- Adhiraj Deshmukh (adhiraj.deshmukh@research.iiit.ac.in) -
2021121012 - Puneeth Sai Tumbalabeedu (puneeth.sai@students.iiit.ac.in) -
2019101064
When dealing with Medical Data, the size of the datasets are in TBs and thus its not feasible to store off it a local storage, thus its really hard to work on these datasets as a whole. Data Foundation System enables the users of the dataset to store these datasets on the DFS system and enable them to query on multiple datasets having similar attributes without revealing the identity of the Medical Data.
For this system to work, Data Ingestion system is very essential. Specifically our task deals with designing a generic data ingestion system, which can be used to ingest data from multiple sources and stored in a generic way, which allows these attributes to be queried seperately with different types of dataset.
The user can input multiple datype of data, which can vary in size, type, and use cases, and the system in expected to be able to parse excel sheets, CSVs, and other data formats, which may be stored in a hierarchical, segmented, or single-file fashion. The system will contain a novel JSON schema that can be generated without understanding the data, but will maintain enough context to allow for a near one-one mapping to a DB schema.
This projected is divided into 3 parts, each having its independent functionality:
- The first task is to create JSON Schema such that it can be be mapped to a DB schema, and it should work for most generic data systems, taking into accound databases with multiple fields, constraints, varying relationships mong fields and tables.
- The schema should contain enough metadata in order to provide suitable scope for loading phase, specifying the number of tables, rows, and overall structure.
- There also should be abstract representation of tables in the JSON format with regards to data type of field, constraints and relationship mapping.
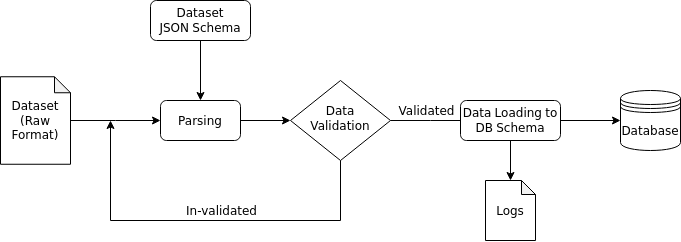
- This tasks involves parsing the row data of various formats, with respect to the JSON schema, along with basic data and system validations. This stage is necessary for monitoring any top-level faults that may occur during the generic data loading process.
- For parsing the data, files are loaded, varying as per their format, and then are cross-checked with the JSON schema for any faults.
- In the validation phase, if there are any critical breaking errors, like absence of table, realation, or key/field mis-matchand , appropriate errors will be logged.
- At this point we will need to cleanse, transform and anonymize the data if needed. (Not our deliverables, but would require some collaboration from other teams)
- The loading part involves generating a data loader, that is able to sequentially load the entire raw data, and adapt it to the generated DB schema.
- This data is simultaneously outputted to the final DB, and logs for this process are maintained.
- Upon completion, a summary of this process, containing the final schema, execution logs, and other details, will be generated. At the end of this step, user is able to obtain a final DB from their raw data and JSON schema.
- All the common constants that are being used are imported from a dedicated file for constants which makes the process of debugging very easy .
- The logic that is used for parsing the data from a specific format can be reused for parsing other formats of data . Most of the modules that we use are standard modules and there is very less chance of version mismatch of modules .
- This helps in maintaining the code for a long time and also helps in the process of debugging .
- All the data that we recieve will be parsed and stored in a Relational MySQL database
- We are using MySQL to make the data more related to each other and put some logic into it .
- There is only one type of user who needs to upload the data to the user module .
- The system then recieves the raw data from the user module and it will be parsed , validated and then ingested into the database if the data provided is valid .
- The system is designed such that it can be easily integrated with the user module from where the data is collected.
- Integration with other systems such as search and querying systems , analytic systems are also
- Validating data that is being sent by the user module and mapping the attributes to their respective logical attributes and form a relationship between the data .
- Creating a specific format of data to which all the raw data is to be converted .
- Searching and querying the ingested data in not in the scope of the project .
- Collecting data from users is not a part of the system . It will be implemented in the user module .
Most tasks in this project will be implemented in Python.
- The parsing, validation, loading, and dumping of the data will be handled with dedicated python modules and classes.
- Some pre-processing of given raw-data, and validation of final output DB will involve MySQL.
- NiFi pipelines will be used for Migration to SQL DB.