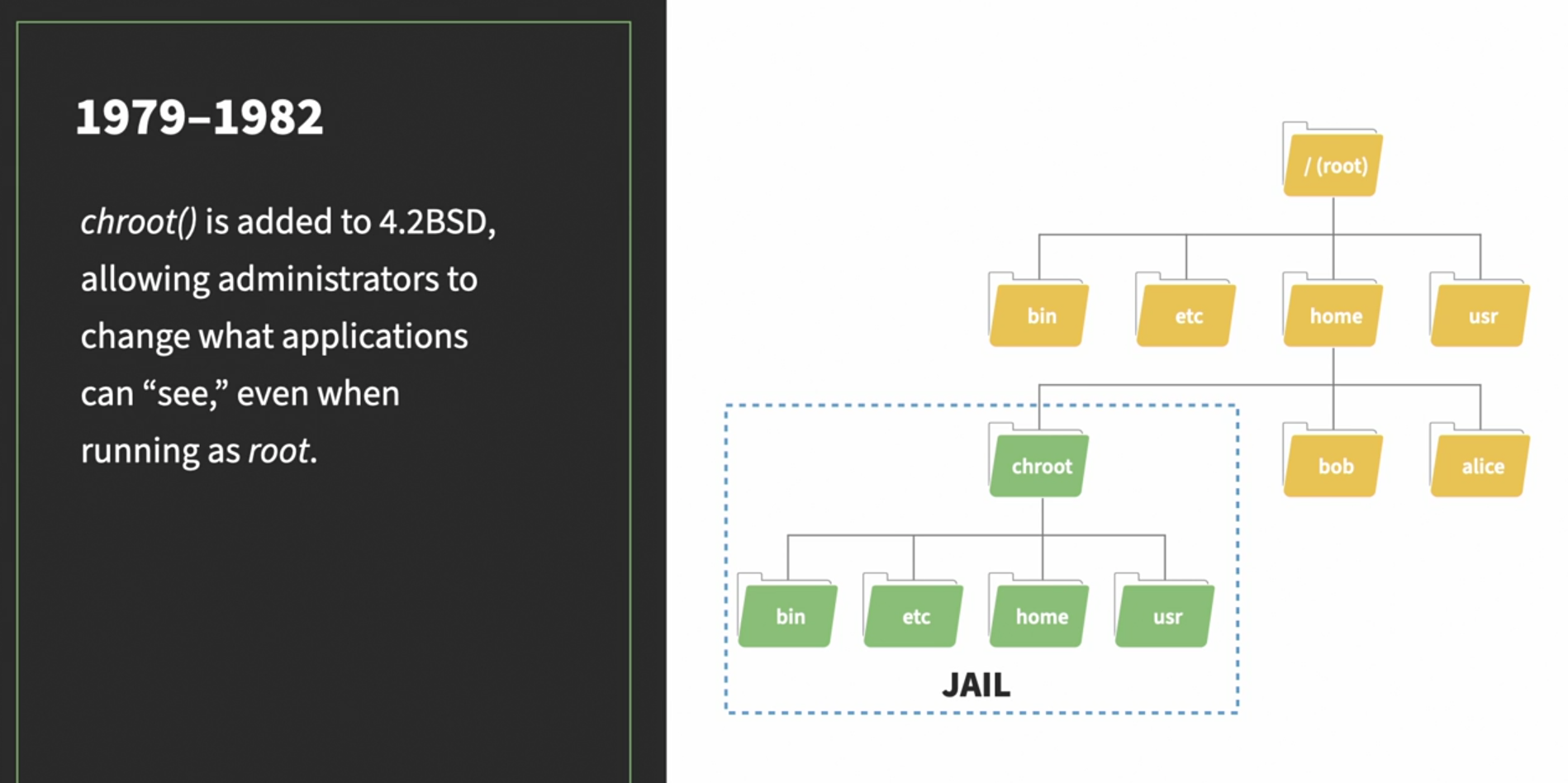
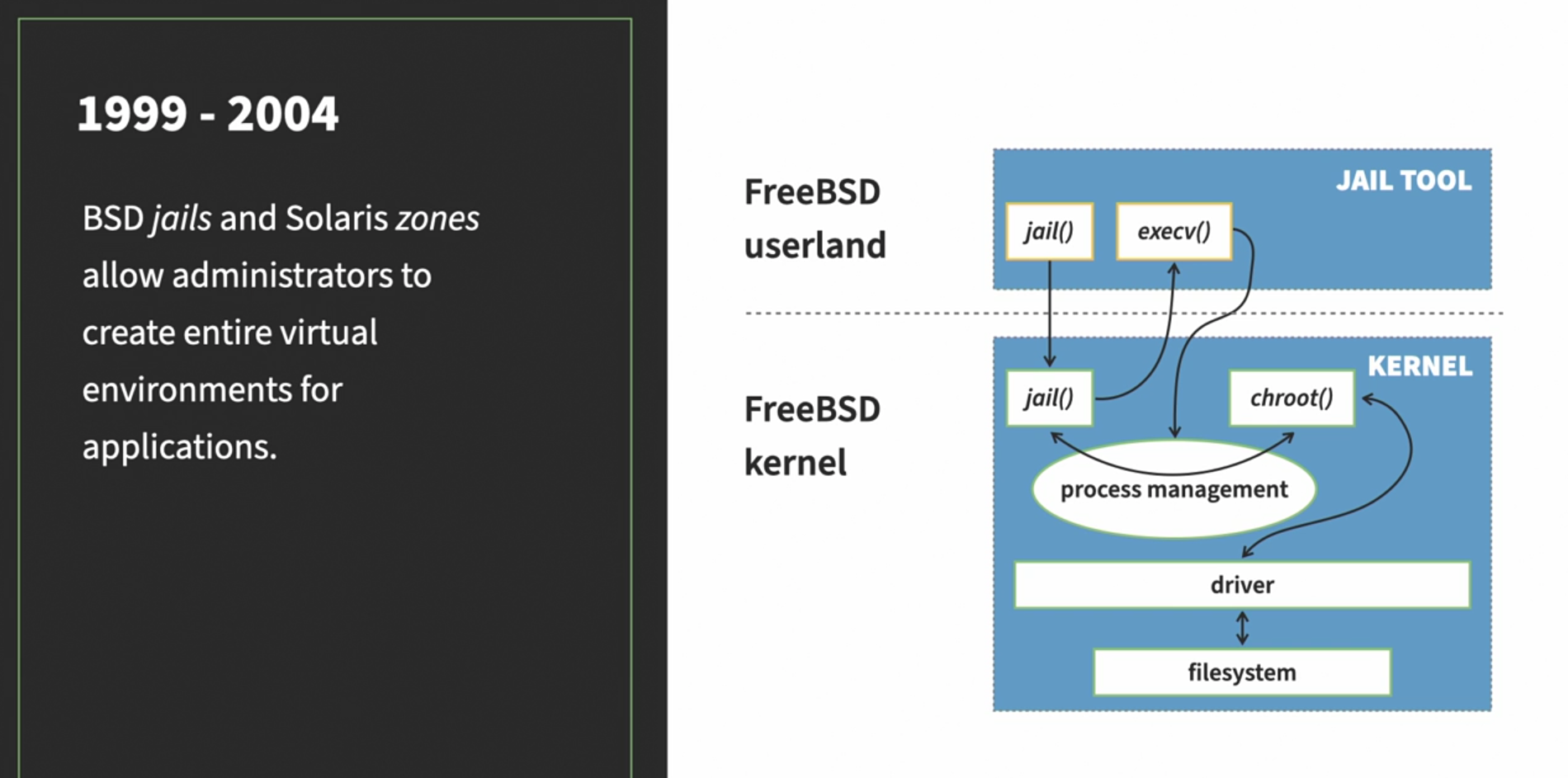
The big difference between containers and virtual machines is that virtual machines virtualize hardware whereas containers virtualize operating system kernels.
- Use the hypervisor to emulate real hardware
- Can take up a lot of space 🗄️
- Require you to install/configure operating system 🛠️
- Can run multiple apps at the same time 🔄
- Cannot interact with their hosts 🚫
- Do not emulate any hardware and do not need to boot up ⚡
- Do not require operating system installation 🧩
- Take up much less space 🪶
- Can run only one app at a time (by design) 🏃♂️
- Can interact with their hosts 🔗
| Containers | Virtual Machines |
|---|---|
| Run in container runtimes | Run on top of hypervisors |
| Work alongside operating systems | Need hardware emulation |
| Do not require OS configuration | Require OS configuration |
| Run one app at a time (usually) | Can run many apps at once |
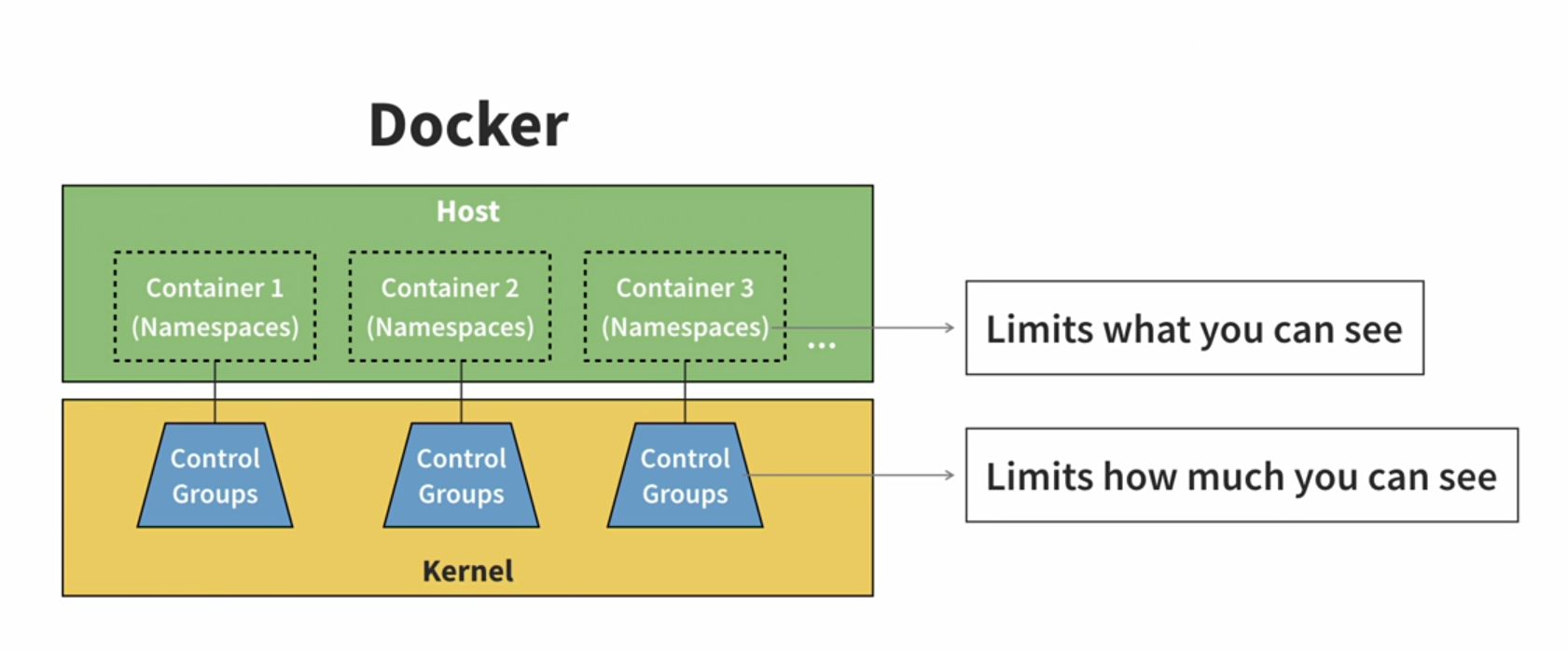
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| USERNS | User Lists |
| Mount | Access to file systems |
| NET | Network communication |
| IPC | Interprocess communication |
| Time | Ability to change time (Not supported by Docker) |
| PID | Process ID Management |
| CGROUP | Create control groups |
| UTC | Create host/domain names |
- Monitor and restrict CPU usage
- Monitor and restrict network and disk bandwidth
- Monitor and restrict memory consumption
Assign disk quotas(Not supported by Docker)
- Natively only runs on Linux 🐧
- Container images are bound to their parent operating systems ⚓
Feel free to ask more questions or dive into the specific sections for detailed explanations! 😊